All issues

Volume 29, Issue 11
Displaying 1-17 of 17 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Masaharu NAKAYAMA, Ayu SATOArticle type: Rapid Communications
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1017-1020
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have fabricated a thin film of multilayered MnO2 whose interlayer is occupied with hexadecylpyridinium (HDPy) cations, using a simple anodic approach. The resulting film can effectively sorb iodide anions from aqueous solutions, even in the presence of NaCl or Na2SO4. The maximum sorption capacity was estimated to be 256 mg/g-MnO2, whereas a layered MnO2 film intercalated with K+ ions showed no significant sorption. The layered structure of the HDPy/MnO2 composite remained unchanged after a sorption experiment. This indicates the incorporation of I− ions between MnO2 layers due to their specific affinity toward HDPy.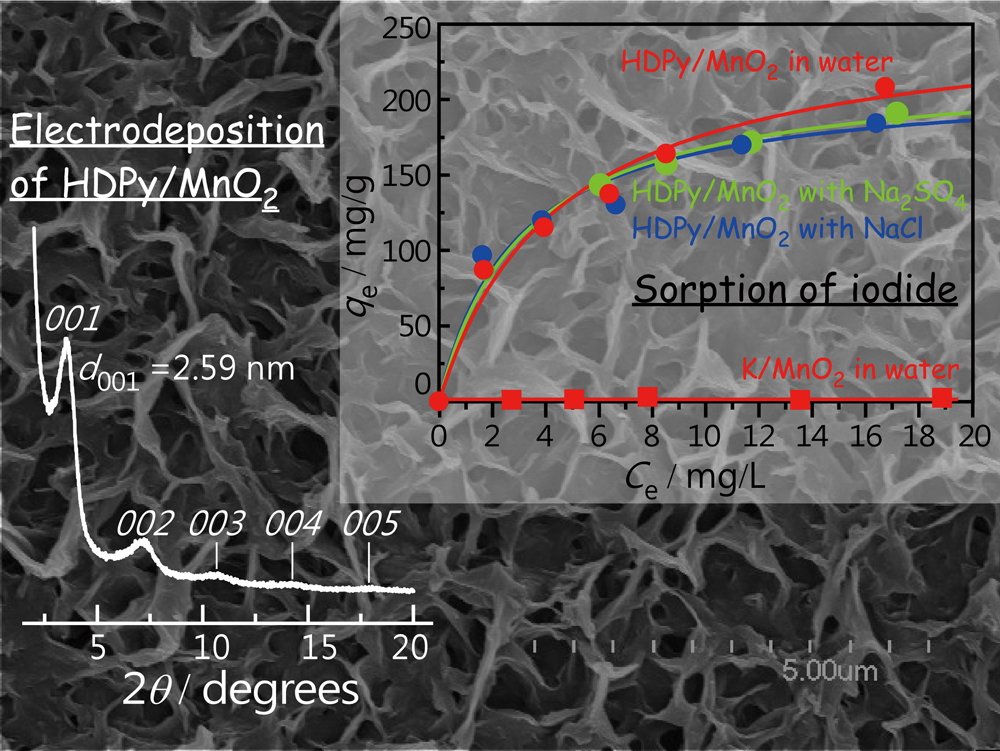 View full abstractDownload PDF (1104K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1104K)
Original Papers
-
Hajime KATANO, Shu TAIRA, Kohei UEMATSU, Hisashi KIMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1021-1025
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and convenient method of reducing monosaccharide assay is proposed. A Si(IV)–Mo(VI) solution (pH 4.9) was yellow due to the formation of the 11- and/or 12-molybdosilicate(VI) anions. By the addition of a reducing saccharide, glucosamine, the mixture turned to blue gradually, indicating that the Mo(VI) species was reduced by the saccharide to form a blue molybdosilicate anion. The molybdenum blue formation occurred more quickly when a water-miscible organic solvent, dimethyl sulfoxide, was added to the Si(IV)–Mo(VI) solution. Thus, 0.01% level glucosamine can be determined colorimetrically with microtiter plate. Oligochitosan would not interfere with the determination of the glucosamine at the same concentration. Also, a remarkable blue color development of the Si(VI)–Mo(VI) solution was observed by the addition of glucose. On the other hand, maltose, cellobiose, and water-soluble starch at the same concentration level gave no significant coloration of the reaction mixture. Thus, the present monosaccharide assay can be applied advantageously to evaluate the saccharification to produce glucosamine and glucose. View full abstractDownload PDF (4709K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4709K) -
Yanbei ZHU, Akiharu HIOKI, Koichi CHIBAArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1027-1033
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSEighteen elements in the cotyledon, the embryonic axis, and the testa of peanut seeds were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) after microwave acid digestion, while the gravimetric standard addition with internal standard was applied for the calibration of the elemental concentrations. The detection limit and the procedure blank value for each element were low enough to ensure the precise analysis of the elements, with a relative expanded uncertainty of less than 5%. The concentrations of the elements in peanut seed samples covered 6 orders of magnitude from approximately 0.01 mg kg−1 of Co to approximately 7000 mg kg−1 of K. The correlation coefficient factor was around 0.98 for the elemental concentrations in peanut seeds grown in Japan and those grown in China, indicating a good correlation. Most of the elements distributed in the cotyledon in large amounts because of the cotyledon’s relatively high mass fraction. By contrast, Na, Ca, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ga, Sr, Cd, and Ba were apparently enriched in the testa and the relative enrichment factor (REF) values of the elements were over 4. The relative enrichment of Mo, Fe, Zn and other elements was observed in the embryonic axis samples with REF values over 2. The relative enrichment of Cd in the testa of peanut seed indicates that about 15 to 25% of the Cd intake through peanut seeds could be effectively lowered by removal of the testa (roughly 2.5 to 3.5% of the peanut seed).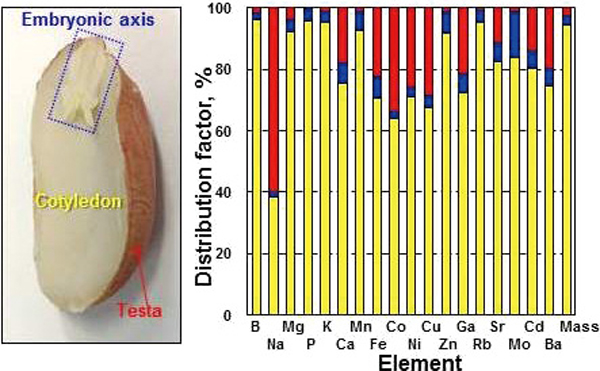 View full abstractDownload PDF (545K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (545K) -
Takashi ASANO, Junya SUZUKI, Kenro HASHIMOTO, Tatsuya FUJINOArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1035-1039
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialBy using 2,4,6-trihydroxyacetophenone adsorbed to cation-substituted zeolite, laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for six kinds of bioactive substances was carried out. The compounds, which were usually difficult to observe by conventional matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry, were ionized by cation adduction from the zeolite surface. View full abstractDownload PDF (435K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (435K) -
Junichi ODO, Masahiko INOGUCHI, Susumu OHIRA, Shinjiro TSUKIKAWA, Misa ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1041-1048
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn iron(III) complex of thiacalix[4]arenetetrasulfonate attached to an anion-exchanger (Fe3+-TCASA-500) showed high peroxidase-like catalytic activity at pH 5 – 8 for the formation of quinoid dye, following the color reaction between 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone (MBTH) and N-ethyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl)aniline (ALPS) in the presence of H2O2. This catalytic activity of Fe3+-TCASA-500 for the MBTH-ALPS system was applied for the spectrophotometric determination of H2O2, glucose, uric acid, and cholesterol. The calibration curves were linear in the concentration range from 1.0 to 15 μg of H2O2 in a 1.0-mL sample solution, and from 5.0 to 60 μg of glucose, 2.0 to 30 μg of uric acid, and 11.6 to 116 μg of cholesterol in a 0.5-mL sample solution. The apparent molar absorptivity of H2O2 was determined as 2.31 × 104 L mol−1 cm−1, which was about 70% of that by peroxidase under the same conditions. The determination method using Fe3+-TCASA-500 was applied for the determination of glucose and uric acid in both control sera I and II. View full abstractDownload PDF (931K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (931K) -
Yuuki TANAKA, Ken OKAMOTO, Ayako MATSUSHIMA, Tomoki OTA, Yoshitsugu MA ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1049-1053
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe complete hydrolysis of konjac glucomannan (KGM) with an acid or enzyme generally takes a long time. To accelerate KGM hydrolysis without diminishing the conventional quality, a diluted acid hydrolysis of KGM with sulfuric acid was conducted using a microwave digestion system. The optimum conditions of microwave-assisted acid hydrolysis for KGM were: 10 mL of 0.25 M sulfuric acid, hydrolysis temperature of 135°C (microwave power of 600 W), and total microwave-irradiation time of 45 min. The yields of the component sugars, mannose and glucose, from two konjac powders were similar to those by conventional acid hydrolysis with 1 M sulfuric acid in a boiling water bath for 5 h. Furthermore, a pretest for microwave-assisted acid hydrolysis using mixtures of konjac powder and starch at different ratios proved that their konjac content can be calculated by determining the mannose generated by the new rapid hydrolysis method, if the raw materials are provided. View full abstractDownload PDF (427K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (427K) -
Mir Mahdi ZAHEDI, Mojtaba SHAMSIPUR, Seied Mahdi POURMORTAZAVIArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1055-1059
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel on-line flow-injection liquid-phase microextraction (FI-LPME) and spectrophotometric determination of the Cu2+ ion using trithia-9-crown-3 (TT9C3) as a sensitive and selective charge transfer complexing agent was developed. After phase segmentation by pulsating motions of a peristaltic pump, the phase separation takes place by the aid of gravitation forces. The optimum values of the pH (= 5 of phosphate buffer) and ionic strength (5 mM Na2SO4) of the solution, amount of ligand (2.0 × 10−3 mol L−1), nature of the counter ion (10 mM SDS), volume of the organic solvent (150 μL), coil length (3 m) and extraction time (2 min) for an efficient extraction were determined. The calibration curve was found to be linear over a concentration range of 0.008 – 4.2 μg mL−1 (R2 = 0.9985) with a limit of detection of 0.37 ng mL−1. The enrichment factor and relative standard deviation (n = 7) were 16 and 5.7%, respectively. Finally, the proposed method was applied to the determination of copper(II) as an impurity in the several commercial metallic salts. View full abstractDownload PDF (580K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (580K) -
Mohammad ASGHAR, Mohammad YAQOOB, Naheed HAQUE, Abdul NABIArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1061-1066
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and sensitive flow-injection (FI) method is reported for the determination of thiram and aminocarb pesticides in natural water samples based on the strong enhancing effects of these pesticides on the tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)-diperiodatoargentate(III) (Ru(bipy)32+-DPA) chemiluminescence (CL) system. Under the optimum experimental conditions, the CL intensity was linear over the range of 1.0 – 1000 and 1.0 – 10000 ng mL−1 (R2 = 0.9998 (n = 7) and 0.9994 (n = 11)) for thiram and aminocarb, respectively, with relative standard deviations (RSDs; n = 3) in the range 1.0 – 2.6%. The limits of detection (S/N = 3) were 0.1 ng mL−1 for both pesticides with injection throughputs of 150 h−1. The key chemical and physical variables (reagent concentrations, flow rates, sample volume, PMT voltage) were optimized and potential interferences investigated. The method was successfully applied to natural water samples and the results obtained were not significantly different (95% confidence interval) from results obtained by the previously reported FI–CL and HPLC methods. Thiram could be determined in the presence of aminocarb using Triton X-100. The possible CL reaction mechanism is also discussed briefly. View full abstractDownload PDF (488K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (488K) -
Toshio TAKAYANAGIArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1067-1073
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAcid dissociation constants of 3′,3″,5′,5″-tetrabrompohenolphthalein (TBPP) were determined in an aqueous solution by capillary zone electrophoresis at an ionic strength of 0.01 mol/L. Two steps of the fast acid-dissociation equilibria including precipitable species of H2TBPP were analyzed at a weakly acidic pH region by using the change in effective electrophoretic mobility of TBPP with the pH of the separation buffer. On the other hand, an acid-dissociation reaction of TBPP at an alkaline pH region was reversible, but very slow to reach its equilibrium; the two TBPP species concerned with the equilibrium were detected as distinct signals in the electropherograms. After reaching its equilibrium, the acid-dissociation constant was determined with the signal height corresponding to its dianion form. Thus, three steps of the acid dissociation constants of TBPP were determined in an aqueous solution as pKa1 = 5.29 ± 0.06, pKa2 = 6.35 ± 0.02, and pKa3 = 11.03 ± 0.04. View full abstractDownload PDF (1356K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1356K) -
Jianbo LIU, Yan DONG, Jianbin ZHENG, Yaping HE, Qinglin SHENGArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1075-1081
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe conformation change of bovine hemoglobin (Hb) during the unfolding process induced by urea and acid was investigated by an electrochemical method. Hb unfolding induced by urea of different concentrations was realized by bonding Hb onto a 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) modified gold electrode. The difference in unfolding percentage showed that the Hb unfolding induced by urea was a two-step, three-state transition process, while the unfolding induced by acid was a two-state transition process. The results obtained by the electrochemical method coincided closely with those obtained by UV-vis spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy. Some thermodynamic parameters during the conformational change were also calculated to study the intermediate state during the Hb unfolding process. The present work may lead to an easy and effective way to study metalloproteins unfolding, and holds great promise for the design of novel sensitive biosensors. View full abstractDownload PDF (594K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (594K) -
Dah-Yeon YOO, In-Hyeong YEO, Won Il CHO, Yongku KANG, Sun-il MHOArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1083-1088
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe Li+ ion diffusion coefficients (DLi+) in V2O5 (2.12 × 10−12 cm2 s−1) and in the intermediate α-, ε-, and δ-LixV2O5 phases (1.6 × 10−14, 8.0 × 10−15, and 8.5 × 10−15 cm2 s−1, respectively), reversibly formed during charging/discharging processes of the crystalline-V2O5 and PEDOT (poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) composite-film electrode, are precisely determined by the galvanostatic intermittent titration technique. The specific surface area of the composite film is estimated to be 13.600 m2 g−1, where the external surface area and the nanopore area are 10.704 and 2.896 m2 g−1, respectively. The V2O5 crystals are coated and interconnected by a conductive polymer network in the composite film, thereby improving the electrode characteristics. V2O5 and PEDOT composite-film cathodes showed high specific capacities (290 mA h g−1 at a 1 C rate), excellent rate capabilities (178 mA h g−1 at a 10 C rate), and superior cycling stabilities (ca. 15% degradation after 500 consecutive cycles). View full abstractDownload PDF (1146K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1146K) -
Masashi KITAMURA, Atsushi ASANOArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1089-1093
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe investigated temperature distribution in a solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) sample rotor under magic angle spinning (MAS) experiments by analyzing the 207Pb chemical shift of solid lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2). The analysis corrected a mismatch of the temperature dependence of 1H spin-lattice relaxation time (T1H) obtained from different sample positions in the rotor. We prepared three rotors that consisted of Pb(NO3)2 partitioned into the three different parts with Teflon spacers, and measured the temperature distribution related to the placement using the prepared three rotors. The obtained temperature distribution showed a large gradient in the sample rotor. The temperature distribution was related to the placement in the rotor and successfully visualized. Finally, the divergent temperature dependence of T1H obtained at different placement positions in the sample rotor was successfully corrected to accurate temperature dependence.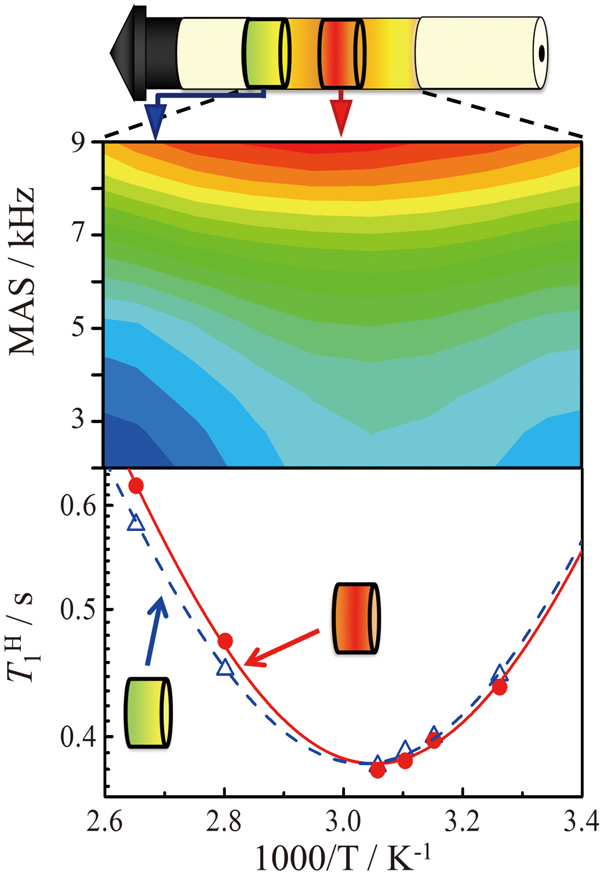 View full abstractDownload PDF (1772K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1772K)
Notes
-
Hajime KATANO, Hiro WATANABE, Masahiro TAKAKUWA, Chitose MARUYAMA, Yos ...Article type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1095-1098
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA colorimetric pyrophosphate assay based on the formation and reduction of the 18-molybdopyrophosphate ([(P2O7)Mo18O54]4−) anion in an acetonitrile–water mixed solvent was modified and improved. The [(P2O7)Mo18O54]4− anion is precipitated from the acetonitrile–water solution containing MoO42− and HCl, and is re-dissolved in neat acetonitrile or propylene carbonate. This separation process decreases the interference by ATP, and prevents a yellow coloration of the reducing agent, ascorbic acid, due to excess Mo(VI) species. In the organic solvent, the [(P2O7)Mo18O54]4− anion is reduced to a more intense blue molybdopyrophosphate species. The application of the colorimetry to the assay of adenylation enzymes is also described in this note.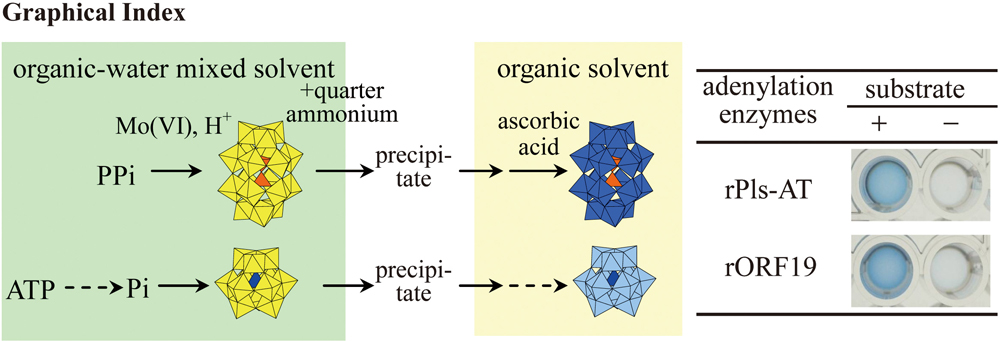 View full abstractDownload PDF (2275K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2275K) -
Toru TAKAHASHI, Jun KAWANA, Yuuki TAMURA, Hitoshi HOSHINOArticle type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1099-1102
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple, rapid, and precise dynamic coating capillary electrophoretic separation method for water-soluble humic substances is proposed. An aqueous solution containing hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and pH buffer component was employed for both the dynamic coating agent and the separation medium. The procedure for the coating of the capillary inner wall was simply filling the buffered polymer mixture solution into the capillary that had been treated with 1 M aqueous HCl solution. The solution for the capillary coating was directly used as the electrophoretic buffer solution for CE separation. Excellent performance for the separation of humic acid was obtained using the solution containing 0.5% (w/v) HEC, 1.0% (w/v) PEG 10000, and 0.1% (w/v) PEG 8000000. Excellent reproducibility and durability were obtained even at slightly alkaline conditions at pH levels above 8. The separation of 0.1 – 2 kbp of DNA ladder by the proposed method showed was also achieved.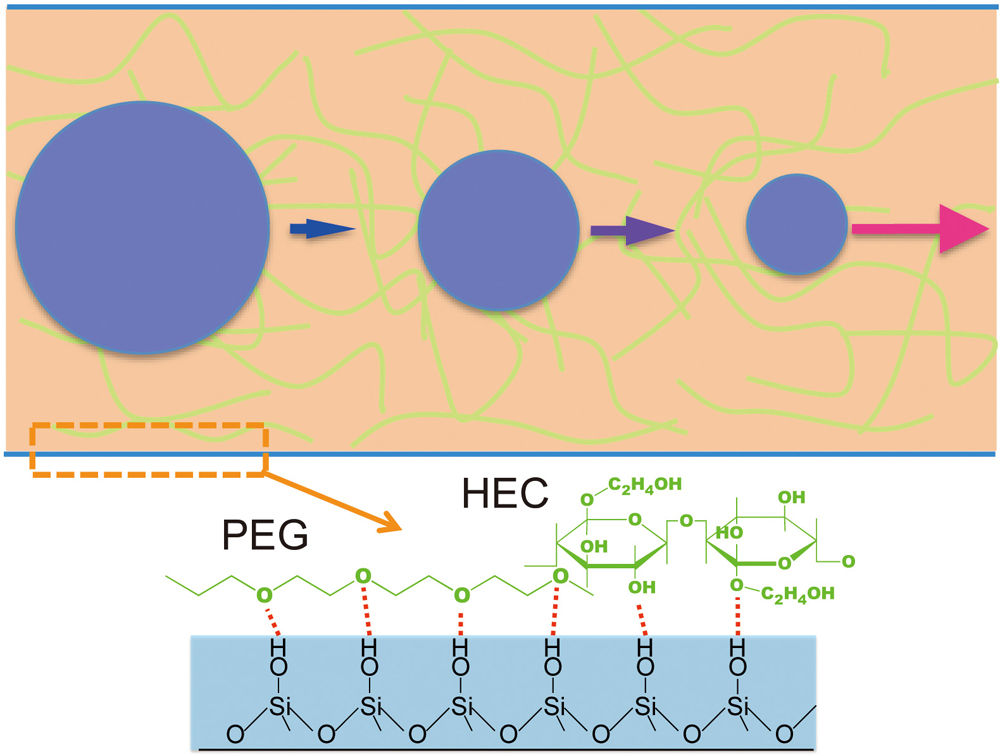 View full abstractDownload PDF (372K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (372K) -
Kiyoharu NAKATANI, Yuichi MAKINO, Yuki SHIMURA, Tomohiro FURUMURA, Kei ...Article type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1103-1106
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe insolubilization of cadmium in the soil of a naturally cadmium-contaminated paddy field was studied using an atomized iron powder and an extracting reagent. Cadmium in the soil was extracted into the water phase by calcium chloride. The extracted cadmium was deposited on the iron powder. The deposition of cadmium was significantly influenced by calcium chloride, since the surface area of the iron powder increased with the increasing calcium chloride concentration. We discuss the potential of the technique and the insolubilization mechanism. View full abstractDownload PDF (461K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (461K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Shigehiro KAGAYA, Yumi SAEKI, Daiki MORISHIMA, Riko SHIROTA, Takehiro ...Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1107-1112
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe potential of Presep® PolyChelate as a chelating resin was studied in detail. The chelating resin with extraction capacity for Cu of 0.30 mmol L−1 could quantitatively extract Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mo, Ni, Pb, V, and Zn at pH 4 or 5.5; however, only very scant amounts of Na, K, Mg, and Ca were captured at pH levels below 7. The quantitative extraction could be achieved in 100 – 1000 mL of artificial seawater and at a flow rate of 3 – 30 mL min−1. The performance of Presep® PolyChelate was compared to the other aminocarboxylic acid-type chelating resins, including Nobias Chelate-PA1, Chelex 100, Muromac B-1, Lewatit TP 207, and NTA Superflow, under the same conditions. The solid-phase extraction of the nine elements in the certified reference material (ES-L-1, ground water) and a commercially available table salt was also demonstrated.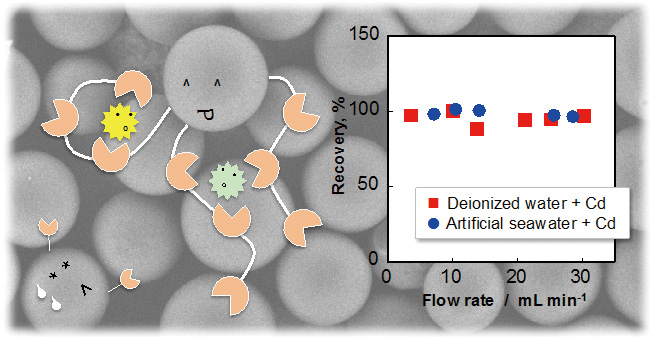 View full abstractDownload PDF (3343K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3343K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2013 Volume 29 Issue 11 Pages 1113
Published: November 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1669K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|