All issues

Volume 32, Issue 6
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 599
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (206K)
-
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 601-602
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (827K)
Rapid Communications
-
Kazuki HASEGAWA, Mutsuyoshi MATSUMOTO, Kazuo HOSOKAWA, Mizuo MAEDAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 603-606
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe report on a detection method for methylated DNA on a microfluidic chip, which needs no external power for fluid pumping. The methylated DNA was sandwiched by immobilized probe DNA and an anti-methylcytosine antibody. The fluorescence signal was amplified by our original amplification technology. The detection method was first optimized using a 22-mer DNA sequence, then further validated using a 60-mer DNA sequence adapted from the SEPT9 gene. We were able to detect the methylated 60-mer DNA at 0.4 nM within 18 min. View full abstractDownload PDF (1236K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1236K)
Original Papers
-
Jianmei ZOU, VanManh NGUYEN, Xuehua YIN, Zeming WU, Qingyun CAIArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 607-610
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA step-wise structural ZnSe/CdS co-sensitized TiO2 nanotube (NT) electrode was prepared by pulse-electrodeposition and successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR), with an aim towards enhancing the absorption efficiency of TiO2 NTs in visible light region and enhancing the photo-electrical transform efficiency. The as-prepared CdS/ZnSe/TiO2 NTs were applied to the photoelectrocatalytic inactivation of E. coli. A complete inactivation of 3.0 × 108 cfu mL−1 E. coli was observed after 60 min of photoelectrocatalysis process under the illumination of visble light. View full abstractDownload PDF (6437K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (6437K) -
Beril ANILANMERT, Muhammet AYDIN, Resat APAK, Gülfidan Yenel AVCI ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 611-616
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDirect analyses of explosives in soil using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) methods are very limited in the literature and require complex procedures or relatively high amount of solvent. A simple and rapid method was developed for the determination of pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN), 3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazacyclohexane (RDX) and octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine (HMX), which are among the explosives used in terrorist attacks. A one-step extraction method for 1.00 g soil with 2.00 mL acetonitrile, and a 8-min LC-MS/MS method was developed. The detection limits for PETN, RDX and HMX were 5.2, 8.5 and 3.4 ng/g and quantitation limits were 10.0, 24.5, 6.0 ng/g. The intermediate precisions and Horwitz Ratio’s were between 4.10 – 13.26% and 0.24 – 0.98, in order. This method was applied to a model post-blast debris collected from an artificial explosion and real samples collected after a terrorist attack in Istanbul. The method is easy and fast and requires less solvent use than other methods. View full abstractDownload PDF (956K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (956K) -
Sunitha TAKALKAR, Hui XU, Jiao CHEN, Kwaku BARYEH, Wanwei QIU, Julia X ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 617-622
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe present a rapid and highly sensitive approach for visual detection of microRNA (miRNA) using a gold nanoparticles coated silica nanorod label and lateral flow strip biosensor. Gold nanoparticles were decorated on the silica nanorod surface by a seeding and growth procedure. A single strand DNA probe was immobilized on the gold nanoparticles-silica nanorod surface by a self-assembling process, and the formed DNA-gold nanoparticles-silica nanorod conjugate was used to construct the lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor for detecting miRNA. The captured gold nanoparticles-silica nanorods by sandwich-type hybridization reactions (DNA-RNA-DNA) on the test zone of the lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor produced the characteristic color bands, enabling visual detection of miRNA. After systematic optimization, the new lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor was capable of detecting 10 pM of the miRNA target without instrumentation, which is six times lower than that obtained with the gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor. The gold nanoparticles coated silica nanorod thus provides a new and sensitive nanolabel for visual detection of biological molecules on the lateral flow biosensor.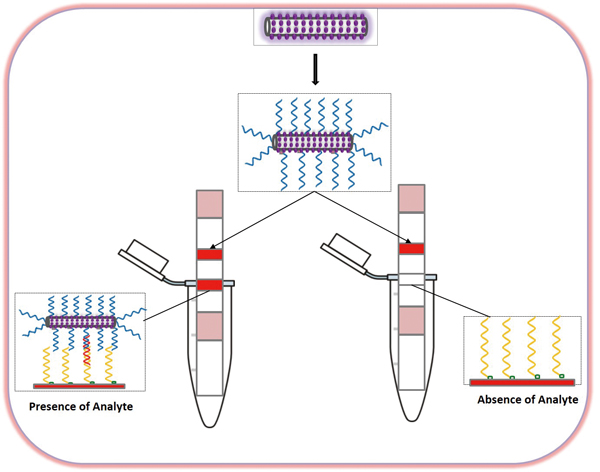 View full abstractDownload PDF (1382K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1382K) -
Takao OHTOMO, Aya YOKOYAMA, Mitsuyuki KONNO, Osamu OHNO, Shukuro IGARA ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 623-629
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe rate of the complexation reaction between anionic porphyrins and 11 metal ions was found to be accelerated by the presence of β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) in aqueous media at room temperature without the need for additional heating or sonication. The porphyrin complexation reaction with metal ions under aqueous conditions can be difficult due to the strong hydration energy between the metal ions and water. In this study, the specific role of β-CD as an accelerator was determined and found to enhance the typically slow reaction of the porphyrin with metal ions. A significant acceleration effect was exhibited when the model anionic porphyrin, 5,10,15,20-tetraphenyl-21H,23H-porphine-tetrasulfonic acid, and Pb(II) ions were combined in the presence of β-CD. Other than for Hg ion, the addition of β-CD decreased the metalation reaction time from 30 to 2 min. The order in the degree of acceleration was Pb >> Zn, Cd > Cu > Fe, Pd > Sn >> Ag, Co, Mn. Using Pb(II) as the model ion, it was determined that the complexation rate constant was enhanced by a factor of 2.4, while the dissociation rate constant was diminished by a factor of 135 in the presence of added β-CD relative to that in its absence. Overall, the complex was much more stable (formation equilibrium constant 324-fold greater in the β-CD medium. The formation of a ternary complex (cf. bicapped complex; (β-CD)2-porphyrin-metal ion) was demonstrated through the use of nuclear magnetic-resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. This acceleration effect is expected to be applicable systems in which porphyrin ligands are employed for determining of metal ions in chemical analysis and separation science.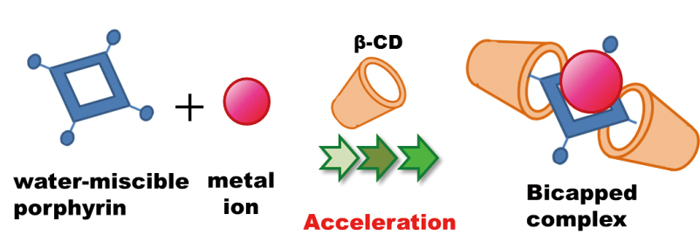 View full abstractDownload PDF (796K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (796K) -
Shuang-Qing ZHANGArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 631-637
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIcaritin (ICT), a major component in herb Epimedium brevicornum Maxim., shows beneficial effects for the treatment of osteoporosis and various cancers, and is predominantly metabolized to glucuronidated icaritin (GICT). Although clinical trials of ICT have exhibited good safety and tolerance, the dynamic bioditributions of ICT and GICT have not been reported. In the present study, the chemical structure of GICT was firstly reported, and a reliable ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method (UHPLC-MS/MS) was firstly established for the simultaneous quantifications of ICT and GICT in rat tissues. The dynamic distribution of ICT and GICT in rat tissues and their pharmacokinetic parameters have been reported for the first time. ICT, GICT and the internal standard coumestrol were separated on a C18 column with a gradient mobile phase of acetonitrile and water containing ammonium formate and formic acid at a flow rate of 0.3 mL min−1. The analytes were quantified by a triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer in the negative ionization mode. The lower limit of quantification values for ICT and GICT were 0.2 and 2 ng mL−1, respectively. Good selectivity, linearity, accuracy, precision and recovery were achieved, and no significant matrix effect was observed. The UHPLC-MS/MS was firstly applied to a dynamic biodistribution study of ICT and GICT in rats, following an intraperitoneal administration of ICT at a dose of 10 mg kg−1.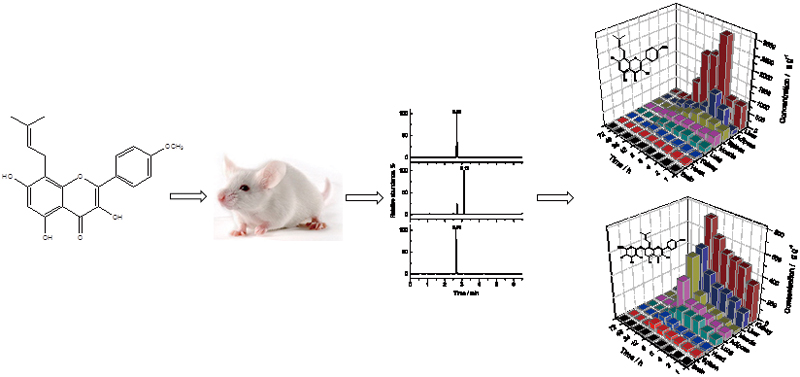 View full abstractDownload PDF (1073K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1073K) -
Jarinya SITTIWONG, Fuangfa UNOBArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 639-643
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new paper platform was developed for the colorimetric detection of creatinine. The filter paper was coated with 3-propylsulfonic acid trimethoxysilane and used as the platform. Creatinine in a cationic form was extracted onto the paper via an ion-exchange mechanism and detected through the Jaffé reaction, resulting in a yellow-orange color complex. The color change on the paper could be observed visually, and the quantitative detection of creatinine was achieved through monitoring the color intensity change. The color intensity of creatinine complexes on the paper platform as a function of the creatinine concentration provided a linear range for creatinine detection in the range of 10 – 60 mg L−1 and a detection limit of 4.2 mg L−1. The accuracy of the proposed paper-based method was comparable to the conventional standard Jaffé method. This paper platform could be applied for simple and rapid detection of creatinine in human urine samples with a low consumption of reagent.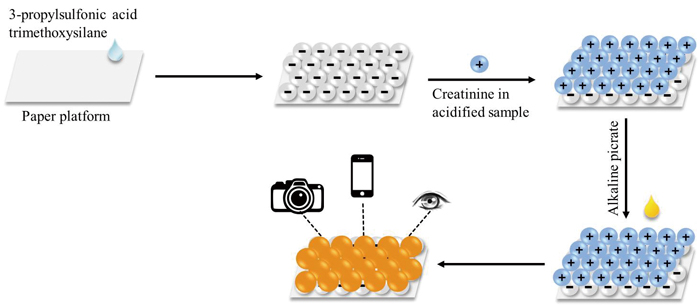 View full abstractDownload PDF (950K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (950K) -
Aiying SONGArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 645-652
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPesticides and antidepressants are frequently misused in drug-facilitated crime because of their toxicological effect and easy-availability. Therefore, it is essential for the development of a simple and reliable method for the determination of these organic toxicants in biological fluids. Here, we report on an applicable method by the combination of optimized liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) procedure and high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) to identify and quantify dimethoate, omethoate, dichlorvos, carbofuran, fenpropathrin, diazepam, estazolam, alprazolam, triazolamm, chlorpromazine, phenergan, barbitone and phenobarbital in human blood. The method demonstrated a linear calibration curve in range of 20 – 500 μg/L (r > 0.994). The accuracy evaluated by recovery spiked at three different concentrations (50, 100 and 200 μg/L) was in the range of 58.8 – 83.1% with a relative standard deviations (RSD) of 3.7 – 7.4%. The limits of quantification ranged over 6.7 – 33.3 μg/L. This method was proved to be simple and reliable, and was thus successfully applied to forensic toxicology.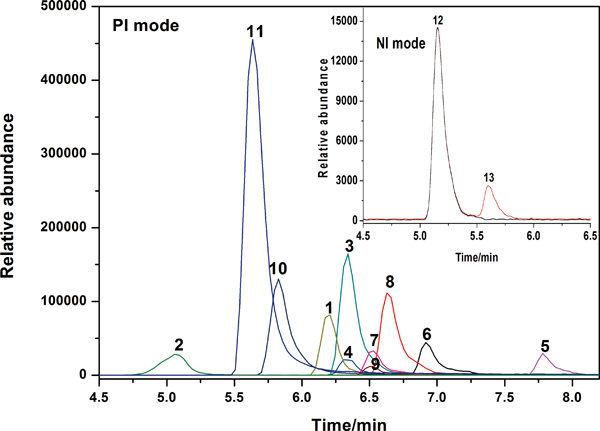 View full abstractDownload PDF (727K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (727K) -
Tiantian WANG, Jasmine Pramila DEVADHASAN, Do Young LEE, Sanghyo KIMArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 653-658
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present study, we developed a polypropylene well-integrated complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) platform to perform the loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique for real-time DNA amplification and detection simultaneously. An amplification-coupled detection system directly measures the photon number changes based on the generation of magnesium pyrophosphate and color changes. The photon number decreases during the amplification process. The CMOS image sensor observes the photons and converts into digital units with the aid of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). In addition, UV-spectral studies, optical color intensity detection, pH analysis, and electrophoresis detection were carried out to prove the efficiency of the CMOS sensor based the LAMP system. Moreover, Clostridium perfringens was utilized as proof-of-concept detection for the new system. We anticipate that this CMOS image sensor-based LAMP method will enable the creation of cost-effective, label-free, optical, real-time and portable molecular diagnostic devices. View full abstractDownload PDF (2121K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2121K) -
Salomé SOLER-SEGUÍ, Carolinakn-aut-sei= BELENGUER-SAPI&N ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 659-665
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSolid-phase extraction (SPE) coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with fluorescence detection were employed to determine trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. In this way, the use of cartridges containing cyclodextrin-silica hybrid microporous solid phases was proposed. The experimental results indicated that the method provided relative standard deviations of below 15% and detection limits recorded were 12, 1.2, 12, 38, 4, 6 and 4 ng L−1 for benzo[b]fluoranthene, benzo[k]fluoranthene, benzo[g,h,i]perylene, indeno[1,2,3]pyrene, benzo[a]pyrene, dibenzo[a,h]anthracene and benzo[a]anthracene, respectively. Moreover, the method was successfully applied for the determination of these organic compounds in water samples, where they were found to be in the 7 to 580 ng L−1 range. It can be concluded that the major advantages of cyclodextrin-silica hybrid microporous solid phases are that they reduce the consumption and the toxicity of the solvent and the time consumption of the sample treatment step. View full abstractDownload PDF (595K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (595K) -
Bedrana BITIRMIS, Digdem TRAK, Yasin ARSLAN, Erdal KENDÜZLERArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 667-671
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMn2+ was separated and preconcentrated using both solid-phase extraction (SPE) and a slotted quartz tube (SQT), and detected by a flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) system. Firstly, Mn2+ was retained on a column filled with Amberlite CG-120 resin, and then retained Mn2+ ions on the Amberlite CG-120 resin eluted with 5 mL of 4 mol/L HNO3. This part was called the “first preconcentration step”. Furthermore, to determine the Mn2+ in a walnut sample, the SQT device was also used after the separation and preconcentration of Mn2+ from the Amberlite CG-120 resin so as to further improve the sensitivity of system. This part was called the “second preconcentration step” in this study. The enrichment factor and limit of detection values were found to be 360 fold and 0.22 μg/L, in turn, after a two-step preconcentration method. The good accuracy of method was confirmed with the use of standard reference material (spinach leaves, NIST-1570a).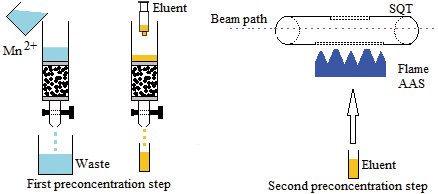 View full abstractDownload PDF (462K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (462K) -
Jie ZHAN, Koji FURUI, Hizuru NAKAJIMA, Noriaki KANEKI, Ryoichi ISHIMAT ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 673-679
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA portable-type surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor, composed from a new optical system for multi-sensing, has been developed to apply to environment analysis, clinical diagnosis etc., where many samples are desired to be analyzed at high throughput. The optical system of the sensor consists of a light-emitting diode, a pair of cylindrical lenses, a pair of collimator lenses, a correction lens, a prism, a polarizer and a linear CCD sensor with 2048 pixels. Reflected light from a sensor chip of the width of 6 mm at a certain incident angle was detected by ca. 618 pixels of the linear CCD sensor as an SPR sensor signal. An SPR sensor signal at a specified incident angle is controllable for optimization by adjusting the position of the CCD sensor. A sensor chip having a 30-stripe linear pattern (100 μm width/stripe) was prepared. The spatial resolution as well as the performance of the sensor were evaluated by using sucrose solutions. As a result, the acquisition of SPR sensor signals from 30 sensing points was successfully achieved with a spatial resolution of 100 μm (distance between 2 sensing points). A lower detection limit of ca. 3.2 – 5.5 × 10−5 RIU with a standard deviation of ±4.5% was obtained by averaging the signals from 6 – 7 pixels of the CCD sensor per one sensing stripe.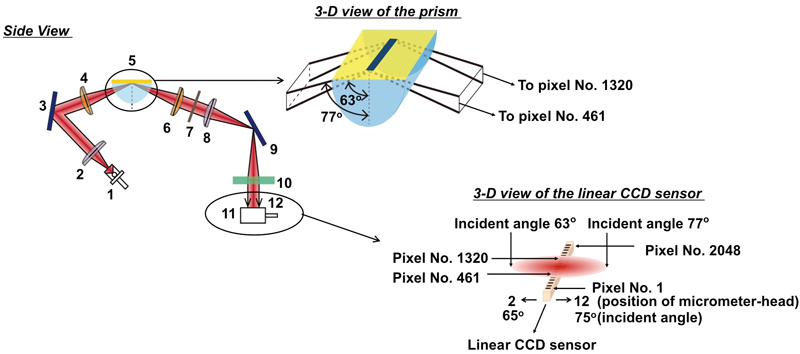 View full abstractDownload PDF (1453K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1453K) -
Euna KO, Joonki HWANG, Ji Hye KIM, Joo Heon LEE, Sung Hwan LEE, Van-Kh ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 681-686
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe present a method for the electrochemical patterning of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) or silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on porous silicon, and explore their applications in: (1) the quantitative analysis of hydroxylamine as a chemical sensing electrode and (2) as a highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrate for Rhodamine 6G. For hydroxylamine detection, AuNPs-porous silicon can enhance the electrochemical oxidation of hydroxylamine. The current changed linearly for concentrations ranging from 100 μM to 1.32 mM (R2 = 0.995), and the detection limit was determined to be as low as 55 μM. When used as SERS substrates, these materials also showed that nanoparticles decorated on porous silicon substrates have more SERS hot spots than those decorated on crystalline silicon substrates, resulting in a larger SERS signal. Moreover, AgNPs-porous silicon provided five-times higher signal compared to AuNPs-porous silicon. From these results, we expect that nanoparticles decorated on porous silicon substrates can be used in various types of biochemical sensing platforms. View full abstractDownload PDF (6174K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (6174K) -
Syazana A LIM, Minhaz U AHMEDArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 687-693
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this work we exploited the electrostatic interaction of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) with drug components to construct a simple, but highly sensitive, DNA-electrochemical sensor for detecting ciprofloxacin. The following straightforward three-step procedure was performed to determine ciprofloxacin: (i) dsDNA-layer immobilization on the surface of the working graphene-modified screen-printed carbon electrode; (ii) dsDNA-ciprofloxacin interaction for 2 min; and (iii) electrochemical measurement using square-wave voltammetry. An increased oxidation of the guanine component was observed, at +1.0 V, as a result of the electrostatic interaction of positively charged ciprofloxacin with the negatively charged nucleic acid sugar phosphate. Based on the International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines, a linear relationship between the guanine oxidation peak and ciprofloxacin concentration (0.1 to 100 μM) was obtained with a detection limit of 0.1 μM. Our developed sensor is straightforward to construct and use, requiring no multi-step time-consuming preconditioning of electrodes. It is highly sensitive and selective in the detection of ciprofloxacin, and has the potential to be useful in the future fabrication of rapid and portable on-site food safety analysis devices. View full abstractDownload PDF (892K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (892K) -
Hiroto MASUNAGA, Yuji HIGO, Mizuo ISHII, Noboru MARUYAMA, Shigeo YAMAZ ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 695-700
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHerein, we report a new device that generates a high-purity acid solution. It comprises three compartments divided by anion-exchange membranes and filled with ion-exchange resins. Fluorochemical cation-exchange membranes, which tolerate electrochemical wear and permit bulk flow, are inserted between each electrode and the anion-exchange resin. A bipolar boundary is a composite boundary comprising anion and cation exchangers. This device has four bipolar boundaries to separate the location of acid generation from the location where water is electrolyzed. It can tolerate high pressures, resist degradation due to electrolysis at the electrodes, and produce high-purity acid solutions that are free from gases and cationic impurities. The acid solution is generated on the basis of an electrokinetic phenomenon at the surfaces of ion-exchange resins and membranes in an electric field; its concentration can be controlled at rates from 0.01 to 100 μmol/min by adjusting the electrical current applied to the device. View full abstractDownload PDF (1028K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1028K)
Notes
-
Hajime KATANO, Masahiro TAKAKUWA, Hajime HAYAKAWA, Hisashi KIMOTOArticle type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 701-703
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA colorimetric method for the glucosamine (GlcN) assay was applied for the determination of chitin, which can be hydrolyzed to produce GlcN. A 10-mg sample was mixed with 10 mL of a 5 mol/L HCl aqueous solution, and the mixture was kept at 100°C for 12 h. Under these conditions, chitin was completely depolymerized and deacetylated to produce GlcN, even when the sample was a crab shell. A 20-μL aliquot of the hydrolysate was mixed with 20 μL of a 5 mol/L NaOH aqueous solution and 200 μL of a 50 mmol/L Na2SiO3, 600 mmol/L Na2MoO4, 1.5 mol/L CH3COOH and 30% (v/v) dimethyl sulfoxide solution. The mixture was kept at 70°C for 30 min. In the mixture, GlcN reduced the Mo(VI) species to form a blue molybdosilicate anion, which gave an absorbance maximum at around 750 nm. Since N-acetylglucosamine and chitin oligosaccharides could not render the reaction mixture blue, GlcN in the hydrolysate could be assayed colorimetrically with high selectivity. When a standard chitin sample was examined, the GlcN concentration in the hydrolysate was determined to be 0.97 ± 0.02 g/L (as hydrochloride salt), indicating that the sample contained 10.0 ± 0.2 mg chitin (as an N-acetylglucosamine homopolymer). Calcium cation, amino acids, and proteins did not interfere with the GlcN assay. Thus, the proposed method was successfully applied to determine chitin in a crab shell sample.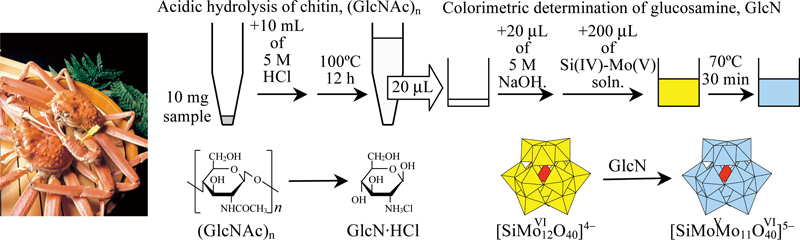 View full abstractDownload PDF (1366K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1366K) -
Wei WANG, Shaozhong LUO, Yaping CHEN, Bo LI, Masao HATTORIArticle type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 705-707
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn effective separation and simultaneous determination of corynoxeine and its metabolites using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry was developed and validated. The method was applied to pharmacokinetics and in vivo distribution investigations in rats after oral (0.105 mmol kg−1) and intravenous (0.0105 mmol kg−1) doses of corynoxeine. Its brain uptake index was of 3.08 × 10−11 mol g−1 at 3 h and 3.75 × 10−11 mol g−1 at 74 min after oral and intravenous doses, respectively. View full abstractDownload PDF (415K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (415K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2016 Volume 32 Issue 6 Pages 709
Published: June 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2863K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|