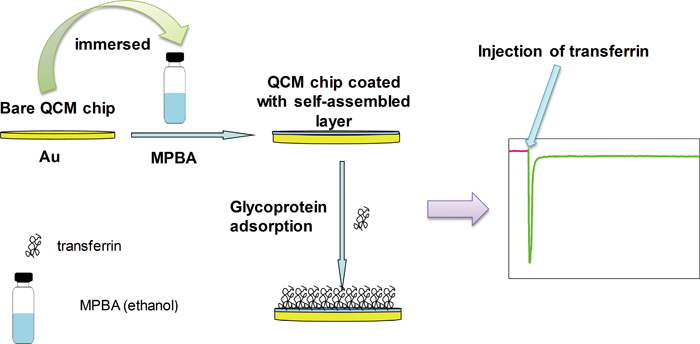
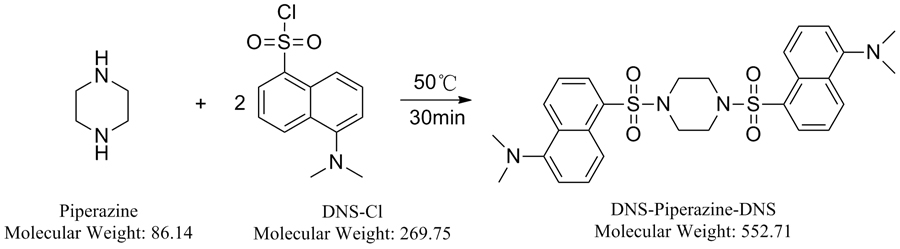
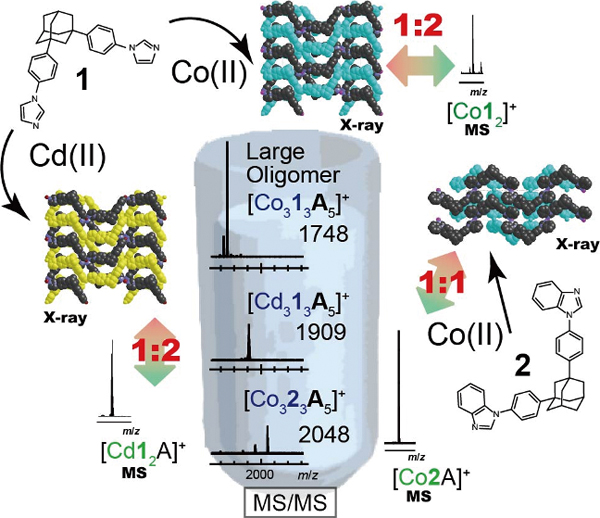
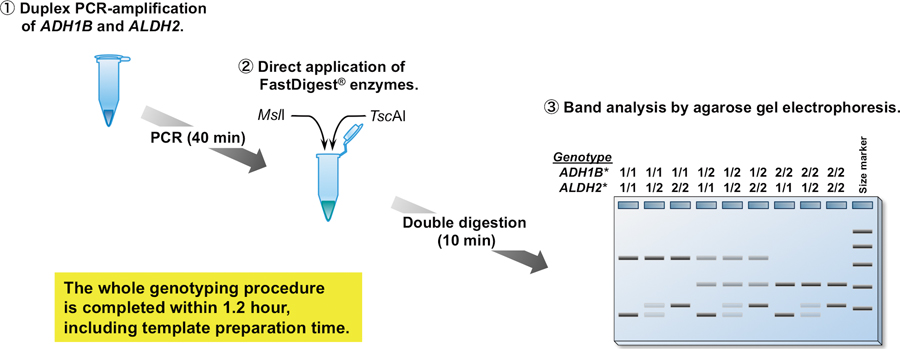
Volume 32, Issue 12
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1269-1276
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (766K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1277-1282
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (945K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1283-1289
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (1480K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1291-1294
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (2404K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1295-1300
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (1952K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1301-1305
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (714K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1307-1314
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (1944K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1315-1320
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (958K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1321-1325
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (612K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1327-1332
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (542K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1333-1338
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (891K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1339-1345
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (1456K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1347-1352
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (1110K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1353-1357
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (581K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1359-1362
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (1806K) -
Article type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1363-1366
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (709K) -
Article type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1367-1370
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (746K) -
Article type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1371-1374
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (623K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1375-1379
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (11850K) -
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1381-1384
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (2460K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2016 Volume 32 Issue 12 Pages 1385
Published: December 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2016
Download PDF (2948K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|