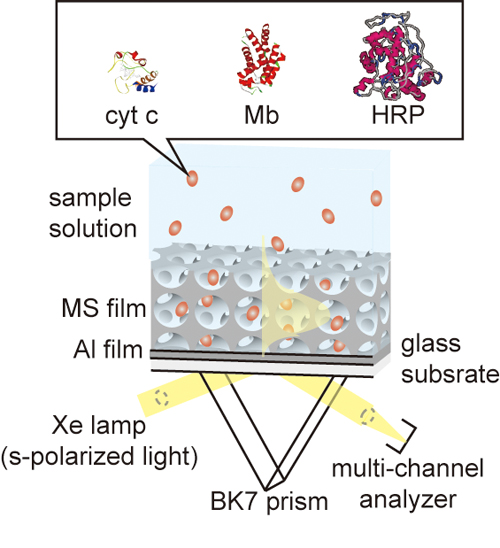
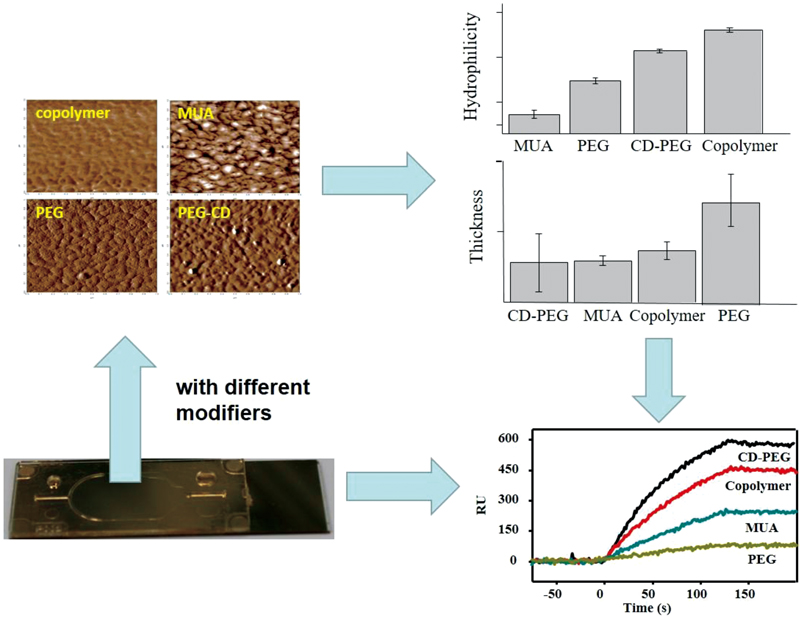
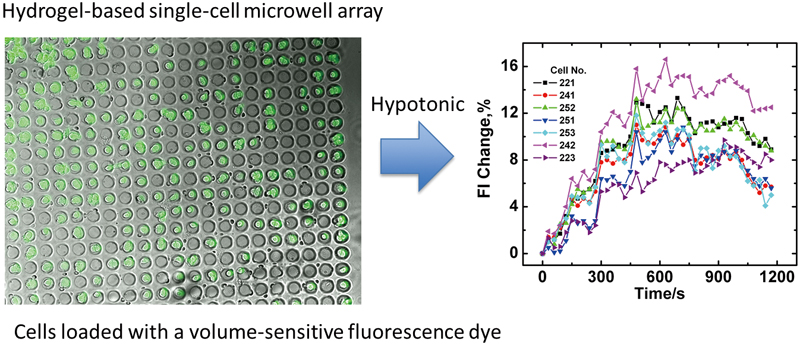
Volume 33, Issue 4
Displaying 1-23 of 23 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Article type: Guest Editorial
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 415
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (157K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 417-426
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (4384K) -
Article type: Reviews
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 427-433
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1799K)
Original Papers
-
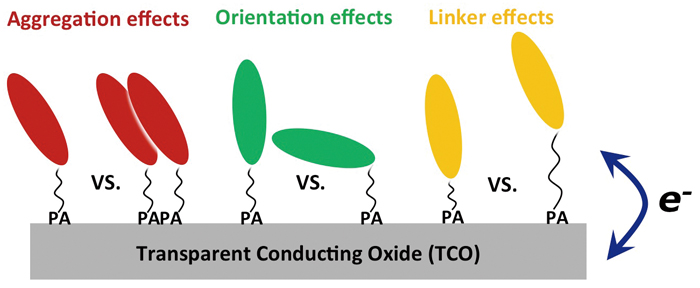
Electron-Transfer Rate in Potential-Modulated Redox Reactions with Electro-Active Optical WaveguidesArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 435-441
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1121K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 443-447
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1705K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 449-455
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (815K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 457-460
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (582K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 461-463
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (804K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 465-467
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (684K) -
Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 469-472
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (572K) -
Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 473-476
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (705K) -
Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 477-479
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (702K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 481-486
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (2599K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 487-491
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (759K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 493-498
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1094K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 499-504
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1857K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 505-510
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (2980K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 511-517
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1438K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 519-524
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (878K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 525-530
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (1919K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 531-536
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (3031K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 537-544
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (2386K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017 Volume 33 Issue 4 Pages 545
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2017
Download PDF (3070K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|