All issues

Volume 31, Issue 1
Displaying 1-10 of 10 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 1
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (180K)
Rapid Communications
-
Fumitaka MARUYAMA, Shigehiko FUJIMAKI, Yuki SAKAMOTO, Yukihiko KUDO, H ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 3-5
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA study on the rapid identification of phthalates in polymer materials has been conducted by employing gas chromatography–mass spectrometry coupled with a pyrolyzer (Py–GC/MS). Since Py–GC/MS does not require any complex solvent-extraction process, a rapid screening of phthalates should be possible. In this study, polymer samples were directly introduced into the pyrolyzer in order to thermally extract phthalates from the polymer under specific heating conditions. By optimizing the Py–GC/MS parameters, a sequential testing cycle of 35 min per sample was feasible without causing any major decomposition of the base materials. Thus, a rapid screening of over 20 samples per day was achieved without any time constraints by effectively utilizing specifically prepared reference polymer sheets for quality control. Py–GC/MS was found to be suitable and effective for identifying phthalates in polymer materials.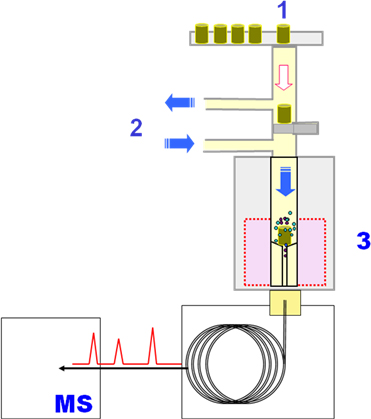 View full abstractDownload PDF (613K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (613K)
Special Reviews
-
Hiroki HOTTA, Kin-ichi TSUNODAArticle type: Special Reviews
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 7-14
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecent studies from our laboratory on electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) for the quantification of inorganic cations and anions are reviewed. Metal ions were determined by ESI-MS in negative-ion mode as monovalent negative ions of their aminopolycarboxylate (APC) complexes, where excess amounts of the APC agents were added to sample solutions. Among the APCs studied, we found trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (CyDTA, the chemical forms in a complex were expressed as Hncydtan−4) as the best chelating agent. A size exclusion column was used for on-line separation of the metal–APC complexes from matrix salts in samples. Total amounts of Al, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Pb in the biological certified reference materials (CRM), Olive Leaves (BCR-062) and Plankton (BCR-414), and in a soil CRM (JSAC-0401) were successfully determined by the proposed method. Halide ions (X− = F−, Cl−, Br− and I−) and cyanide (CN−) were determined by ESI-MS based on the formation of ternary complexes of metals, chelating agents and the analyte anions. Negative ions of the ternary complexes of group 13 elements, nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA, Hnntan−3), and halides, i.e., [AlF(nta)]− for F−, and [InX(nta)]− for other halides, were measured; the limits of detection (LODs) were 10 nmol dm−3 for F−, 0.31 μmol dm−3 for Cl−, 3.8 nmol dm−3 for Br−, and 1.6 nmol dm−3 for I−, respectively. In the case of CN−, an LOD of 20 nmol dm−3 was obtained based on measurements of the ternary complex of CuII, CN− and 4-(2-pyridylazo)resorcinol (PAR, Hnparn−2), i.e., [63CuII(CN)(par)]− (m/z 302). Moreover, quantitative methods for CrVI and CrIII by ESI-MS were developed, where HCrO4− (m/z 117) for CrVI and [CrIII(cydta)]− for CrIII were used for measurements.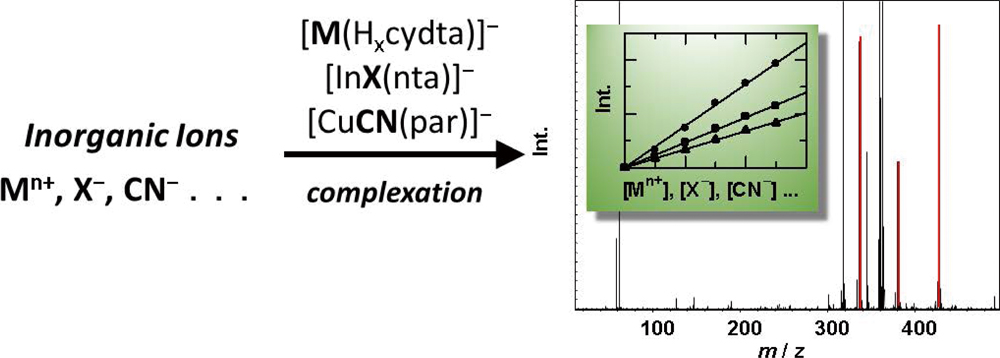 View full abstractDownload PDF (784K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (784K)
Original Papers
-
Tsuyoshi SUGITA, Masanobu MORI, Akinori MASE, Shin-nosuke NOGUCHI, Tor ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 15-21
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, a photocatalytic plate bound to highly dispersible silica-doped titanium dioxide (SiT) on a trimethoxysilyl-propyldiethylenetriamine (dien)-coated glass plate (dien-plate) was newly synthesized, and was evaluated by a flow analytical (FA) system, which consists of a photocatalytic reactor and a spectrophotometer, to continuously monitor the absorbance of tested chemicals. The method was not required to collect any sample solution at a constant period. The SiT–dien-plate facilitated the photodecomposition of methylene blue (MB) and indigo carmine (InC) in aqueous solutions. Notably, MB was quantitatively photo-decomposed following 18 h of UV-light irradiation, related to the electrostatic adsorption of surface-bound particles. A water-treatment ability of visible-light-responsive vanadium-modified nitrogen/silica co-doped titanium dioxide fixed on the dien-plate was also evaluated by the FA system. It clarified to decompose MB and InC under visible-light irradiation. Finally, the decomposition of a humic substance dissolved from Middle West China peaty soils by the SiT–dien-plate under UV-irradiation was assessed as applying the FA system with a photocatalytic plate. View full abstractDownload PDF (3574K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3574K) -
Tetsuo KUWABARA, Ryota SATAKE, Haocheng GUOArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 23-27
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTwo benzocrown ether–bipyridinium conjugates, 1 and 2, each having a different length of alkyl chains with butyl and dodecyl groups, respectively, have been synthesized for the purpose of developing a new guest-responsive color-change chemosensor. Both 1 and 2 showed yellow colors with broad absorption bands around 400 nm in acetonitrile. These are associated with the intramolecular charge transfer (CT) absorption, in which the benzocrown ether and bipyridinium units act as the donor and acceptor, respectively. Upon addition of the guest; such as Na+, they faded in color due to the blue shift in their intramolecular charge transfer absorption bands. These are associated with the formation of 1:1 host–guest inclusion complex. Analogues, 3 and 4, both being similar in structure to 1 and 2 with non-crown ether unit, also showed intramolecular CT absorptions around 400 nm, but did not change their absorption spectra upon addition of the guest because of the lack of guest-binding abilities. The guest-induced color change of 1 and 2 can be used for alkali and alkaline metal ion sensing. Both 1 and 2 could detect divalent cations such as Mg2+ and Ca2+ rather than univalent ones, Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+. Although a marked difference between 1 and 2 was not observed in their guest sensing abilities, the remarkable recognition of 1 and 2 for Mg2+ and Ca2+ was found compared with that of 5, which has benzyl unit instead of alkyl chains of 1 and 2. The sensitivity values of 1 and 2 were roughly proportional to their binding constants, as shown by the binding constants with Li+, Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ with the values of 910, 260, 820, and 2300 M−1 for 1 and 930, 290, 1270, and 2790 M−1 for 2, while the binding constants of 5 were estimated to be 930, 440, 210, and 1200 M−1 for Li+, Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, respectively. The limit concentration of detection of 2 for Ca2+ was estimated to be 0.016 mM, which was the smallest value in this system.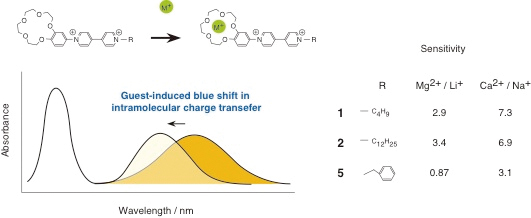 View full abstractDownload PDF (584K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (584K) -
Neuma das Mercês PEREIRA, Fernando Mota de OLIVEIRA, Nara R&uacu ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 29-35
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis work describes the highly sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides employing the cobalt(II) 4,4,4,4-tetrasulfo-phthalocyanine (CoTSPc) macrocycle complex, carbon nanotubes (CNT), and 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (OMIM[BF4]). The technique is based on enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition. The composite was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, and amperometry. The AChE was immobilized on the composite electrode surface by cross-linking with glutaraldehyde and chitosan. The synergistic action of the CoTSPc/CNT/OMIM[BF4] composite showed excellent electrocatalytic activity, with a low applied potential for the amperometric detection of thiocholine (TCh) at 0.0 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The calculated catalytic rate constant, kcat, was 3.67 × 103 mol−1 L s−1. Under the optimum conditions, the inhibition rates of these pesticides were proportional to their concentrations in the ranges of 1.0 pmol L−1 to 1.0 nmol L−1 (fenitrothion), 2.0 pmol L−1 to 8.0 nmol L−1 (dichlorvos), and 16 pmol L−1 to 5.0 nmol L−1 (malathion). View full abstractDownload PDF (1975K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1975K) -
Junichi ODO, Masahiko INOGUCHI, Hiroyuki AOKI, Yuto SOGAWA, Masahiro N ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 37-44
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe fluorescent derivatization of aromatic carboxylic acids by the catalytic activity of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the presence of excess H2O2 was investigated. Four monocarboxylic acids, nine dicarboxylic acids, and two tricarboxylic acids, all of which are non- or weakly fluorescent, were effectively converted into fluorescent compounds using this new method. This technique was further developed for the fluorometric determination of trace amounts of terephthalic acid (3c) and lutidinic acid (2b), and linear calibration curves for concentrations between 2.5 and 20.0 nmol of terephthalic acid (3c) and 1.0 and 10.0 nmol of lutidinic acid (2b) were demonstrated. Compound III, an intermediate of HRP, played an essential role in this process. Additionally, lactoperoxidase and manganese peroxidase, peroxidases similar to HRP, showed successful fluorescent derivatization of nicotinic acid (1b), lutidinic acid (2b), and hemimellitic acid (4a) in the presence of excess H2O2.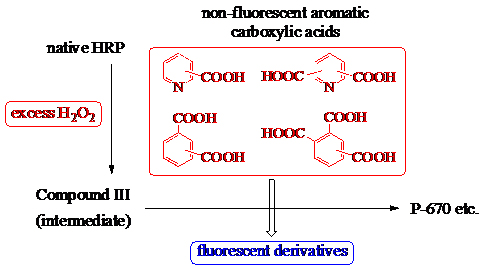 View full abstractDownload PDF (2642K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2642K) -
Jian GUO, Tomomi SAIKI, Kumrungsee THANUTCHAPORN, Wanying LIU, Akihiro ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 45-50
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study investigates the characteristics of a partially sulfonated ethylstyrene–divinylbenzene copolymer for the separation of di-peptides by high-performance liquid chromatography. Di-peptides (VE, VA, VH, VK, and VR) with different isoelectric points (pI, 4.0 to 9.7) and log P values (−1.63 to −0.72) were used to optimize the separation conditions of the columns packed with sulfonated copolymer resin. The retention factor (k) of the di-peptides on the column with a 0.81 wt% sulfo group content decreased with increasing concentrations of phosphate salts (2.5 – 20 mmol L−1) in the mobile phase. The complete separation of the five di-peptides was obtained with a gradient of 10% methanol containing 5 mmol L−1 NaH2PO4 (pH 4.8) to 50% methanol containing 5 mmol L−1 Na2HPO4 (pH 8.9) for 60 min at 0.5 mL min−1 at 50°C. Under the optimal conditions, a good relationship between the k and pI values of the di-peptides, with the exception of VE (pI 4.0), was observed, suggesting that the retention of the di-peptides on the column packed with sulfonated copolymer resin was dependent on the pI value, when it was greater than 5. The log P value also influenced the separation characteristics of the column; peptides possessing the same pI value (6.4 for GH, VH, IH, and FH) showed a higher retention on the column with increasing log P values. In conclusion, the prototype sulfonated ethylstyrene–divinylbenzene copolymer column was applicable for the separation of basic di-peptides, and the separation depended on the pI and hydrophobicity of the di-peptides. View full abstractDownload PDF (661K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (661K)
Notes
-
Takao SAKURAI, Shoji KURATA, Kenji OGINOArticle type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 51-54
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel field sensing method for concentrated acid solutions was developed. The sensor is composed of a dye, Oil Red O, and florisil as a support for the dye. When the dye is supported on the florisil surface, its color change properties against the acid solution drastically changes compared to in solution, and the sensor is applicable to sensing for acids of relatively low concentration. The significant phenomenon could not be observed when silica gel was used as a support, suggesting that the florisil plays an important role in the color changing phenomenon. The amount of dye absorbed on the florisil surface is related to the color change properties. View full abstractDownload PDF (678K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (678K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015 Volume 31 Issue 1 Pages 55
Published: January 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2608K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|