All issues

Volume 32, Issue 5
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Yusuke SUZUKI, Aya OKANO, Kazuya KABAYAMA, Atsuyoshi NISHINA, Minoru T ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 487-490
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFluorescence derivatization of the oligosaccharides released from glycoconjugates is widely used for precise structural characterization. To ensure labeling of the oligosaccharides, a large excess of fluorescence reagents is usually added to the reaction tube. Therefore, any excess reagents and by-products of the labeling reaction should be removed by several column chromatographies, including using a cellulose cartridge or spin columns. However, these purification steps are often time-consuming, expensive, and laborious. In this study, we found that 1,2-dichloroethane extraction could effectively and easily purify pyridylaminated oligosaccharides with a high recovery rate.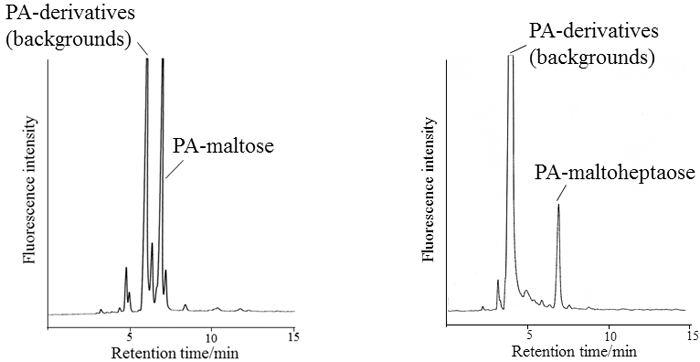 View full abstractDownload PDF (728K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (728K)
Original Papers
-
Liyakat Hamid MUJAWAR, Adel Abdulaziz FELEMBAN, Mohammad Soror EL-SHAH ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 491-497
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe present article reports the application of hexamethylsilazane (HMDS) modified filter paper for ultrasensitive detection of Hg2+, Co2+ and Zn2+. By chemical vapor deposition of HMDS, a highly hydrophilic filter paper was fabricated to a low wetting (hydrophobic) substrate. The water contact angle (θ) of modified paper was ∼128°, whereas scanning electron and atomic force microscopy confirmed the surface modification. Using chromogenic reagents, a one-step assay for aforementioned ions was demonstrated onto pristine as well as hydrophobic paper. The assay was completed in less than 10 min and the end-result was in form of a color change that could be easily read by the naked eye. The limit of detection on modified paper was 0.5 ppb, which was 5-order of magnitude superior to that observed on pristine paper. The proposed method was successfully applied for semi-quantitative determination of Hg2+ ions in real wastewater samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (2756K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2756K) -
Yerigui , Xiu-Hong WU, Xi-Jun WANG, Chao-Mei MAArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 499-503
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn ultra-high-performance liquid chromatograph–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry has been established and validated for the simultaneous quantification of 15 bile acids in four traditional animal medicines and their preparations. The separations of bile acids were performed on an Agilent ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column (50 × 2.1 mm; 1.8 μm) with methanol–0.1% formic acid as the mobile phase. Glycyrrhetinic acid was added as internal standard owing to its similar physiochemical properties with the bile acids. Using this condition, detected in the multiple reaction monitoring mode, the 15 bile acids, including three groups of isomers, were well quantified individually. Method validation showed that the linear regression relationship (r2, 0.9993 – 0.9999), precisions (intra-day RSD, 0.96 – 4.31%; inter-day, 1.73 – 4.43%), and recovery (95.3 – 120.9%) were all satisfactory. The analysis results showed that bear bile and bezoar (Niu Huang) as well as their formulations contained large amounts of most of the 15 bile acids. In addition, this research revealed for the first time the presences of bile acids in animal waste medication used in traditional medicine from two clinics, Hei-Bing-Pian (discharges of wild boar) and Trogopterus Dung. The established method could be used for the quantification of other bile- or animal waste-based crude drugs and their formulated products. View full abstractDownload PDF (527K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (527K) -
Ayaka SEICHI, Nanami KOZUKA, Yuko KASHIMA, Miyuki TABATA, Tatsuro GODA ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 505-510
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn electrochemical detection system for an isothermal DNA amplification method using an ion-selective electrode (ISE) was developed as a low-cost, simple and real-time monitoring system. The system is based on potentiometry using an ethidium ion (Et+) selective electrode that relies on monitoring DNA amplification by measuring potential changes in the reaction solution containing ethidium bromide (EtBr) as an intercalator to DNA. With progressing primer generation-rolling circle amplification (PG-RCA) under isothermal condition at 37°C, EtBr is bound to the newly formed DNA, resulting in a lowered free EtBr concentration in the sample solution. In this case, the Et+ ISE potential allows real-time monitoring of the PG-RCA reaction in the range of 10 nM – 1 μM initial target DNA. View full abstractDownload PDF (1421K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1421K) -
Mehdi KARIMI, Alireza BADIEI, Ghodsi MOHAMMADI ZIARANIArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 511-516
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel organic-inorganic hybrid optical sensor (NUS) was designed and prepared in two steps: the grafting of 3-(isocyanatopropyl)trimethoxysilane onto the surface of SBA-15, and then the attachment of naphthalene-1-amine. The obtained materials were characterized using low-angle XRD, N2 adsorption-desorption, TGA, FT-IR, and TEM techniques. A fluorescence study revealed that the NUS was a highly selective optical sensor for the detection of Cr2O72− among various anions, including F−, I−, Cl−, Br−, CO32−, HCO3−, NO3−, H2PO4−, CH3COO−, and NO2− with a good linearity between the fluorescence intensity and the concentration of Cr2O72− as well as a detection limit of 1.2 × 10−7 M in a 100% aqueous medium. Moreover, the applicability of real samples of the sensor is also discussed. View full abstractDownload PDF (1601K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1601K) -
Min FENG, Hengye LI, Lin ZHANG, Jingyou ZHANG, Jianping DAI, Xiaojin W ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 517-521
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNovel magnetic molecularly imprinted composites were prepared through a facile method using sulfadimethoxine (SDM) as template. The inorganic magnetic nanoparticles were linked with the organic molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) through irreversibly covalent bond. So, the resulted composites showed excellent stability and reusability under acidic elution conditions. The magnetic MIP composites showed good selectivity, high binding capacity and excellent kinetics toward SDM. Adopting the magnetic MIP composites as extraction material, an off-line magnetic solid-phase extraction (SPE)/high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was established. The calibration curve was linear in the range of 0.05 – 15 mg kg−1 (r2 = 0.9976). The LOD and LOQ were 0.016 and 0.052 mg kg−1, respectively, while the recoveries were in the range of 89.3 – 107.0%. These novel magnetic MIP composites may become a powerful tool for the extraction of template from complex samples with good efficiency. View full abstractDownload PDF (815K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (815K) -
Weiwen HU, Jian ZHANG, Jinming KONGArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 523-527
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHerein, we applied hypericin (Hyp) for the detection of DNA on streptavidin-functionalized magnetic beads (SA-MB) through non-covalent π-π stacking interaction between 1-pyrenebutanoic acid (PBA) and Hyp. Briefly, the target DNA (tDNA) was hybridized to morpholino oligonucleotide (MO) that was immobilized on the surface of SA-MB. PBA was incorporated to the backbone of tDNA by means of phosphate-zirconium-carboxylate coordination reaction. Then, fluorescent Hyp was linked to PBA via π-π stacking interaction. Under the optimal conditions, this biosensor displayed a good linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity and the tDNA concentrations in the range from 1 to 100 nM with a low detection limit of 2.9 nM. The mismatch type in a specific DNA sequence can also be efficiently discriminated. Compared with some other reports, this method is more convenient, and has great potential for practical applications.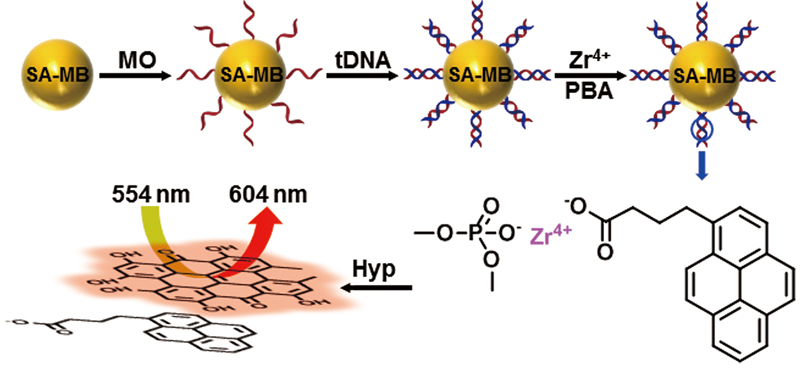 View full abstractDownload PDF (2458K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2458K) -
Takeshi FUKUDA, Tomokazu KURABAYASHI, Nayuta FUNAKI, Hikari UDAKA, Mih ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 529-534
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialConjugates of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) and organic dyes have been receiving attention as fluorescence biological sensing materials. In designing such sensors, a most important parameter is the number of organic-dye molecules that conjugate to a QD. If a precise separation method was developed, it might be possible to control conjugation without knowing the exact number of conjugated dye molecules per QD. In this study, the difference in linear velocities in a gel filtration column between CdSe/ZnS QDs and 5-(and 6)-carboxynaphthofluorescein succinimidyl ester is used. The velocities differ because the hydrophilicity of CdSe/ZnS QDs is much higher than that of the organic dye; hence, CdSe/ZnS-organic-dye conjugation can be controlled by changing the fraction number. Furthermore, the concentrations of CdSe/ZnS QDs and organic dye in fractionated solutions can be determined by measuring fluorescence spectra, and we demonstrate a fluorescence-type pH sensor based on the conjugate, which has a pH-sensitivity range from 7.5 – 9.5.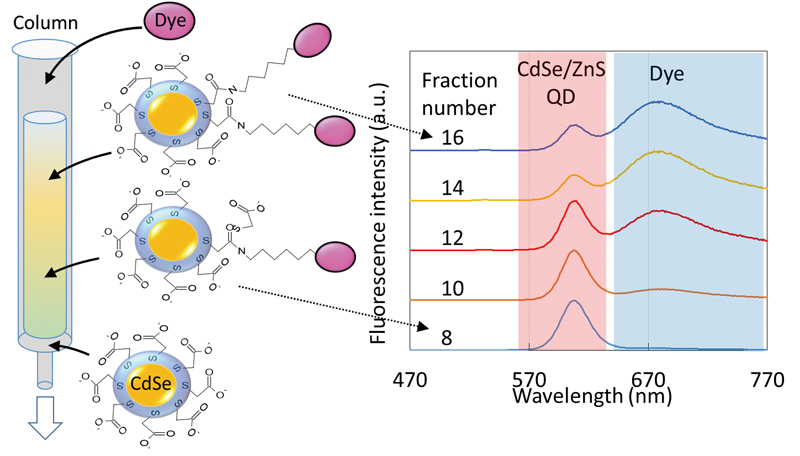 View full abstractDownload PDF (1905K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1905K) -
Kazuaki WAGATSUMA, Kozue SATOHArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 535-541
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper describes a plasma-diagnostic method using an enhancement factor on the Boltzmann distribution among emission lines of iron atom in an argon radio-frequency inductively-coupled plasma (ICP). It indicated that Boltzmann plots of the atomic lines having lower excitation energies (3.4 to 4.8 eV) were well fitted on a straight line while those having more than 5.5 eV deviated upwards from a linear relationship. This observation could be explained by the fact that ICP is not in a complete thermodynamic equilibrium between direct excitation to energy levels of iron atom, ionization of iron atom, and radiative decay processes to the ground state. Especially, the recombination of iron ion with captured electron should accompany cascade de-excitations between closely-spaced excited levels just below the ionization limit, the rates of which become slower as a whole; as a result, these high-lying levels might be more populated than the low-lying levels as if a different LTE condition coexists on the high energy side. This overpopulation could be quantitatively estimated using an enhancement factor (EF), which was a ratio of the observed intensity to the expected value extrapolated from the normal distribution on the low energy side. The EFs were generally small (less than 3); therefore, the cascade de-excitation process would slightly contribute to the population of these excited levels. It could be considered from variations of the EF that the overpopulation proceeded to a larger extent at lower radio-frequency forward powers, at higher flow rates of the carrier gas, or at higher observation heights. The reason for this is that the kinetic energy of energetic particles, such as electrons, becomes reduced under all of these plasma conditions, thus enabling the high-lying levels to be more populated by cascade de-excitation processes from iron ion rather than by collisional excitation processes with the energetic particles. A similar Boltzmann analysis using the EF was also carried out in emission lines of nickel atom, which confirmed the conclusion concerning the atomic lines of iron. View full abstractDownload PDF (1419K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1419K) -
Akira TSUCHIYA, Siti N. HASHIM, Shoko ISE, Takafumi FURUHATA, Kiyohiko ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 543-547
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn on-cell aptamer sensor has the potential to reveal cell–cell communications by signalling molecules. We attempted to design new fluorescent aptamer sensors for the sensing of IFN-γ and adenine compounds on cells. BODIPY-labeled external quencher-free aptamer sensors have allowed a turn-on detection of the target molecule with improved off/on efficiency. View full abstractDownload PDF (847K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (847K) -
Shigehisa UCHIYAMA, Yui SENOO, Hideki HAYASHIDA, Yohei INABA, Hideki N ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 549-555
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe developed an analytical method for analyzing electronic cigarette (E-cigarette) smoke, and measured the carbonyl compounds and volatile organic compounds generated by 10 brands of second-generation E-cigarettes. A glass filter (Cambridge filter pad) for particulate matter and a solid sorbent tube packed with Carboxen-572 for gaseous compounds were used to collect E-cigarette smoke. These were then analyzed using a two-step elution method with carbon disulfide and methanol, followed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Formaldehyde (FA), acetaldehyde (AA), acetone (AC), acrolein (ACR), propanal (PA), acetol (AT), glyoxal (GO), and methyl glyoxal (MGO) were detected by HPLC in some E-cigarettes. Propylene glycol (PG), glycerol (GLY), and some esters were detected by GC/MS. GO and MGO exist mainly as particulate matter. AA, AC, ACR, PA, and AT exist mainly as gaseous compounds. FA exists as both particulate matter and gaseous compounds. These carbonyl compounds have carbon numbers C1 – C3. The main components of E-liquid are PG (C3) and GLY (C3). Therefore, the oxidation of liquids, such as PG and GLY in E-cigarettes upon incidental contact with the heating element in E-cigarette, is suggested as being a possible cause for carbonyl generation. When the puff number exceeds a critical point, carbonyl generation rapidly increases and then remains constant. The results of this study are now being used to determine the following E-cigarette smoking protocol: puff volume, 55 mL; puff duration, 2 s; and puff number, 30. E-cigarette analysis revealed very large variation in carbonyl concentration among not only different brands, but also different samples of the same product. Typical distributions of carbonyl concentration were not observed in any of the E-cigarettes tested, and the mean values greatly differed from median values.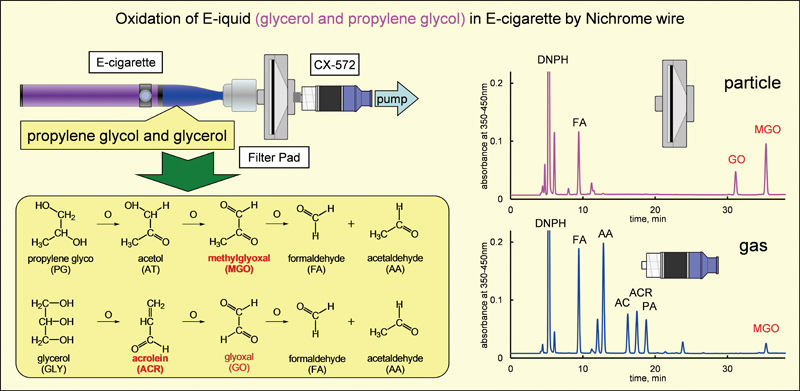 View full abstractDownload PDF (3805K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3805K) -
Takashi YARITA, Takamitsu OTAKE, Yoshie AOYAGI, Masahiko NUMATA, Akiko ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 557-580
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSProficiency testing was organized by the National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) as a measure of analytical competency in the quantification of pesticide residues in husked wheat powder. Seventy-one participants submitted analytical concentrations of the target pesticides (diazinon, fenitrothion, malathion, and etofenprox) along with details of the analytical method employed. Two types of assigned values were obtained for each target pesticide, i.e., the participants’ analytical results and the results obtained by NMIJ based on isotope-dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS). The former values were lower than the latter due to the incomplete recovery yield of the target pesticides during the pretreatment process. The discrepancy between the two assigned values was particularly pronounced for malathion because of the longer duration of water-soaking used for the test samples. Two corresponding types of z-scores were then calculated to evaluate the analytical performance of the participants, where the z1-score indicates the performance of a participant relative to all participants, and the z2-score indicates the relative deviation of the analytical results of the participant from the IDMS value. View full abstractDownload PDF (879K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (879K) -
Ying LIANG, Jing SU, Yong HUANG, Xiaohua LI, Yiwen TAO, Chaofeng LU, J ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 565-569
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn the present work, a sensitive electrochemical aptasensor was designed for the detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) with hemin/graphene oxide nanosheets (HGNs). Firstly, the ATP aptamer was self-assembled on gold electrode surface, and then HGNs were captured to the modified electrode by π-π stacking. The captured HGNs could catalyze the disproportionation reaction of H2O2, and produced a detectable electrochemical signal by chronoamperometry. ATP was competitively bound to aptamer which led to the release of HGNs from the electrode surface after adding ATP. The decrease of the electrochemical signal, which was calculated by the difference of amperometric responses before and after incubation of ATP, provided a quantitative signal for ATP detection. A linear correlation was achieved between the difference of the amperometric responses and the logarithmic concentration of ATP ranging from 0.5 to 100 nM with a detection limit of 0.08 nM. Besides, the aptasensor also exhibited good selectivity toward ATP against other analogs. View full abstractDownload PDF (756K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (756K) -
Biswajit MANDAL, Prasanta Kumar SINHA, Ranjan SEN, Ashis Kumar MANDALArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 571-576
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present study, Fe-doped barium borosilicate glass has been melted at 1250°C under microwave heating. The iron redox ratio (Fe2+/total Fe) in the glass is investigated by two spectrophotometric methods. A novel decomposition technique has been optimized to measure the ferrous oxidation state in glass. Ferrozine was chosen as a specific complexing reagent; it forms a deep violet color complex with Fe2+ and has a broad absorbance peak centered at ∼562 nm. 1,10-ortho-phenanthroline develops an orange color complex with Fe2+ (having an absorbance peak centered at ∼510 nm) and has been used to determine ferrous ion in glass. Both the methods are compared and the estimated redox ratio was found to be higher in the ferrozine method. The error limit of measurement has been determined as 0.012 and 0.023 for the ferrozine and 1,10-ortho-phenanthroline methods, respectively.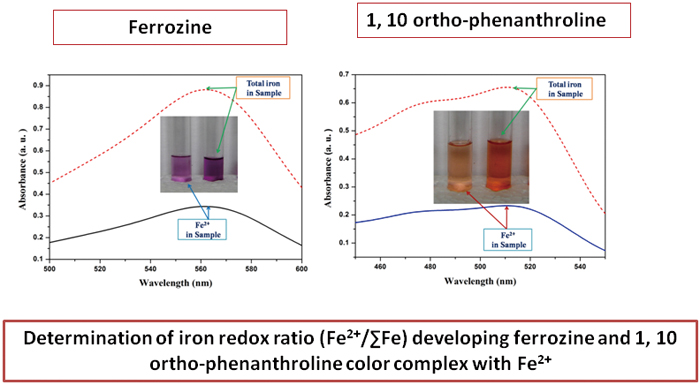 View full abstractDownload PDF (1595K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1595K) -
Daisuke YAMASHITA, Atsushi ISHIZAKIArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 577-580
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPhotoemission yield spectroscopy in air (PYSA) was applied for the characterization of catechins in water in ambient conditions. According to the results of measurements on aqueous solutions of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg) of various concentrations, the photoemission yield is almost proportional to the concentration of EGCg. Contrarily, the threshold energy of photoemission, EPET, is almost constant at 5.46 ± 0.02 eV. Moreover, we measured aqueous solutions of epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC), and epicatechin gallate (ECg). The values of EPET of EC, EGC, ECg were estimated to be 5.72 ± 0.02, 5.68 ± 0.01, and 5.45 ± 0.02 eV, respectively, and a dependence on the molecular structure was found. Furthermore, changes in the photoemission yield spectra of heated EGCg were well explained by molecular orbital calculations on the basis of an assumption of epimerization. View full abstractDownload PDF (682K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (682K) -
Hong MA, Shanshan YANG, Hong LU, Yaozhou ZHANGArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 581-586
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new strategy for the convergence of two-dimensional preparative high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and real-time cell analysis (RTCA) was developed for rapidly separating and screening anti-tumor components from the ethyl acetate extract of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), Euphorbia kansui. Eight compounds: esulone A (1), kansuinin A (2), (3β,11β)-3,11-dihydroxylanosta-8,24-dien-7-one (3), kansuinin E (4), kansuinin B (5), isoscopoletin (6), kansuinin D (7) and kansuinin G (8) were efficiently isolated with purity above 97%. Of all the compounds, esulone A has been isolated from this plant for the first time. The structures were identified by NMR spectroscopy and comparisons were made with the data in previous literature. The anti-tumor bioassay was performed on A549 (human lung cancer cells) and Hep-G2 (human liver cancer cells) with a newly developed RTCA system. The result revealed that compounds 1, 3, 7 and 8 almost entirely inhibited the proliferation of A549 cells and that compound 8 was also thought to be the most active compound against Hep-G2 cells. The method provided considerable assistance for the efficient separation of different polar compounds and rapid screening of anti-tumor active compounds. View full abstractDownload PDF (1074K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1074K) -
Tomoyuki OZAWA, Issey OSAKA, Satoshi HAMADA, Tatsuya MURAKAMI, Akio MI ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 587-591
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPlant leaves administered with systemic insecticides as agricultural chemicals were analyzed using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS). Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is inadequate for the detection of insecticides on leaves because of the charge-up effect that occurs on the non-conductive surface of the leaves. In this study, surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization with a sputter-deposited platinum film (Pt-SALDI) was used for direct analysis of chemicals in plant leaves. Sputter-deposited platinum (Pt) films were prepared on leaves administered with the insecticides. A sputter-deposited Pt film with porous structure was used as the matrix for Pt-SALDI. Acephate and acetamiprid contained in the insecticides on the leaves could be detected using Pt-SALDI-MS, but these chemical components could not be adequately detected using MALDI-MS because of the charge-up effect. Enhancement of ion yields for the insecticides was achieved using Pt-SALDI, accompanied by prevention of the charge-up effect by the conductive Pt film. The movement of systemic insecticides in plants could be observed clearly using Pt-SALDI-IMS. The distribution and movement of components of systemic insecticides on leaves could be analyzed directly using Pt-SALDI-IMS. Additionally, changes in the properties of the chemicals with time, as an indicator of the permeability of the insecticides, could be evaluated. View full abstractDownload PDF (959K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (959K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 593
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (3438K)
Errata
-
Koji FUJISAKI, Hiroshi MATSUMOTO, Yukiko SHIMOKAWA, Kenji KIYOTAKIArticle type: Errata
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 597
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOn page 168, the left column, line 26 to 29, the sentence,
Working standard solutions (1, 5, 7.5, and 10 ng mL−1) were prepared from the iodine stock solution by dilution with 7.0% (v v−1) nitric acid, 5.0% (v v−1) acetic acid and 1.2% (v v−1) hydrogen peroxide.
should read
Working standard solutions (1, 5, 7.5, and 10 ng mL−1) were prepared from the iodine stock solution by dilution with 7.0% (v v−1) nitric acid and 5.0% (v v−1) acetic acid.View full abstractDownload PDF (134K) -
Satoshi OHMURO, Kan FUJII, Takashi YASUI, Kazutake TAKADA, Akio YUCHI, ...Article type: Errata
2016 Volume 32 Issue 5 Pages 598
Published: May 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOn page 343, the abstract, the second line,
with which octadecylsilyl silica (ODS), was impregnated with was studied
should read
with which octadecylsilyl silica (ODS) was impregnated, was studied.View full abstractDownload PDF (135K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|