
- Issue 4 Pages 349-
- Issue 3 Pages 241-
- Issue 2 Pages 135-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Kazutada Ikeuchi2024 Volume 72 Issue 4 Pages 349-359
Published: April 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEllagitannins, a class of polyphenols with divergent structures, have attracted considerable attention from synthetic organic chemists. The basic structures in ellagitannins contain esters of D-glucose with galloyl or hexahydroxyldiphenoyl groups, as well as diaryl ether structures. Thus, the synthesis methodologies of such components have been developed by various groups, including our group. This review describes the synthetic methods reported by our group during 2017–2023, aimed at increasing the number of ellagitannins that can be chemically synthesized. In addition, recent related reports are introduced.
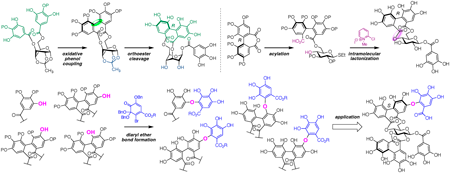 View full abstractDownload PDF (2380K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2380K) Full view HTML
-
Hiroyuki Mutoh, Yuuki Watanabe, Daiki Kamakura, Koichi Hagiwara, Masay ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 4 Pages 360-364
Published: April 03, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialBatrachotoxin (1) is a potent cardio- and neurotoxic steroid isolated from certain species of frogs, birds, and beetles. We previously disclosed two synthetic routes to 1. During our synthetic studies toward 1, we explored an alternative strategy for efficiently assembling its 6/6/6/5-membered steroidal skeleton (ABCD-ring). Here we report the application of intermolecular Weix and intramolecular pinacol coupling reactions. While Pd/Ni-promoted Weix coupling linked the AB-ring and D-ring fragments, SmI2-mediated pinacol coupling did not cyclize the C-ring. Instead, we discovered that SmI2 promoted a 1,4-addition of the α-alkoxy radical intermediate to produce the unusual 11(9→7)-abeo-steroid skeleton. Thus, this study demonstrates the convergent assembly of the skeleton of the natural product matsutakone in 11 steps from 2-allyl-3-hydroxycyclopent-2-en-1-one.
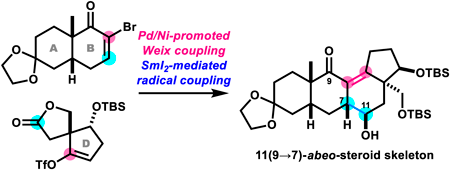 View full abstractDownload PDF (782K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (782K) Full view HTML -
Min-Seong Lee, Ji-won Noh, Byung-Cheol Lee2024 Volume 72 Issue 4 Pages 365-373
Published: April 04, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: April 04, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialObesity is known to be associated with increased inflammation and dysregulated autophagy, both of which contribute to insulin resistance. Saikosaponin-A (SSA) has been reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering properties. In this research, we employed a combination of computational modeling and animal experiments to explore the effects of SSA. Male C57BL/6 mice were categorized into four groups: normal diet, high-fat diet (HFD), HFD + atorvastatin 10 mg/kg, and HFD + SSA 10 mg/kg. We conducted oral glucose and fat tolerance tests to assess metabolic parameters and histological changes. Furthermore, we evaluated the population of Kupffer cells (KCs) and examined gene expressions related to inflammation and autophagy. Computational analysis revealed that SSA displayed high binding affinity to tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, nuclear factor (NF)-κB, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), and autophagy-related 7 (ATG7). Animal study demonstrated that SSA administration improved fasting and postprandial glucose levels, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index, as well as triglyceride, free fatty acid, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)-cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)-cholesterol levels in HFD-fed mice. Moreover, SSA significantly reduced liver weight and fat accumulation, while inhibiting the infiltration and M1 activation of KCs. At the mRNA level, SSA downregulated TNF-α and NF-κB expression, while upregulating FGF21 and ATG7 expression. In conclusion, our study suggests that SSA may serve as a therapeutic agent for addressing the metabolic complications associated with obesity. This potential therapeutic effect is attributed to the suppression of inflammatory cytokines and the upregulation of FGF21 and ATG7.
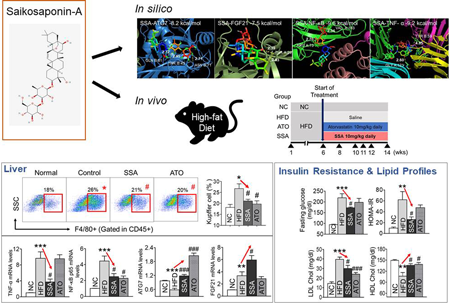 View full abstractDownload PDF (5796K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5796K) Full view HTML -
Takeru Yano, Atsushi Oshiro, Shuji Ohsaki, Hideya Nakamura, Satoru Wat ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 4 Pages 374-380
Published: April 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: April 09, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTablets are the most commonly used dosage form in the pharmaceutical industry, and their properties such as disintegration, dissolution, and portability are influenced by their strength. However, in industry, the mixing fraction of powders to obtain a tablet compact with sufficient strength is determined based on empirical rules. Therefore, a method for predicting tablet strength based on the properties of a single material is required. The objective of this study was to quantitatively evaluate the relationship between the compression properties and tablet strength of powder mixtures. The compression properties of the powder mixtures with different plasticities were evaluated based on the force-displacement curves obtained from the powder compression tests. Heckel and compression energy analyses were performed to evaluate compression properties. During the compression energy analysis, the ratio of plastic deformation energy to elastic deformation energy (Ep/Ee) was assumed to be the plastic deformability of the powder. The quantitative relationship between the compression properties and tensile strength of the tablets was investigated. Based on the obtained relationship and the compression properties of a single material, a prediction equation was put forward for the compression properties of the powder mixture. Subsequently, a correlation equation for tablet strength was proposed by combining the values of K and Ep/Ee obtained from the Heckel and compression energy analyses, respectively. Finally, by substituting the compression properties of the single material and the mass fraction of the plastic material into the proposed equation, the tablet strength of the powder mixture with different plastic deformabilities was predicted.
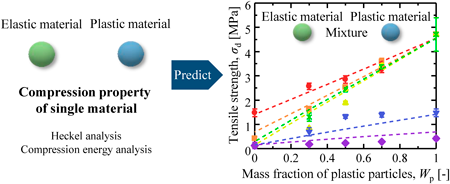 View full abstractDownload PDF (1476K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1476K) Full view HTML
-
Taishi Higashi, Taito Goto, Risako Onodera, Tatsunori Hirotsu, Hanako ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 4 Pages 381-384
Published: April 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: April 15, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialBietti’s crystalline dystrophy (BCD) is an autosomal recessive chorioretinal degeneration caused by mutations in the CYP4V2 gene. It is characterized by cholesterol accumulation and crystal-like deposits in the retinas. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CyD) exerts therapeutic effects against BCD by reducing lysosomal dysfunction and inhibiting cytotoxicity in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-RPE cells established from patient-derived iPS cells. However, the ocular retention of HP-β-CyD is low and needs to be improved. Therefore, this study used a viscous agent to develop a sustained-release ophthalmic formulation containing HP-β-CyD. Our results suggest that HP-β-CyD-containing xanthan gum has a considerably higher sustained release capacity than other viscous agents, such as methylcellulose and sodium alginate. In addition, the HP-β-CyD-containing xanthan gum exhibited pseudoplastic behavior. It was less cytotoxic to human retinal pigment epithelial cells compared with HP-β-CyD alone. Furthermore, the slow release of HP-β-CyD from xanthan gum caused a sustained decrease in free intracellular cholesterol. These results suggest that xanthan gum is a useful substrate for the sustained release formulation of HP-β-CyD, and that HP-β-CyD-containing xanthan gum has potential as an eye drop for BCD treatment.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1453K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1453K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|