All issues

Volume 33, Issue 5
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Kengo ISHIKI, Hiroshi SHIIGI, Tsutomu NAGAOKAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 551-553
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA simple method for the detection of metal ions in solution is proposed, using Shewanella oneidensis, which has the ability to reduce metal ions into metal nanoparticles on the cell surface. The method can be used to identify metal ions in solution using the light-scattering characteristics of the metal nanoparticles formed on the cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (616K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (616K)
Reviews
-
Toshimasa TOYO’OKAArticle type: Reviews
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 555-564
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLiquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is one of the most prominent analytical techniques due to its inherent selectivity and sensitivity. LC-MS is currently the first choice for high-throughput bioanalysis due to the advancements in MS instruments and the analytical software. Based on this situation, we are developing various types of derivatization reagents, including chiral reagents for MS and/or MS/MS detection. These developed reagents are adopted for the detection of biomarker candidates related to diseases. The biomarker candidates include not only achiral molecules, but also chiral ones. Although determining the already-identified chiral molecules is relative easy, it is very difficult to identify and/or determine unknown enantiomer(s) in real samples. To solve this difficulty, we proposed a new strategy to identify unknown enantiomeric biomarkers related to diseases. This review paper deals with the development of derivatization reagents for amines and carboxylic acids in LC-MS analysis and their application to bioanalysis. View full abstractDownload PDF (1164K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1164K)
Original Papers
-
Ambika KUMAR, R. K. DUTTAArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 565-571
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialPresented here is a simple yet rapid and efficient analytical method for visual as well as spectroscopic method for sensing of trace concentrations of Cu2+ ions in aqueous medium by systematic photoluminescence quenching of a highly water soluble probe made of CdS quantum dots surface modified by thiourea. The salient features of this work describe rapid detection (2 min equilibration time) of Cu2+ ions at wider linear concentration range (0.025 – 10 mg/L) corresponding to a sensitivity of 2.81(mg/L)−1 and limit of quantification of 47.3 μg/L, respectively, suitable for Cu2+ sensing in drinking water and ground water. Further, the detection of Cu2+ ion was free from most interfering cations and anions, except for minor interference from Cr3+, Hg2+ and Pb2+. The robustness of our probe for Cu2+ sensing is demonstrated from efficient Cu2+ spike recovery analysis in groundwater and river water samples.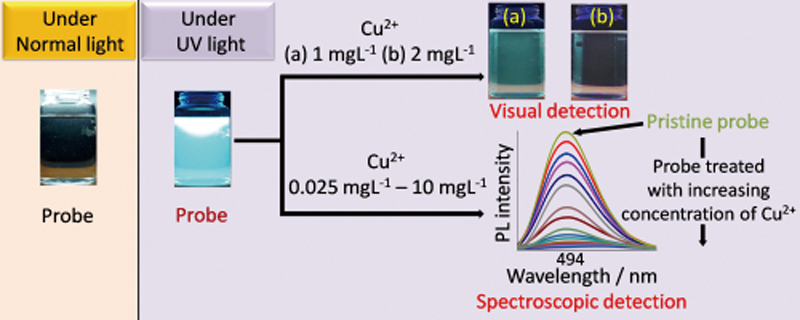 View full abstractDownload PDF (5554K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5554K) -
Hui LI, Su-fang FAN, Yan WANG, Shi-gang SHEN, Dian-xing SUNArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 573-578
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA method was developed for analyzing broad spectrum small molecule metabolites in the serum of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients based on ultrafast liquid chromatography–ion trap–time of flight tandem mass spectrometry (UFLC-IT-TOF MS). Serum samples were collected from 80 HCC patients and healthy persons. After pretreatment process for protein precipitation, the supernatant was analyzed with the UFLC-IT-TOF MS to obtain information on the metabonomics of small molecules. The eight compounds of glycocholic acid, choline glycerophosphate, acetyl-L-phenylalanine, oleamide, tetradecanamide, acetylcarnitine, lysolecithin and glycochenodeoxycholic acid in the HCC group were identified with significant differences from those in the health group (P <0.01). By using multidimensional analysis of variation coefficient and principal component analysis for the repeatability and 48 h stability, the method was demonstrated to have good repeatability, excellent precision, and high stability, which can satisfy the metabonomics research requirement. The high throughput and practical usability of the method further shows perspective for metabonomic analysis of large-batch serum samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1221K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1221K) -
Yuan ZENG, Zhiqin PENG, Bing WANG, Zhiwen HU, Junmin WAN, Yang ZHOUArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 579-583
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe enzymatic degradation of silk by protease XIV has been investigated by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance of cross-polarization/magic angle spinning (13C CP/MAS solid state NMR) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). Micro-morphology of protease XIV aged samples showed that microfilaments were stripped out from the surface of silk fibers. The results of FTIR and 13C CP/MAS solid-state NMR indicated that the enzymatic degradation process could be divided into two stages. The EPR spectra indicated that the enzymatic degradation process was related to the free radical with the g-factor value of 2.0043. We also proposed that at the first degradation stage, the free radicals were apt to lose activities due to the loose structure of the non-crystalline region; at the second degradation stage, the free radicals produced in the crystalline region tended to be stored. View full abstractDownload PDF (950K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (950K) -
Xiaoqian ZHU, Min HUANG, Jiao LI, Hanping HE, Xiuhua ZHANG, Shengfu WA ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 585-590
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this paper, a novel electrochemical sensor was developed for the rapid detection of G-G mismatched DNA based on hexaammineruthenium(III) chloride ([Ru(NH3)6]Cl3) as a redox indicator. The sensor platform was constructed by immobilizing small molecules (NC-linker) on the gold electrode via amide bonds. The as-prepared NC-linker as the nucleic acids recognition molecule can interact with the G base of DNA. After the sensor was incubated with G-G mismatched DNA, the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) acted as carriers of the signal tags-[Ru(NH3)6]Cl3, which resulted in a remarkable electrochemical signal. More binding of [Ru(NH3)6]Cl3 led to increases of the electrochemical signal. Other mismatched DNA produced only a low response, as well as complementary DNA. Thus G-G mismatched DNA can be easily discriminated from other mismatched and complementary DNA based on the sensor. Furthermore, the method was simple, rapid and repeatable for the detection of G-G mismatched DNA. The selective detection of target dsDNA was achieved by a relative current ratio of the target and control DNA. These results demonstrated that this strategy could provide great promise for the rapid and specific detection of other sequence-specific DNA. View full abstractDownload PDF (1757K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1757K) -
Hong WANG, Jian CHEN, Yongxiang HONG, Kun LV, Maolin YU, Peisheng ZHAN ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 591-597
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, amphiphilic diblock copolymers were designed and synthesized via the incorporation of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer radical polymerization (RAFT) and a subsequent grafting technique. Subsequently, Hg2+-sensitive water-soluble fluorescent polymeric micelles (FNs) were prepared by a reprecipitation strategy. The spectroscopic characteristics demonstrate that the fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) was successfully linked into the polymer. Due to the promoted reaction of desulfurization cyclization by Hg2+, the fluorescence of fluorescein in FNs was obviously quenched. The as-prepared FNs showed admirable Hg2+-sensitivity (detection limit: 54 nM), excellent water-solubility and high selectivity. In addition, FNs were successfully used to determine Hg2+ in blood serum. We expected that the as-prepared FNs could perform potential applications in imaging, sensing, and bioanalytic chemistry. View full abstractDownload PDF (4808K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4808K) -
Yongrong LI, Yusuke WASHINO, Tsuyoshi HYAKUTAKE, Tsuyoshi MICHINOBUArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 599-604
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSide chain clicked polystyrene derivatives formed by the Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) reaction showed colorimetric ion sensing behaviors when donor-acceptor chromophores, prepared by a [2+2] cylcoladdition-retroelectrocyclization between electron-rich alkynes and tetracyanoethylene (TCNE)/7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ), were attached to the triazole rings. The metal ion sensing behaviors could be explained according to the theory of hard and soft acids and bases (HSAB). Hard acidic metal ions were mainly recognized by the hard basic anilino-nitrogen moieties, resulting in a decrease in the charge-transfer (CT) bands. In contrast, soft acidic metal ions led to a bathochromic shift in the CT bands due to the selective interactions with the soft basic cyano-nitrogen atoms. With the triazole spacers, more soft (and/or borderline) metal ions were recognized by the donor–acceptor chromophores probably due to more space for the various sized metal ions. The chemodocimetric anion sensing behaviors of the clicked polystyrenes were almost the same as those of the counter polystyrenes without the triazole spacers. Overall, the triazoles in this study do not serve as colorimetric sensor units towards both metal ions and anions, but they are effective spacers between the polymer main chain and ion sensing donor–acceptor side chain chromophores.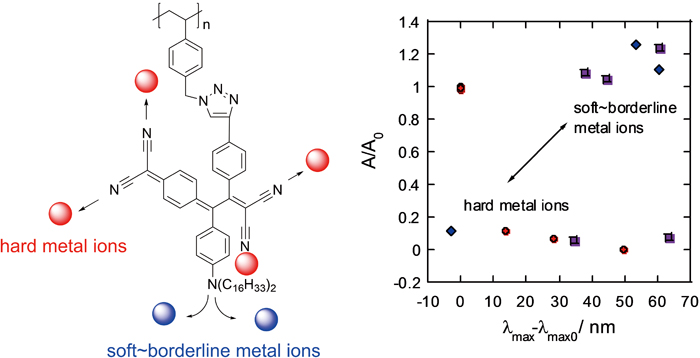 View full abstractDownload PDF (2339K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2339K) -
Natalia P. ZAKSAS, Alexander F. VERYASKINArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 605-609
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe possibility of direct analysis of soils by two-jet plasma atomic emission spectrometry was investigated using certified reference materials of black earth, grey desert and red soils. It was shown that As, B, Cd, Cu, Hg, P, and V could be determined after a 2-fold, and Be, Co, Cr, Ga, Nb, Pb, and Zn—after a 10-fold dilution of the samples by a spectroscopic buffer using calibration samples based on graphite powder. The strongest matrix effects were revealed for red soil having the highest Al and Fe concentration, which led to the overstated concentrations of some elements. The overstating factor depended on analyte concentration and was no more than 2. A clear advantage of the suggested technique over existing methods is the simple sample preparation process, which requires no reagents except a spectroscopic buffer, and possibility of using the same calibration samples for analysis of different soils. View full abstractDownload PDF (727K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (727K) -
Xiaoxia LI, Kyung Ho ROWArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 611-617
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDeep eutectic solvents (DES) are potential ecofriendly surfactants for the preparation of materials. In this study, both molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and mesoporous siliceous materials (MSMs) were modified by betaine-based DES. Six materials were employed as solid phase extraction (SPE) adsorbents for the rapid purification of levofloxacin. The DES-based materials showed better selective adsorption than the conventional materials. The adsorption curves of DES-MIP showed superior molecular recognition ability and binding capability for levofloxacin compared to the other materials. The limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the method were 0.01 and 0.03 μg/mL for levofloxacin, respectively. The method recoveries at three spiked levels were 97.2 – 100.2% for DES-MIP, with an RSD <1.8%. DES-MIP showed the highest selective recovery (95.2%) for levofloxacin from the green bean extract, and could remove the interferent effectively.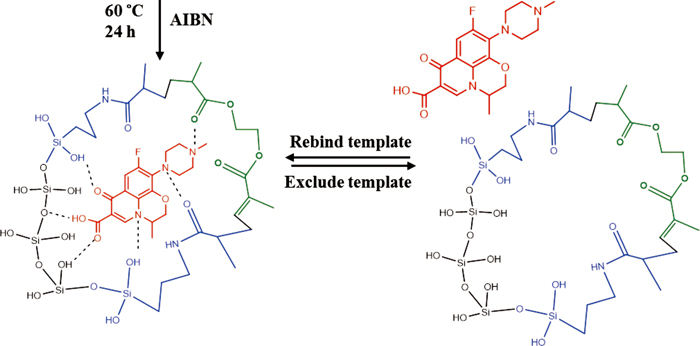 View full abstractDownload PDF (1966K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1966K) -
Nobuyuki TAKAYAMA, Lee Wah LIM, Toyohide TAKEUCHIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 619-625
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe retention behavior of inorganic anions was studied in hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). In this study, five kinds of HILIC stationary phases (amino, imidazole, amide, pyridine and zwitterionic) were investigated. It was found that only amino and imidazole columns exhibited the separation of inorganic anions under HILIC conditions. The retention mechanism was further investigated under both columns. A reversed elution order of inorganic anions was observed under the HILIC condition compared with those observed under the ion-exchange chromatography mode (IEC). The effect of salt species and their concentration in the eluent were investigated under constant acetonitrile (ACN) content. Sodium chloride and sodium perchlorate were chosen as the salt, and the salt (sodium perchlorate) concentration was varied from 10 to 40 mM to confirm the effect of the electrostatic interaction. The slope values of the plots of the log retention factor (k) versus the log eluent concentration were calculated to be between –0.43 and –0.45 for the amino column, while those obtained on the imidazole column were between –0.68 and –0.73. Various concentrations of ACN were also examined with 20 mM sodium perchlorate, and the typical HILIC retention behavior was observed on both amino and imidazole columns. Due to the obtained results, it is considered that the separation of inorganic anions under the HILIC condition was achieved by both electrostatic interaction and partition. View full abstractDownload PDF (919K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (919K) -
Ming-Ju WU, Guan-Fu YE, Ching-Hao WANG, Hong-Ting Victor LIN, Chien-Ch ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 625-630
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHollow, poly(L-lactic acid) microtube array membranes (MTAM) were used in preparing membranes that contained immobilized yeast cells. To evaluate the performance of the developed system for continuous and fed-batch fermentation, a gas chromatography/milli-whistle device was used to on-line monitor the production of ethanol. The milli-whistle was connected to the outlet of a GC capillary, and when the fermentation gases and the GC carrier gas passed through it, a sound with a fundamental frequency was produced. The online data obtained for frequency-change vs. retention time can be recorded after a fast Fourier transform. In typical bioethanol fermentation, the yeast cells cannot be recycled, whereas the artificial yeast-MTAMs can be. The hollow-MTAM containing immobilized yeast cells significantly enhanced to bioethanol productivity, and represent a novel, promising technology for bioethanol fermentation. Our data indicate that the gas chromatography/milli-whistle device, which is economical and stable, is a very useful detector for long-term monitoring. View full abstractDownload PDF (1055K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1055K) -
Nobuyuki TAKAYAMA, Lee Wah LIM, Toyohide TAKEUCHIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 631-634
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialZwitterionic monolithic columns were synthesized by a one-pot reaction using [2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl]dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl)ammonium hydroxide, ethylene dimethacrylate, methanol and 2,2′-azobis(isobutyronitrile) as the monomer, cross-linker, porogen and initiator, respectively. The optimum conditions for polymerization and the efficiency of the prepared columns were examined for ion chromatography. The separation of five kinds of inorganic anions was achieved. The back pressures were monitored as increasing flow-rate, and the resulting plate heights (i.e. height equivalent of a theoretical plate, HETP) of SCN− were calculated at the inspected flow-rates. It was found that the increment rates of both the back pressure and HETP were rather slight. Mobile phases containing various cations or acid increased the retention times of the anions. Divalent cations could be separated, while monovalent cations could not be resolved due to their weak retention on the stationary phases. View full abstractDownload PDF (698K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (698K) -
Shinsuke KUNIMURA, Tomoki SHINKAIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 635-638
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSUsing a portable total-reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) spectrometer with a collodion film sample holder, a spectrum of an analyte containing 50 ng of aluminum was measured. The Al Kα line (1.49 keV) that partially overlaps with the Si Kα line (1.74 keV) from a quartz glass substrate usually used as a sample holder for TXRF analysis, was clearly detected when using the collodion film sample holder. To investigate the quantitative performance of the portable spectrometer with a collodion film sample holder, the concentrations of Cr, Mn, and Fe in a certified reference material of river water (JSAC 0302-3b), whose certified values are 10.0, 5.1, and 59.6 μg/L, respectively, were determined by the internal-standard method. We showed that approximate concentrations of these elements were determined. View full abstractDownload PDF (840K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (840K)
Notes
-
Hajime KATANO, Shota NOBA, Kimihiko SATO, Hisashi KIMOTOArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 639-642
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and rapid method for separation and purification of chitin oligosaccharides, (GlcNAc)n, with n ≥ 5 is presented. A commercially available chitin oligosaccharides sample, consisting of (GlcNAc)n with n = 1 – 7, was used as the starting material. Ten milligrams of the material was mixed with 100 μL of the 1 mol/L HCl. All the (GlcNAc)n species were dissolved in the aqueous medium. The aqueous solution was mixed with 900 μL of EtOH; the mixture was centrifuged, and the supernatant was removed to obtain a precipitate. The precipitate was found to consist mainly of (GlcNAc)n with n ≥ 5, indicating the significant difference in solubility between the short-chain (GlcNAc)n species with n ≤ 3 and the longer ones. By the repetition of the operations, a high purity long-chain (GlcNAc)n sample with n ≥ 5 could be prepared successfully. Since the long-chain (GlcNAc)n species are known to have excellent elicitor activity, this sample would be useful in the study of plant pathology, as well as chitin and chitosan chemistry. View full abstractDownload PDF (807K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (807K) -
Shigehiro KAGAYA, Tomonori MAENO, Kazuma ITO, Makoto GEMMEI-IDE, Rober ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 643-646
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn important reason for the inefficient extraction of Cr(VI) from its acidic solutions into polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs), consisting of poly(vinyl chloride) as the base-polymer and Aliquat 336 as the carrier, was found to be associated with the leaching of Aliquat 336 from the PIMs into the solutions, where it subsequently reduced the anionic Cr(VI) species to cationic Cr(III) species. The PIM extraction efficiency for Cr(VI) was significantly improved by the addition of NaNO3 to the solutions, which suppressed the leaching of Aliquat 336 and the reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III). View full abstractDownload PDF (711K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (711K) -
Tatsumi SATO, Katsuya HATA, Kiyoharu NAKATANIArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 647-650
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe intraparticle diffusion of a fluorescent dye in single microparticles in an aqueous solution was analyzed using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching, with a confocal fluorescence microscope. The fluorescence depth profile of single microparticles, and the fluorescence recovery at the particle center, were measured; further, the intraparticle diffusion coefficient was determined through simulations of three-dimensional diffusion in the respective microparticles. The intraparticle diffusion of coumarin 102 in octadecylsilyl silica gel was limited by the surface diffusion. View full abstractDownload PDF (541K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (541K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017 Volume 33 Issue 5 Pages 651
Published: May 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (3104K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|