All issues

Volume 33, Issue 6
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 657-658
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (892K)
Original Papers
-
Xueting YIN, Sai WANG, Xiaoyun LIU, Chenmeng HE, Yali TANG, Qimeng LI, ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 659-664
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, a simple and sensitive aptamer-based colorimetric method for the detection of Ochratoxin A by using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) has been developed. In this assay, unmodified gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were used as probes with a 36-mer aptamer as recognition element. In the absence of ochratoxin A, free aptamer could be adsorbed onto the surface of AuNPs and protect AuNPs from aggregation even with high concentrations of salt. The salt-induced aggregation of AuNPs was caused by the specific recognition of aptamers with OTA. Under optimum conditions, calibration modeling showed that the analytical linear range covered from 32 to 1024 ng/mL and the detection limit of 20 ng/mL was realized successfully. This proposed colorimetric bio-assay also showed high selectivity over other antibody based methods. Meanwhile, this strategy was further used to determine the concentrations of ochratoxin A in white wine sample with satisfying recovery rates.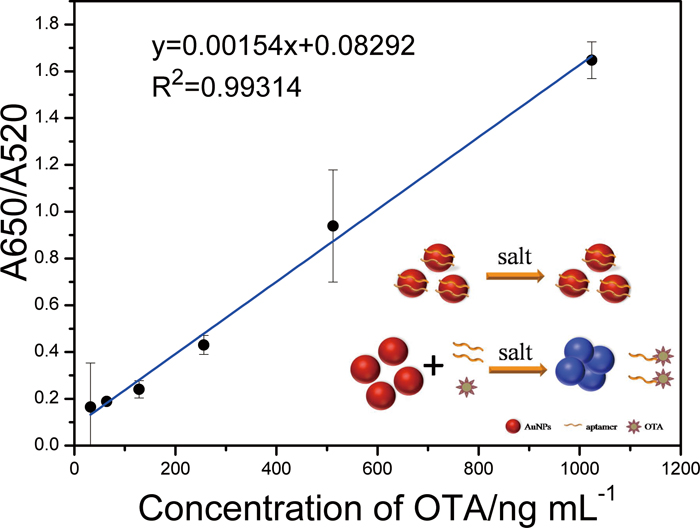 View full abstractDownload PDF (3144K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3144K) -
Shenghui MEI, Leting ZHU, Xingang LI, Jiaqing WANG, Xueyun JIANG, Haiy ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 665-670
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMethotrexate (MTX) plasma concentration is routinely monitored to guide the dosage regimen of rescue drugs. This study aims to develop and validate an ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method for plasma MTX analysis, and to establish its agreement with the fluorescence polarization immunoassay (FPIA) in patients with high-dose MTX therapy. Separation was achieved by gradient elution with methanol and water (0.05% formic acid) at 40°C with a run time of 3 min. The intra- and inter-day inaccuracy and imprecision of the UPLC-MS/MS method were –4.25 to 3.1 and less than 7.63%, respectively. The IS-normalized recovery and matrix effect were 87.05 to 92.81 and 124.43 to 134.57%. The correlation coefficients between UPLC-MS/MS and FPIA were greater than 0.98. The UPLC-MS/MS method was in agreement with the FPIA at high levels of MTX (1.0 – 100 μmol/L), but not at low levels (0.01 – 1.0 μmol/L). Further studies are warranted to confirm these results. View full abstractDownload PDF (1051K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1051K) -
Xing-Juan LI, Jian LING, Cai-Ling HAN, Li-Qiang CHEN, Qiu-E CAO, Zhong ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 671-675
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this paper, chicken egg white purchased from a local market without further purification was directly used to prepare fluorescent gold nanoclusters through a one-step, simple, fast and green synthesis approach for analytical purposes. The as-prepared chicken egg white stabilized gold nanocluster probe has strong red fluorescence emission, which can be quenched by mercury ions and copper ions sensitively. By using an ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) masking method, mercury ions in the range from 0.60 to 10 μM can be linearly detected with the limit of detection (LOD, 3σ) of 0.510 μM in the presence of equivalent copper ions. Since the preparation of a chicken egg white stabilized gold nanocluster probe is fast, easy and cheap, this selective analytical method for mercury pollution monitoring in environmental waters may be widely used in daily life by ordinary people. View full abstractDownload PDF (1074K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1074K) -
Jing WANG, Bin LAN, Hai-Bo LIUArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 677-682
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis paper reports that changing metal ions (Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, or Cd2+) in the 2-(2-thiazolylazo)-p-cresol (TAC)-metal ensemble may generate varied optical responses to anions. The TAC and Ni2+ ensemble can detect and quantify CN− in a highly sensitive and selective manner. CN− competes for the Ni2+ present in the ensemble during recognition events, which thereby triggers colorimetric and absorption spectral changes. CN− and S2− decomposed TAC-Cu2+ ensemble by forming [Cu(CN)x]n− species and CuS, respectively; however, the discrimination of CN− and S2− was not achieved. The TAC-Co2+ ensemble exhibited discriminated interaction with CN− through the absorption channel, but CN− was not quantitatively determined. Although the TAC-Cd2+ ensemble responded to different anions, it did not recognize each anion selectively. These results demonstrated that metal ions can powerfully modulate anion identification to some extent, which can be an effective strategy to achieve selectivity of certain anions by varying the metal ions in the ensemble.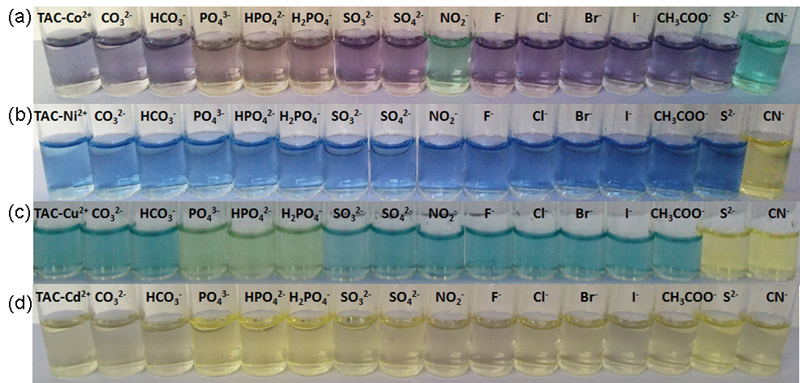 View full abstractDownload PDF (3523K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3523K) -
Kadriye Isil BERKER, Dilek OZYURT, Birsen DEMIRATA, Resat APAKArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 683-689
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFerrozine (FZ) preferentially stabilizes Fe(II) over Fe(III) to raise the ferric reduction potential and oxidize antioxidants. The advantages of the ferric-ferrozine method over other iron-based total antioxidant capacity assays were: (i) higher molar absorptivity and enhanced sensitivity, (ii) lower interference from foreign ions, (iii) wide pH tolerance (iv) additivity of the absorbances for mixtures. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) could be combined with spectrophotometry, because the magenta-colored anionic Fe(II)-FZ complex was quantitatively sorbed on Sephadex QAE A-25 resin. The sensitivity enhancement using the resin enabled us to conduct total antioxidant capacity (TAC) measurements of antioxidant-poor samples. The apparent molar absorptivity, linear concentration range and trolox equivalent antioxidant capacities (TEAC) of certain antioxidants were found. The calibration curves (lines) of trolox, rutin, and rosmarinic acid individually and in herbal infusions—by using the method of standard additions—were parallel, confirming that the added antioxidants did not interact with herbal constituents to cause chemical deviations from Beer’s law. View full abstractDownload PDF (793K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (793K) -
Toshikuni KATO, Shogo SUGAHARA, Makoto MURAKAMI, Yukiko SENGA, Michiko ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 691-695
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe developed a method for quantifying trace NH2OH in brackish- and sea-water samples. Previously reported methods applicable to fresh water cannot be applied to such samples. We determined that interference in seawater owing to the bromide ion can be removed by the addition of phenol. In our procedure, phenol and hypochlorite solutions were added to a sample solution to oxidize NH2OH to N2O. N2O in the sample was then quantified by headspace analysis. The method is not affected by the salt content or ammonia, nitrate, or nitrite at concentrations of 300 μgN L−1 or less. It has a limit of detection of 0.2 μgN L−1, and can quantify NH2OH in natural water samples with a wide range of salinity. It was applied to samples from Lake Nakaumi, a brackish lake located in the eastern part of Shimane Prefecture, Japan.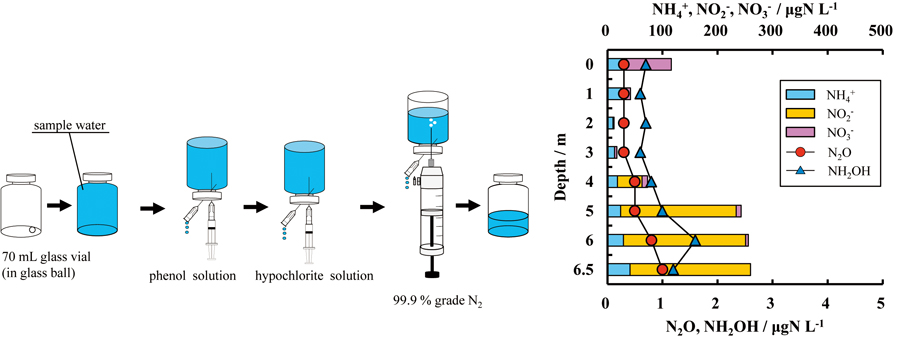 View full abstractDownload PDF (1161K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1161K) -
Aoi MIYAMOTO, Saori NAKANO, Kaishu NAGAI, Naoya KISHIKAWA, Kaname OHYA ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 697-701
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA method for evaluating hydroxyl radical (·OH) scavenging activities using sequential injection analysis (SIA) with chemiluminescence (CL) detection was developed. In this system, CL was produced by the reaction of luminol with ·OH generated from the Fenton reaction. The scavenging activity was expressed as a diminution rate of the CL due to the scavenging of ·OH by a sample. The SIA system allows the automation of a series of experimental procedures including Fenton’s reaction, scavenging of ·OH, and luminol CL reaction. The evaluation of scavenging activities in one sample (n = 3) was completed within 3.0 min. Relative standard deviations (n = 3) of scavenging activity with 700 μM L-ascorbic acid were 2.6% (intraday) and 3.7% (interday). The SIA-CL system was applied to measure ·OH scavenging activities of several antioxidants and pharmaceuticals.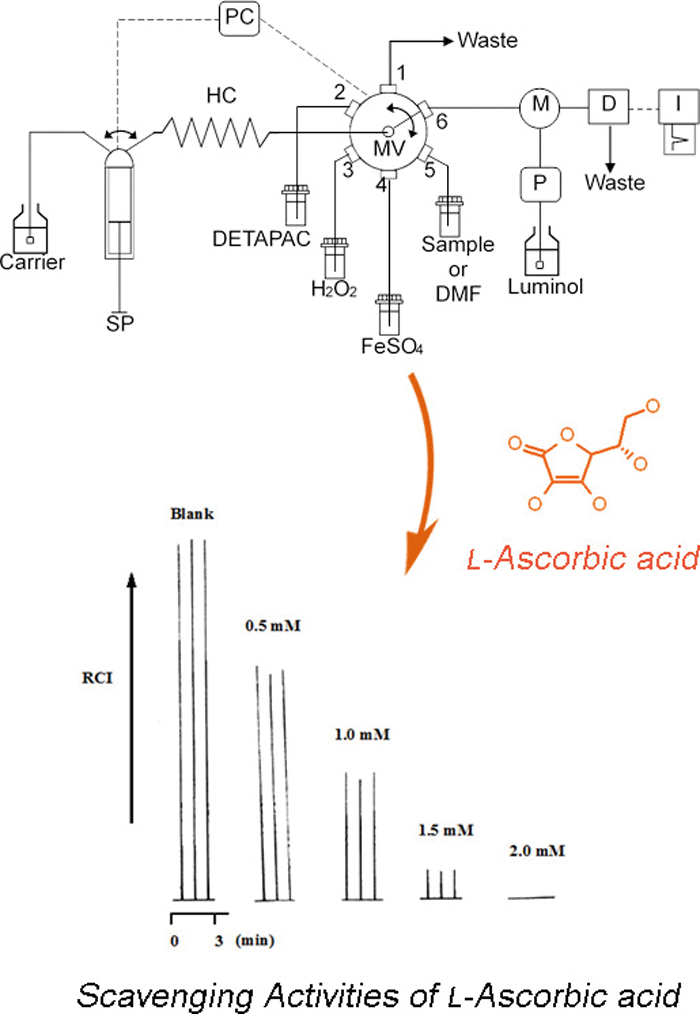 View full abstractDownload PDF (516K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (516K) -
Hiroaki MATSUURA, Takuto TAKAHASHI, Shura SAKAMOTO, Tsubasa KITAMURA, ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 703-707
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn amperometric sensor based on flow injection analysis (FIA) of dissolved hydrogen molecules was first developed using electrodeposited platinum particles on glassy carbon electrodes modified with nitrogen-containing functional groups (Pt-NGC) as the working electrode. A glassy carbon (GC) electrode was covalently modified by electrochemical oxidation/reduction procedures. The redox waves between hydrogen ions and hydrogen molecules at highly positive potential range in the hydrodynamic voltammogram were obtained by using a Pt-NGC electrode. The specific electrocatalytic activity for the electrode oxidation of hydrogen molecules has successfully been applied to the FIA of dissolved hydrogen. The typical current vs. time curve was obtained by the repetitive measurement of dissolved hydrogen, and the measurement of dissolved hydrogen was fully completed in a short time (∼15 s). A linear relationship was obtained between the oxidation current of hydrogen molecules and dissolved hydrogen concentration. This indicates that our proposed technique can be used for the determination of the dissolved hydrogen concentration. The fabrication method of the present sensor is very simple because the direct modification of the glassy carbon electrode surface can be performed, differing from the tedious fabrication method in which electrocatalytic carbon powder prepared must be immobilized to the surface of the glassy carbon electrode using Nafion coating and high temperature treatment.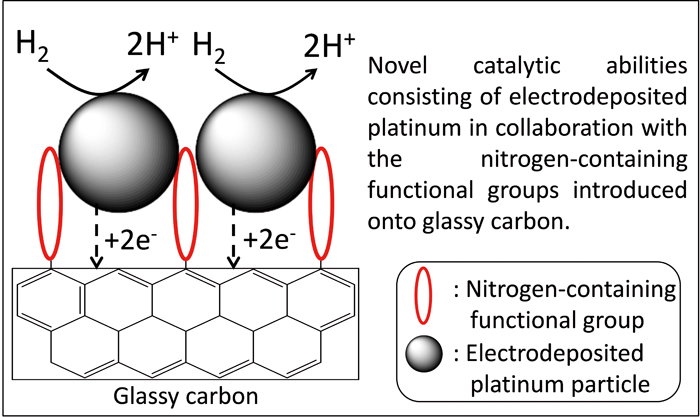 View full abstractDownload PDF (990K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (990K) -
Manami MITSUNOBU, Sakurako KOBAYASHI, Nobuyuki TAKEYASU, Takashi KANET ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 709-713
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCoalescence of oil droplets in an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion was achieved with heating and optical trapping. Three types of O/W emulsions were prepared by adding a mixture of butanol and n-decane to an aqueous solution containing a cationic surfactant (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB), an anionic surfactant (sodium dodecyl sulfate, SDS), or a neutral hydrophilic polymer (polyethylene glycol, PEG) as an emulsifier. Two oil droplets in the emulsions were randomly trapped in a square capillary tube by two laser beams in order to induce coalescence. Coalescence of the droplets could not be achieved at room temperature (25°C) regardless of the type of emulsifier. Conversely, the droplets prepared with PEG coalesced at a temperature higher than 30°C, although the droplets with ionic surfactants CTAB and SDS did not coalesce even at the elevated temperature due to their electrostatic repulsion. The size of the resultant coalesced droplet was consistent with that calculated from the size of the two droplets of oil, which indicated successful coalescence of the two droplets. We also found that the time required for the coalescence could be correlated with the temperature using an Arrhenius plot.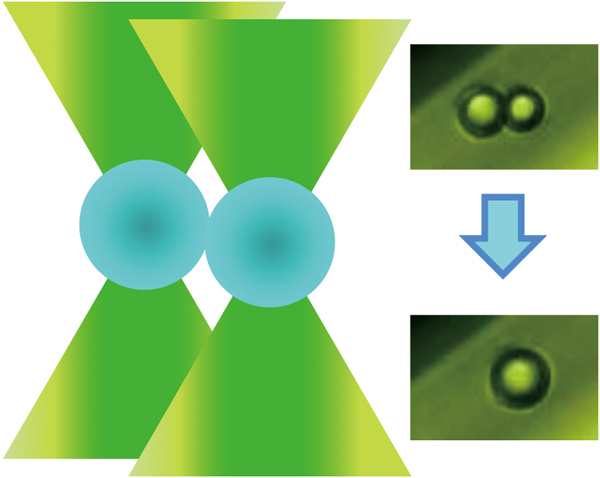 View full abstractDownload PDF (596K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (596K)
Notes
-
Weida WANG, Yegang DU, Zeen XIAO, Yun LI, Bifang LI, Guowu YANGArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 715-717
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialRhodamine B was forbidden in food by law because of its carcinogenic properties to humans. However, due to its low cost, it was often used to dope chili oil by some counterfeiters to improve its natural color. However, it was difficult to quantify rhodamine B in chili oil due to its complex substrates and high viscosity. In this study, deep eutectic solvents, comprised of choline chloride and ethylene glycol, were first used as an extraction medium to separate rhodamine B from chili oil.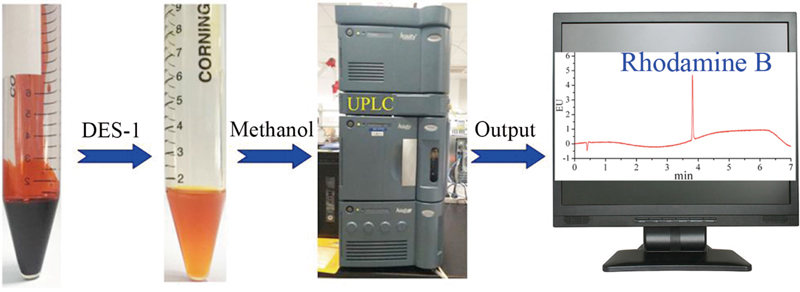 View full abstractDownload PDF (1475K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1475K) -
Rika SHIOTA, Hirotoshi MORITA, Tomoko MATSUMOTO, Atsushi MORIMOTO, Jun ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 719-722
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn analytical method was developed and validated for the measurement of hydroxyproline (Hyp) levels in mouse kidney by high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection (LC/MS/MS) using an analytical column specially designed for the LC/MS/MS analysis for intact amino acids. Tissue hydrolyzed with hydrochloric acid could be directly injected into the LC/MS/MS, as well as separated and detected using the deuterium labelled Hyp as an internal standard. The calibration curve showed good linearity from 5 to 500 nmol/mg of tissue; the precision and accuracy, including within- and between-run, were less than 6% and within 100 ± 6%, respectively. View full abstractDownload PDF (513K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (513K) -
Shun-ichi FUNANO, Nobuyuki TANAKA, Yo TANAKAArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 723-725
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe demonstrated that our previously developed gas-phase fluoroalkylsilane patterning method was applicable to polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and we compared the stability of patterned proteins and cultured cells between PDMS and glass surfaces. The shapes of the protein patterns were stable on both glass and PDMS surfaces for more than 1 week. The cell patterns were stable on glass surfaces for 1 week, while those on PDMS collapsed within a few days. These results indicated that our method was applicable to PDMS, although, compared with glass, PDMS has an unsolved issue for its application to long-term patterning of cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (585K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (585K) -
Xiaoyin SUN, Takao YASUI, Takeshi YANAGIDA, Noritada KAJI, Sakon RAHON ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 727-730
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHere, we report the effect of DNA methylation on the velocity of DNA translocation through a nanochannel, as determined by measuring differences in translocation velocities between methylated and non-methylated DNA molecules. We found that the velocity of translocation of methylated DNA was faster than that of non-methylated DNA, which we attributed to variation in the coefficients of diffusion and friction with the nanochannel wall, due to the increased molecular weight and stiffness, respectively, of methylated DNA.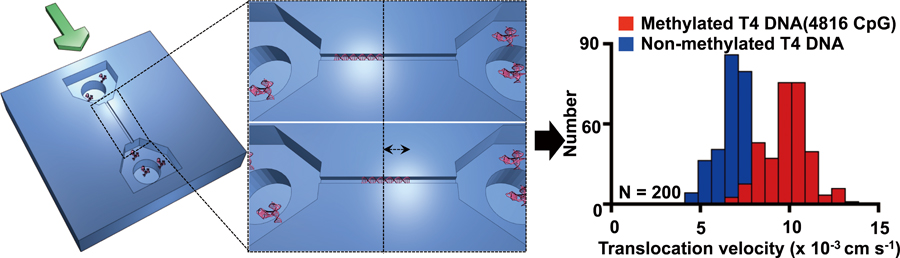 View full abstractDownload PDF (612K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (612K) -
Hikaru YAMAMOTO, Hidaka ISHIGAMI, Tomohiro UCHIMURAArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 731-733
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialLaser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry was applied to the online monitoring of a styrene monomer and dimer in an emulsion. During the measurement of a styrene monomer oil-in-water emulsion for this study, a styrene dimer, 1,3-diphenylpropane, was dropped into the emulsion. As a result, signal spikes from both analytes occurred simultaneously, which suggested that either the dimer had moved to the monomer droplets or that the monomer and dimer droplets had aggregated. We concluded that this method could be useful for the direct monitoring of monomers and oligomers in the early stages of emulsion polymerization.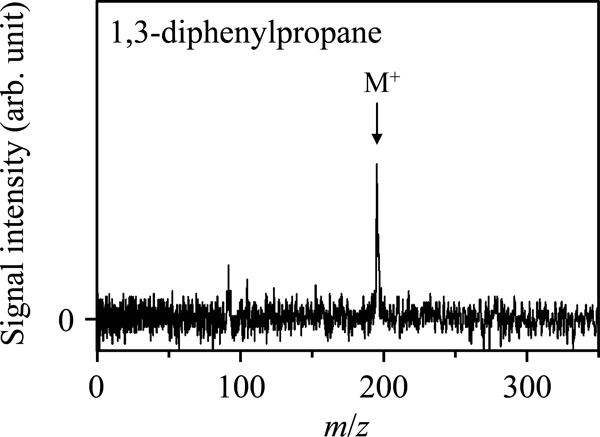 View full abstractDownload PDF (451K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (451K) -
Xiaoyin SUN, Takao YASUI, Takeshi YANAGIDA, Noritada KAJI, Sakon RAHON ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 735-738
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHere, we developed a device integrated with a nanochannel and nanostructures to slow DNA translocation velocity. We found that translocation velocity of a single DNA molecule inside a nanochannel was decreased by pre-elongating it using some nanostructures, such as a shallow channel or nanopillars. This decrease of the translocation velocity was associated with the DNA mobility change, which is an intrinsic parameter of DNA molecules and unaffected by an electric field. View full abstractDownload PDF (725K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (725K) -
Yota KUDO, Manabu SHIBATA, Satoshi NOMURA, Nobuaki OGAWAArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 739-742
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA pH electrode incorporating a reference electrode different from that in conventional electrodes was applied to the measurement of rainwater pH. The reference electrode utilizes a recently proposed ionic liquid salt bridge instead of a conventional potassium chloride salt bridge. The response time of this electrode was remarkably improved in rain sample pH measurements compared to that of conventional pH electrodes. In addition, the measured pH values of rain samples seemed to be more accurate with this electrode.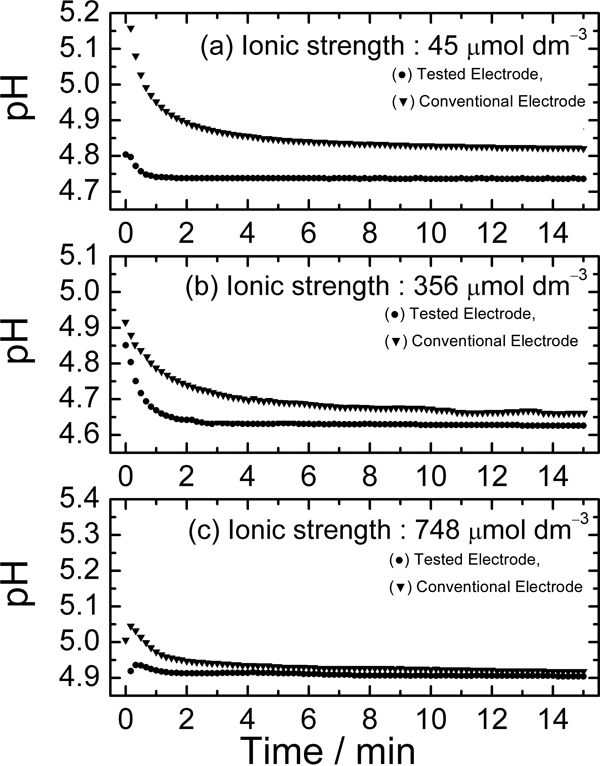 View full abstractDownload PDF (665K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (665K) -
Andrei BITA, George Dan MOGOSANU, Ludovic Everard BEJENARU, Carmen Nic ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 743-746
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe paper describes a new, simple, selective and precise high-performance thin-layer chromatographic (HPTLC) method for the simultaneous identification and quantitative determination of boric acid (BA) and calcium fructoborate (CFB) in bulk and tablet/capsule dosage forms of dietary supplements. HPTLC silica gel G 60 F254 precoated glass plates were used as the stationary phase. The mobile phase consisted of 2-propanol–water 8:2 (v/v). The two boron-based compounds were adequately separated with the Rf values of 0.83 ± 0.01 (BA) and 0.59 ± 0.01 (CFB). View full abstractDownload PDF (515K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (515K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017 Volume 33 Issue 6 Pages 747
Published: June 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (3037K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|