All issues

Volume 30, Issue 7
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 705
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (157K)
Special Reviews
-
Tomonori NOMOTO, Taro TOYOTA, Masanori FUJINAMIArticle type: Special Reviews
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 707-716
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn inhomogeneous distribution of interfacial tension can induce different types of non-equilibrium spontaneous motion at the interface by convective flow, or by the solutal Marangoni effect. Several applications of the quasi-elastic laser scattering (QELS) method used to study these effects are presented here. The relationship between the interfacial tension and the non-equilibrium phenomena has been verified experimentally for each application. In a water/nitrobenzene oscillatory system with continuous surfactant addition to the interface, the local adsorption of surfactants at the interface has been demonstrated and shown to be strongly related to the presence of electrolytes. In a donor/membrane/acceptor system, the dual-beam QELS method shows that surfactant adsorption at the membrane/acceptor interface is responsible for oscillations in the electric potential. The differences in the adsorption/desorption behavior of metal complex catalysts between air/liquid and liquid/liquid interfaces were considered in the propagating chemical waves of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction. We successfully measured the distribution of interfacial tension around a self-propelled camphor boat and an alcohol droplet floating on an aqueous phase, and compared the mechanisms of their motion. View full abstractDownload PDF (1190K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1190K)
Original Papers
-
Tomoko SHIMAMURA, Yoshihiro SUMIKURA, Takeshi YAMAZAKI, Atsuko TADA, T ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 717-721
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn inter-laboratory evaluation study was conducted in order to evaluate the antioxidant capacity of food additives by using a 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay. Four antioxidants used as existing food additives (i.e., tea extract, grape seed extract, enju extract, and d-α-tocopherol) and 6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchroman-2-carboxylic acid (Trolox) were used as analytical samples, and 14 laboratories participated in this study. The repeatability relative standard deviation (RSDr) of the IC50 of Trolox, four antioxidants, and the Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) were 1.8 – 2.2%, 2.2 – 2.9%, and 2.1 – 2.5%, respectively. Thus, the proposed DPPH assay showed good performance within the same laboratory. The reproducibility relative standard deviation (RSDR) of IC50 of Trolox, four antioxidants, and TEAC were 4.0 – 7.9%, 6.0 – 11%, and 3.7 – 9.3%, respectively. The RSDR/RSDr values of TEAC were lower than, or nearly equal to, those of IC50 of the four antioxidants, suggesting that the use of TEAC was effective for reducing the variance among the laboratories. These results showed that the proposed DPPH assay could be used as a standard method to evaluate the antioxidant capacity of food additives.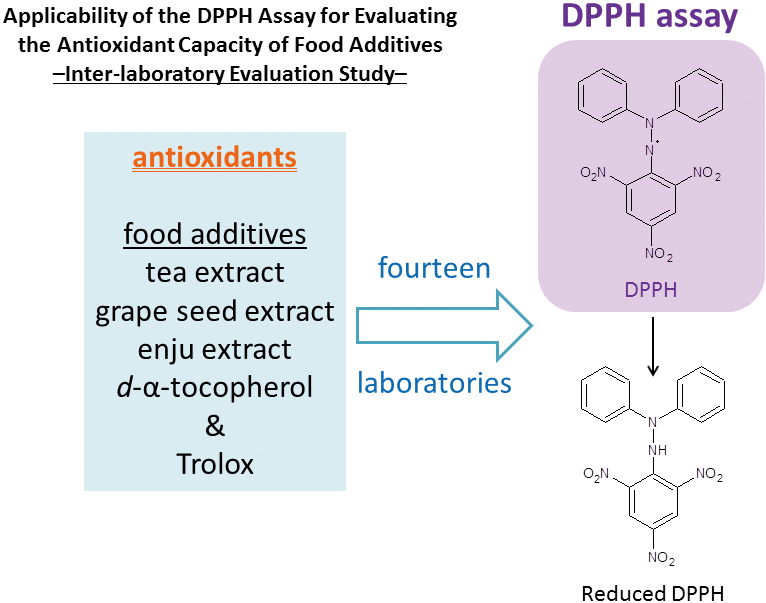 View full abstractDownload PDF (371K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (371K) -
LiJuan OU, XiaoYan LI, HongWei LIU, LiJuan LI, Xia CHUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 723-727
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPolythymine (poly T)-templated copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) were demonstrated as novel and sensitive fluorescence probes for the detection of Pb2+ based on the fluorescence quenching effect. The as-prepared CuNPs displayed strong fluorescence emission. However, the fluorescence of CuNPs was readily quenched in the presence of Pb2+. These changes in fluorescence intensity of CuNPs allowed for the analysis of Pb2+ with rapidity (<10 min), simplicity (label-free), high sensitivity (LOD 0.4 nM), high selectivity (no interference from other metal ions) and at low-cost (without any labels and sophisticated operation). We validated the practicality of using CuNPs for the determination of Pb2+ in environmental samples through analyses of tap water samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1070K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1070K) -
Przemyslaw NIEDZIELSKI, Armand DOSTATNIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 729-734
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis article describes the concept of controlling and correcting interference resulting from flame instability and sample reduction in absorption atomic spectrometry with flame atomization. Using popular laboratory spectrometers, which enable simultaneous or fast sequential measurements of many elements in the course of a single analysis, methods of controlling and correcting problems with instruments (e.g. reduction of sample flow) that directly affect the recorded analytical signal were elaborated.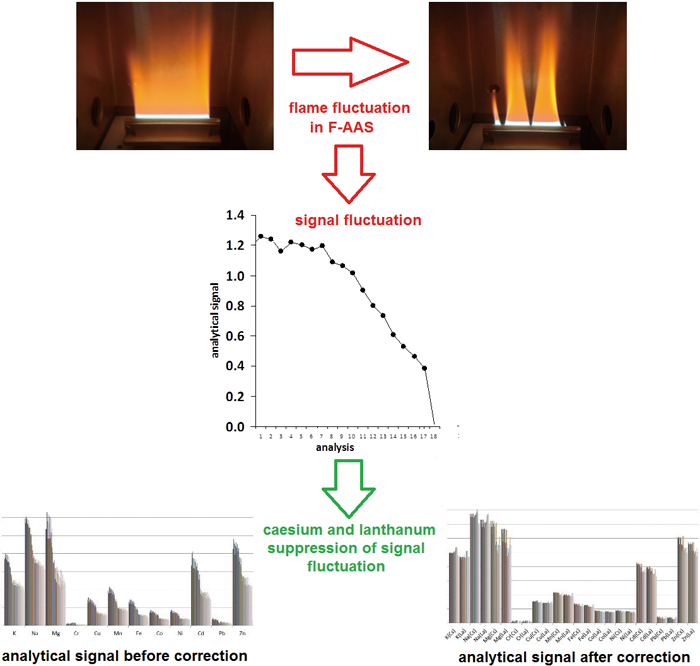 View full abstractDownload PDF (642K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (642K) -
Matti NIEMELÄ, Harri KOLA, Paavo PERÄMÄKIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 735-738
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHigh-purity germanium compounds (e.g. germanium dioxide) are used these days in several applications (e.g. germanium-based detectors, semiconductors, fiber-optic systems). Thus, reliable methods for the routine determination of trace element impurities from germanium compounds must be developed. In this study, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry and/or electrothermal atomic-absorption spectrometry was used for the determination of fifteen impurity elements in germanium dioxide. Possible interference effects due to a germanium matrix were eliminated/minimized by a simple open-vessel volatilization of germanium tetra chloride before the determinations. The results, based on the data gathered over a period of one year, showed that the long-run performance of the method is good, and it can be used for routine analysis of impurity elements in high-purity germanium dioxide. View full abstractDownload PDF (509K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (509K) -
Mami AKABANE, Atsushi YAMAMOTO, Sen-ichi AIZAWA, Atsushi TAGA, Shuji K ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 739-743
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThree reducing monosaccharides (glucose; Glc, galactose; Gal, and mannose; Man) were derivatized with L-tryptophan (L-Trp) under alkaline conditions. The DL-Gal and DL-Man derivatives were chirally resolved by HPLC with an acidic mobile phase, but the DL-Glc derivative was not. All of the three DL-monosaccharide derivatives were simultaneously enantioseparated using HPLC with a SunShell RP-AQUA column (C28) and a basic mobile phase. The optimum mobile phase conditions consisted of 5 mM phosphate and 25 mM tetraborate buffer (pH 9.6) at 20°C. With this system, resolution of D- and L-isomers of the Glc, Gal and Man derivatives were approximately 1.7, 2.2 and 2.4, respectively. When the three monosaccarides were derivatized with L-phenylalanine instead of L-Trp, DL-Gal and DL-Man were enantioseparated under both acidic and basic conditions, but DL-Glc was not. It was observed that enantiomer elution orders of the three monosaccharides derivatized with L-Trp were reasonably reversed when derivatized with D-Trp. It was also revealed that borate anions were required for simultaneous enantioseparation with HPLC.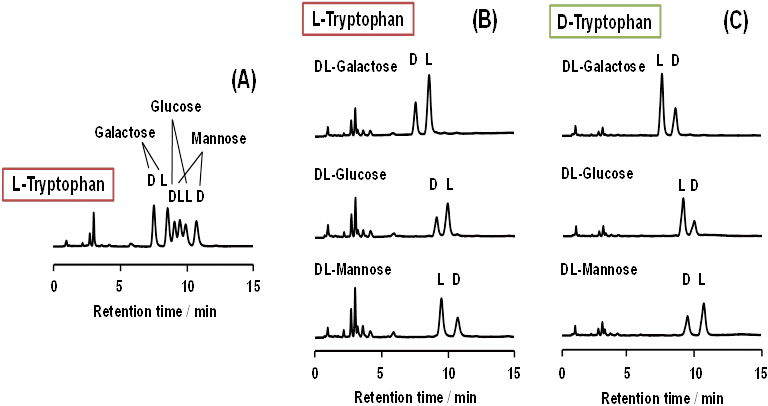 View full abstractDownload PDF (811K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (811K) -
Hitoshi WATARAI, Hoang Trong Tien DUC, Tran Thi Ngoc LAN, Tianyi ZHANG ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 745-749
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA simple zero-velocity method to determine the particle magnetic susceptibility by measuring the magnetophoretic velocity was proposed. The principle is that the magnetophoretic velocity of a particle in a liquid medium must be zero when the magnetic susceptibilities of the medium and the particle are equal, or the gravity force and the magnetophoretic force are balanced. By changing the medium magnetic susceptibility and measuring the magnetophoretic velocity of a particle, the particle magnetic susceptibility was determined from the medium magnetic susceptibility under the zero-velocity condition. The feasibility of the method was demonstrated for polystyrene particles using a Dy(III) solution in the horizontal migration mode and different organic solvents in the vertical migration mode. View full abstractDownload PDF (1147K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1147K) -
Ryoko TOMITA, Kenichiro TODOROKI, Kazuyuki MACHIDA, Sho NISHIDA, Hiros ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 751-758
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialMetabolomic studies conducted for evaluating cancer pathogenesis and progression by monitoring the amino acids metabolic balance hold great promise for assessing current and future anticancer treatments. We performed a comprehensive quantification of 21 amino acids concentrations in cultured human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells treated with the anticancer drugs 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and cisplatin. A precolumn fluorescence derivatization-HPLC method involving 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate was used. Amino acid concentration data were analyzed by principal-component analysis and partial least-squares multivariate statistical methods to represent samples on two-dimensional graphs. The hierarchical cluster analysis and linear discriminant analysis were used to classify the samples on the score plots. Unlike the cluster analysis approach, the linear discrimination analysis classification successfully distinguished anticancer drug-treated samples from the untreated controls. Moreover, three candidate amino acids (serine, aspartic acid, and methionine) were identified from the loading plots as potential biomarkers. Our proposed method might be able to evaluate the effectiveness of anticancer therapy even in small laboratories or medical institutions.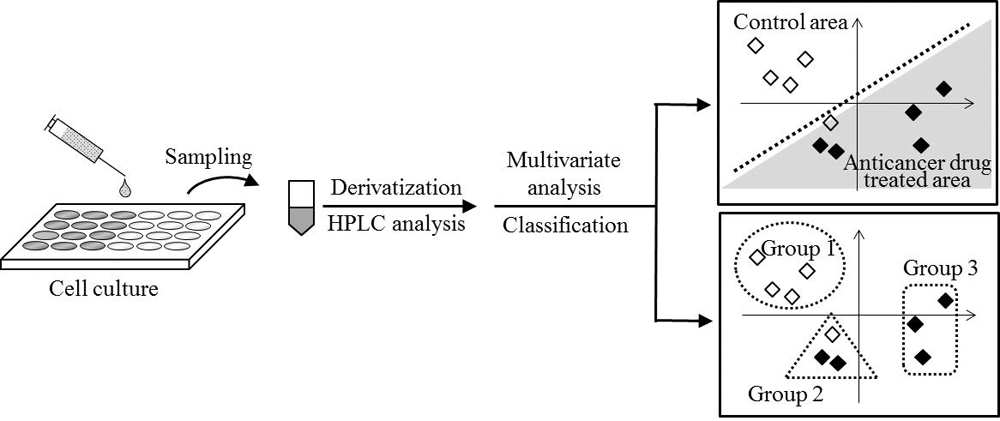 View full abstractDownload PDF (2025K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2025K) -
Liwei CAO, Tao DENG, Siliu LIANG, Xiaofang TAN, Jianxin MENGArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 759-766
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMethods were developed to determine glufosinate (GLUF), glyphosate (GLYP) and its metabolite, aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) by capillary electrophoresis-laser induced fluorescence detection using 5-(4,6-dichlorotriazinylamino) fluorescein (DTAF) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) as the derivatizing reagents. To accelerate the labeling speed, a microwave-assisted derivatization method was adopted. The derivatizing reaction time was reduced to 180 and 150 s for DTAF and FITC, whose reaction time for conventional labeling was 50 min and 5 h, respectively. The optimum separation conditions for derivatives were as follows: a back ground electrolyte (BGE) of 30 mmol L−1 sodium tetraborate containing 15 mmol L−1 brij-35, hydrodynamic injection 15 s and a 10 kV separation voltage. Under these conditions, the LODs (S/N = 3) for DTAF derivatives were 0.32, 0.19 and 0.15 nmol L−1 for GLUF, GLYP, and AMPA, respectively. The LODs (S/N = 3) for FITC derivatives were 2.60, 3.88 and 2.42 nmol L−1 for GLUF, GLYP, and AMPA, respectively. The applicability of the developed method was demonstrated by the detection of the above herbicides and metabolite in water and soil samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (666K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (666K) -
Yuichiro FUJIMOTO, Keisuke SOGABE, Hajime OHTANIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 767-772
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new decomposition method for structural analysis of polysiloxanes (silicones) was developed using methyl orthoformate. The siloxane bonds in samples with vinyl and/or methyl side groups decomposed under relatively mild acidic conditions up to around 70°C and were followed by methoxylation at the cleaved linkages with few side reactions. The product yields with respect to the siloxane monomer units were 98 – 100% for low molecular weight model siloxane compounds. Additionally, this method decomposed the silicone polymer sample in a similar manner with decomposition yields of 98 and 103% for the dimethylsiloxane main chain and dimethylvinylsilyl end groups, respectively. These results demonstrate that the proposed decomposition method should be an effective pretreatment procedure for structural and compositional analyses of silicone polymers. View full abstractDownload PDF (575K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (575K)
Notes
-
Tomoko HARAGA, Shingo SAITO, Yoshiyuki SATO, Shiho ASAI, Yukiko HANZAW ...Article type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 773-776
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA simple and rapid method with low radiation exposure risk was developed for the determination of neodymium in spent nuclear fuel by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection using a fluorescent probe having a macrocyclic hexadentate polyaminocarboxylate structure. The concentration of Nd(III) in a spent nuclear fuel sample was determined with no interference from various matrix elements, including lanthanides and uranium (at a 200-fold excess), with 92 ± 3% recovery. This is due to high resolution based on establishing a ternary complex equilibrium during migration in which the hydroxyl ion plays an auxiliary role (log KLn–L–OH = 3.9 – 5.3). View full abstractDownload PDF (506K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (506K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 7 Pages 777
Published: July 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2542K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|