All issues

Volume 31, Issue 11
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Mikito YASUZAWA, Yuya OMURA, Kentaro HIURA, Jiang LI, Yusuke FUCHIWAKI ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1111-1114
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCellulose nanofiber aqueous solution, which remained virtually transparent for more than one week, was prepared by using the clear upper layer of diluted cellulose nanofiber solution produced by wet jet milling. Glucose oxidase (GOx) was easily dissolved in this solution and GOx-immobilized electrode was easily fabricated by simple repetitious drops of GOx-cellulose solution on the surface of a platinum-iridium electrode. Glucose sensor properties of the obtained electrodes were examined in phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.4 at 40°C. The obtained electrode provided a glucose sensor response with significantly high response speed and good linear relationship between glucose concentration and response current. After an initial decrease of response sensitivity for a few days, relatively constant sensitivity was obtained for about 20 days. Nevertheless, the influence of electroactive compounds such as ascorbic acid, uric acid and acetoaminophen were not negletable.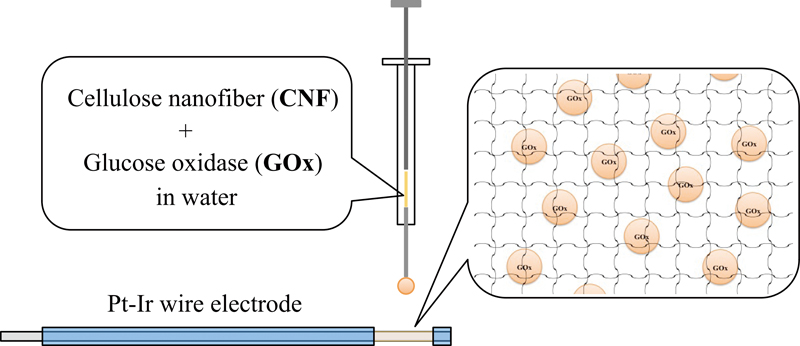 View full abstractDownload PDF (750K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (750K) -
Kenji CHAYAMA, Yuki SANO, Satoshi IWATSUKIArticle type: Rapid Communications
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1115-1117
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA pyridinium-based task-specific ionic liquid (TSIL) with a monothioether group, [3-TPPy][NTf2], extracted typical class b metal ions, such as Ag(I), Cu(I), Pd(II), and Pt(II), in high selectivity. It was found that the composition ratio of the extracted Ag(I) and Cu(I) species depended on the TSIL concentration, and that TSIL extracted these metal ions through mono-S-coordinated complex formation at low TSIL concentrations. [3-TPPy][NTf2] can be recycled in the extraction–recovery process, which is of a great advantage for practical use in environmentally benign separation methods.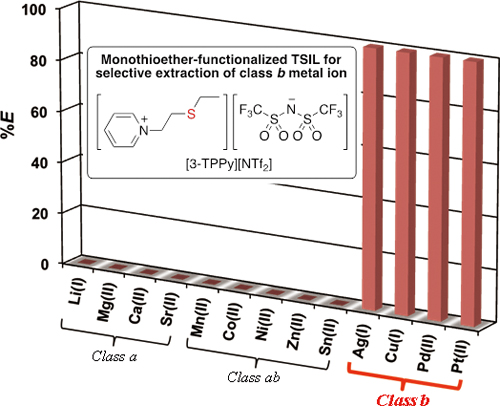 View full abstractDownload PDF (380K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (380K)
-
Article type: Guest Editorial
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1119
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (129K)
Reviews
-
Julius MBUNA, Takashi KANETAArticle type: Reviews
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1121-1128
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCapillary electrophoresis (CE) coupled with laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) is a powerful method for the trace analysis of cellular components. This review presents a summary of topics for the direct analysis of anthracyclines and multidrug resistance proteins in cancerous cells. A micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) method that does not use organic solvents, and hence prevents the precipitation of proteins in cellular samples, was shown to be a reliable method for the determination of several anthracyclines including the epimeric doxorubicin and epirubicin. A fast CE-based immunoassay for investigating transporter multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP1) was also developed for routine or explorative analysis of the levels of transporter proteins in cancerous cells. A combination of the developed MEKC-LIF method and the CE immunoassay (CEIA) method has permitted the analysis of anthracyclines and MRP1 in a cell line to show the relationship between the levels of MRP1 and amount of anthracyclines in cancerous cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (935K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (935K)
Original Papers
-
Tsubasa OYAMA, Rie NAGAI, Mayumi FUJIMOTO, Ryoko KONISHI, Masashi MITA ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1129-1135
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fully-automated on-line oxidation column-switching HPLC system has been developed for the determination of endogenous melatonin in human plasma and saliva. This HPLC system consists of four processes. In the first step, melatonin is fractionated using a reversed-phase C4 column (Proteonavi, 75 mm × 1.0 mm i.d.). In the second step, the obtained melatonin fraction is on-line collected, and oxidized to a highly-fluorescent compound, N-[(6-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)methyl]acetamide (6-MOQMA), by mixing with hydrogen peroxide under alkaline conditions. In the third step, the produced 6-MOQMA is concentrated, and the oxidation reagents are removed using an alkaline resistive reversed-phase column, Asahipak ODP (35 mm × 1.0 mm i.d.). In the final fourth step, the 6-MOQMA is determined by a microbore-ODS column packed with ultrafine particles (CAPCELL PAK C18 IF, 250 mm × 1.0 mm i.d.). The limit of detection of melatonin using this system is about 200 amol/injection, and the determination of endogenous melatonin in a small volume of human physiological fluids, such as 100 μL of plasma and 300 μL of saliva, was successfully accomplished. View full abstractDownload PDF (919K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (919K) -
Toshiaki TAZAWA, Yuuhi MORI, Akira KOBAYASHI, Kenichi NAKANE, Tomoya M ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1137-1141
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA bundle of polymer-coated filaments was successfully introduced as an extraction medium for the preconcentration of an aqueous solution of aromatic compounds. The extraction was simply carried out with pumping the aqueous sample solution to the extraction capillary at ambient temperature. The extracted analytes were sequentially eluted with a flow of pure water using temperature-programmed heating of the extraction capillary in an oven. The results clearly suggest that the polymer-coated fiber-packed capillary could be employed in the sample preparation process for the analysis of various aqueous samples. Introducing the fractions eluted from the fiber-packed capillary to a conventional microcolumn liquid chromatography (micro-LC) system via a home-made valve-based modulator, an on-line coupled extraction/separation system was developed and a possibility to a pseudo-two-dimensional (pseudo-2D) LC separation of aromatic compounds in aqueous matrices has also been demonstrated. View full abstractDownload PDF (912K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (912K) -
Daiki GOTO, Kazuki OUCHI, Masami SHIBUKAWA, Shingo SAITOArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1143-1149
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIt is difficult to control the electrophoretic mobility in order to obtain high resolution among saccharides in complex samples. We report herein on a new affinity capillary electrophoresis (ACE) method for an anionic monosaccharide, N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), which is important in terms of pathological diagnosis, using lanthanide-hexadentate macrocyclic polyazacarboxylate complexes (Ln-NOTA) as affinity reagents. It was shown that Ln-NOTA complexes increased the anionic mobility of Neu5Ac by approximately 40% through selective complexation with Neu5Ac. The extent of change in the mobility strongly depended on the type of central metal ion of Ln-NOTA. The stability constant (K) of Lu-NOTA with Neu5Ac was determined by ACE to be log Kb = 3.62 ± 0.04, which is the highest value among artificial receptors for Neu5Ac reported so far. Using this ACE, the Neu5Ac content in a glycoprotein sample, α1-acid glycoprotein (AGP), was determined after acid hydrolysis. Complete separation between Neu5Ac and hydrolysis products was successful by controlling the mobility to determine the concentration of Neu5Ac. View full abstractDownload PDF (728K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (728K) -
Zone Sharpening of Peptides in Pressurized Capillary Electrochromatography Using Dynamic pH JunctionHideomi UMEDA, Shinya KITAGAWA, Hajime OHTANIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1151-1154
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn HPLC, analytes injected into a separation column broaden naturally during the separation procedure. In this paper, analyte zone sharpening of peptides was achieved in pressurized capillary electrochromatography, which is a separation method that combines capillary HPLC and capillary electrophoresis (CE), by employing dynamic pH junction for CE. When the pH of the mobile phase was altered from basic to acidic in a step gradient, the analyte peptides were focused at the basic/acidic interface with the application of voltage. The effect of both pH and pressurized flow velocity on the zone sharpening was investigated. With the proposed method, the peak height of angiotensin II, [Asn1, Val5]-angiotensin II, and angiotensin III were enhanced 12, 10, and 12 times, respectively. Selective peak zone sharpening for angiotensin II was also demonstrated.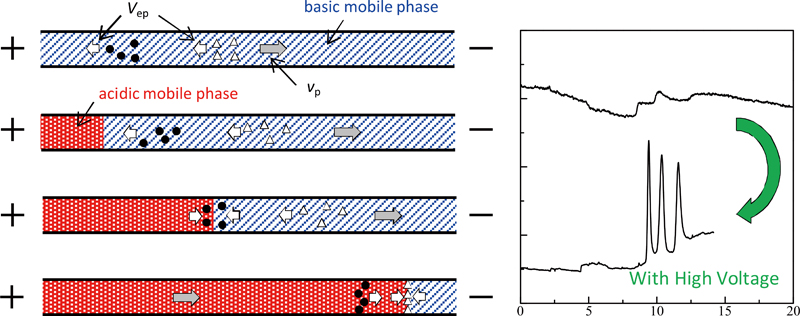 View full abstractDownload PDF (662K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (662K) -
Kenji SUEYOSHI, Yuto NOGAWA, Kasumi SUGAWARA, Tatsuro ENDO, Hideaki HI ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1155-1161
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, a simple and highly sensitive enzyme activity assay based on reagent-release capillary–isoelectric focusing is described. Reagent-release capillaries containing a fluorescent substrate, which produces fluorescent products possessing an isoelectric point after reaction with enzymes, provides a simple procedure. This is because it allows to spontaneously inject a sample solution into the capillary by capillary action, mixing reagents, and subsequently concentrating the fluorescent products based on isoelectric focusing. Fluorescent rhodamine 110 and its monoamide derivative, which were generated as a final product and an intermediate, respectively, were then focused and separated by reagent-release capillary–isoelectric focusing. After 30 min of enzyme reactions, two focused fluorescent bands were clearly isolated along the prepared capillaries. Employing the focused band of rhodamine 110 monoamide allowed for highly sensitive detection of enzyme activity in the 10 pg mL−1 order, while that of the conventional assay using a microplate was in the ng mL−1 order. Furthermore, arraying reagent-release capillaries of different substrates on a chip allowed for simultaneous multi-assay of enzyme activity with good sensitivity in the pg mL−1 order for each protein. View full abstractDownload PDF (5802K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5802K) -
Akihiko ISHIDA, Mitsutaka FUJII, Takehiro FUJIMOTO, Shunsuke SASAKI, I ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1163-1169
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA compact and lightweight liquid chromatography system is presented with overall dimensions of 26 cm width × 18 cm length × 21 cm height and weight of 2 kg. This system comprises a battery-operated compact electroosmotic pump, a manual injector, a microfluidic chip device containing a packed column and an electrochemical detector, and a USB bus-powered potentiostat. The pumping system was designed for microfluidic-based reversed-phase liquid chromatography in which an electroosmotically generated water stream pushes the mobile phase via a diaphragm for the output. The flow rate ranged from 0 to 10 μL/min and had a high degree of precision. The pumping system operated continuously for over 24 h with dry batteries. The column formed in the microfluidic device was packed with 3-μm ODS particles with a length of 30 mm and a diameter of 0.8 mm. The results presented herein demonstrate the performance of the pumping system and the column using alkylphenols, catecholamine, catechin, and amino acids. View full abstractDownload PDF (2692K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2692K) -
Fumihiko KITAGAWA, Syo NAKAGAWARA, Isoshi NUKATSUKA, Yusuke HORI, Kenj ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1171-1175
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and rapid vacuum-drying modification method was applied to several neutral and charged polymers to obtain coating layers for controlling electroosmotic flow (EOF) and suppressing sample adsorption on poly(dimethyl siloxane) (PDMS)-glass hybrid microchips. In the vacuum-dried poly(vinylpyrrolidone) coating, the electroosmotic mobility (μeo) was suppressed from +2.1 to +0.88 × 10−4 cm2/V·s, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) of μeo was improved from 10.2 to 2.5% relative to the bare microchannel. Among several neutral polymers, poly(vinylalcohol) (PVA) and poly(dimethylacrylamide) coatings gave more suppressed and repeatable EOF with RSDs of less than 2.3%. The vacuum-drying method was also applicable to polyanions and polycations to provide accelerated and inversed EOF, respectively, with acceptable RSDs of less than 4.9%. In the microchip electrophoresis (MCE) analysis of bovine serum albumin (BSA) in the vacuum-dried and thermally-treated PVA coating channel, an almost symmetric peak of BSA was obtained, while in the native microchannel a significantly skewed peak was observed. The results demonstrated that the vacuum-dried polymer coatings were effective to control the EOF, and reduced the surface adsorption of proteins in MCE. View full abstractDownload PDF (1361K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1361K) -
Yuji KAWAI, Satoshi FUJINAGA, Masahiko HASHIMOTO, Kazuhiko TSUKAGOSHIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1177-1182
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn open-tubular capillary chromatography system (tube radial distribution chromatography, TRDC) was developed using a ternary solvent (water-acetonitrile-ethyl acetate; volume ratio, 3:8:4) containing 10 mmol L−1 8-quinolinol for the separation of nitrate, chloride, and sulfate compounds of Ni(II), Al(III), and Fe(III). When a mixed solution of the Ni(II) compounds was injected into an untreated fused-silica capillary tube (90 cm × 75 μm i.d.) with a ternary solvent flow rate of 0.8 μL min−1, the compounds were eluted in the following order: [Ni(II)-(8-quinolinol)3] complex, [Ni(II)-(8-quinolinol)]-nitrate ion interaction complex, [Ni(II)-(8-quinolinol)]-chloride ion interaction complex, and [Ni(II)-(8-quinolinol)]-sulfate ion interaction complex. The elution of mixtures of the Al(III) and Fe(III) compounds showed similar trends. View full abstractDownload PDF (4515K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4515K) -
Ronald P. MANGINELL, Curtis D. MOWRY, Adam S. PIMENTEL, Michael A. MAN ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1183-1188
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMiniaturization of gas chromatography (GC) instrumentation enables field detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) for chembio-applications such as clandestine human transport and disease diagnostics. We fabricated a mesoscale pulsed discharge helium ionization detector (micro-PDHID) for integrating with our previously described mini-GC hardware. Stainless steel electrodes fabricated by photochemical etching and electroforming facilitated rapid prototyping and enabled nesting of inter-electrode insulators for self-alignment of the detector core during assembly. The prototype was ∼10 cm3 relative to >400 cm3 of a commercial PDHID, but with a comparable time to sweep a VOC peak from the detector cell (170 ms and 127 ms, respectively). Electron trajectory modeling, gas flow rate, voltage bias, and GC outlet location were optimized for improving sensitivity. Despite 40-fold miniaturization, the micro-PDHID detected 18 ng of the human emanation, 3-methyl-2-hexenoic acid with <3-fold decrease in sensitivity relative to the commercial detector. The micro-PDHID was rugged and operated for 9 months without failure. View full abstractDownload PDF (955K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (955K)
Notes
-
Simple Pretreatment and HILIC Separation for LC-ESI-MS/MS Determination of Adenosine in Human PlasmaHiroya MURAKAMI, Erina OTANI, Tomoko IWATA, Yukihiro ESAKA, Takuma AOY ...Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1189-1192
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple pretreatment method and separation mode for the LC-ESI-MS/MS determination of adenosine in human plasma have been developed. Deproteinization by acetonitrile and ultrafiltration followed by chromatographic separation with a hydrophilic interaction chromatographic (HILIC) column give a highly sensitive MS/MS response without ionic suppression caused by the matrix compounds in human plasma. In addition, the presence of ammonium acetate in the mobile phase contributes to high sensitivity in MS/MS detection, facilitating the ionization of adenosine. This method seems to be amenable to the treatment of many samples in clinical practice.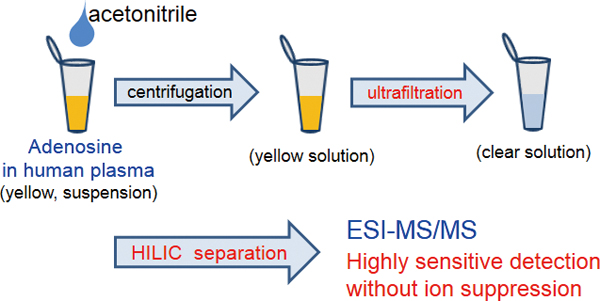 View full abstractDownload PDF (440K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (440K) -
Toshio TAKAYANAGI, Mika AMIYA, Natsumi SHIMAKAMI, Tomoki YABUTANIArticle type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1193-1196
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe acid dissociation constant of pravastatin was determined under degraded conditions. Pravastatin was degraded in an acidic solution (pH = 2.0) for 5 h, and the degradation solution was subjected to the measurement of the effective electrophoretic mobility by capillary zone electrophoresis. Although the amount of pravastatin decreased by the acid degradation, its acid dissociation constant was successfully determined with the residual pravastatin through its effective electrophoretic mobility. The determined acid dissociation constant value agreed well with the one obtained with freshly prepared solution and with some reported values. View full abstractDownload PDF (498K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (498K) -
Micropillars Fabricated on Poly(methyl methacrylate) Substrates for Separation of Microscale ObjectsTakao YASUI, Satoru ITO, Noritada KAJI, Manabu TOKESHI, Yoshinobu BABAArticle type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1197-1200
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDevelopment of polymeric microfluidic devices has played an important role in the recent, rapid progress of biomedical research. Here we report a fabrication method for micropillars on poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) substrates for separation of microscale objects. The fabricated micropillars enable continuous separation of microparticles only by introducing fluids. The present method offers a new strategy to fabricate polymeric prototype devices for R&D work.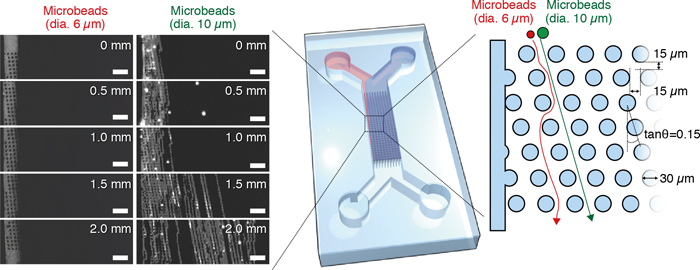 View full abstractDownload PDF (1312K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1312K) -
Adelina SMIRNOVA, Hisashi SHIMIZU, Kazuma MAWATARI, Takehiko KITAMORIArticle type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1201-1204
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMicro- and nanofluidics has attracted much attention, particularly concerning single-cell analysis when small amounts of liquids are examined. In present work we successfully fabricated extended-nano channels that were more narrow and shorter (2 mm) as well as wider and longer (10 mm), and accomplished a reversed-phase HPLC separation of labeled amino acids on these channels after octadecylsilylation (ODS). The separation performance characteristics were compared for both types of nano spaces. At an equal amount of pressure, the longer extended-nano channels showed permeability that was one-order higher (K = 47 × 10−14 m2) and separation impedance (E = 13) that was one-order lower than that of the shorter version. Also, the separation plate number for the longer channel was 4000 with a plate height of 2.5 μm. Both channels have advantages for use in single-cell analysis. The longer channel can be applied for the separation of macromolecules (proteomics), while the short version is more applicable to small molecules (amino acids).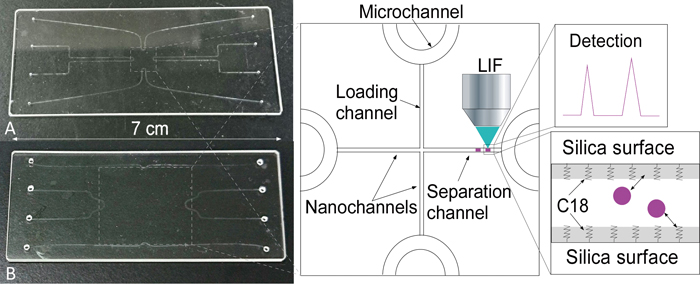 View full abstractDownload PDF (589K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (589K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015 Volume 31 Issue 11 Pages 1205
Published: November 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2746K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|