All issues

Volume 33, Issue 7
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Hideaki HISAMOTOArticle type: Highlights
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 753
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (289K)
Original Papers
-
Meiling CHEN, Jiezhao ZHOU, Le MEI, Fanglin YU, Xiangyang XIE, Yan LIU ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 755-759
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn order to overcome deficiencies for simultaneously determining felodipine (FDP) and metoprolol (MPL) with low recovery and low sensitivity, a new online SPE coupled with the liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (SPE-LC-MS/MS) method for the simultaneous quantitative determination of FDP and MPL in beagle dog plasma was established. The SPE extraction of FDP and MPL was performed on a Retain PEP Javelin column (10 × 2.1 mm, 5 μm), while the chromatographic separation was achieved on a ZORBAX SB-C18 (50 × 2.1 mm, 3.5 μm) analytical column. Multiple reaction monitoring operated in the positive ion mode was adopted in MS detection, and the precursors to the product ion transition values of m/z 384/338.1, 268/74.2 and 436.2/207.1 were used to measure FDP, MPL and the internal standard (valsartan). The high throughput, accurate and sensitive method for FDP and MPL was validated and applied to the bioavailability research of FDP and MPL in beagle dogs. View full abstractDownload PDF (587K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (587K) -
Xiaohan SUN, Shenghong YANG, Mingzhen GUO, Shuang MA, Mingda ZHENG, Ji ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 761-767
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn “on-off-on” mode was developed for the detection of mercury ion (Hg2+) and glutathione (GSH) with high sensitivity and selectivity based on the nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) fluorescent probe. The N-CDs were synthesized through microwave treatment of citric acid and diethylenetriamine for 2 min, and exhibited excellent fluorescence properties and high quantum yield (27.7%). The fluorescence intensity of the N-CDs could be significantly quenched by Hg2+ (turn-off). Upon addition of GSH, the fluorescence intensity of the N-CDs-Hg2+ system could be recovered clearly (turn-on). The limit of detection of Hg2+ and GSH was 23 and 59 nM, respectively. Moreover, the “on-off-on” probe was successfully applied to the determination of Hg2+ in tap water and water from the Yellow River. Meanwhile, due to bright luminescence, good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, the N-CDs-based probe was successfully employed as visualizing the intracellular Hg2+ and GSH sensors in live HeLa cell.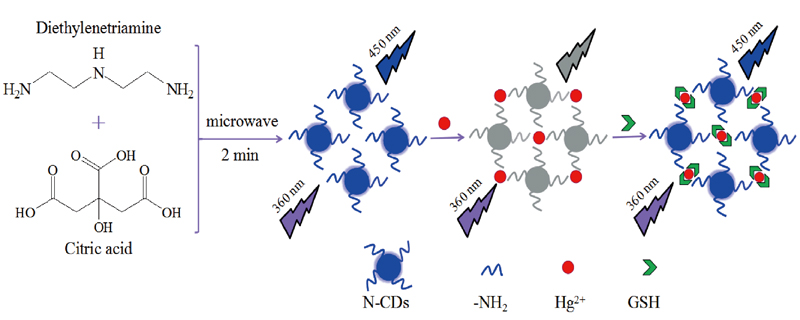 View full abstractDownload PDF (4751K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4751K) -
Leila DOLATYARI, Mohammad Reza YAFTIAN, Sadegh ROSTAMNIA, Mir Saeed SE ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 769-776
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA solid-phase extraction based on a functionalized SBA-15, with the Schiff base ligand, ethylenediaminepropylesalicylaldimine (SBA/EnSA), was developed for the recovery and preconcentration of trace amounts of uranium(VI) in water samples, prior to its determination spectrophotometrically using ArsenazoIII. For optimizing the parameters affecting the adsorption step (pH, adsorbent dose and adsorption time) and those influencing the desorption process (concentration and volume of eluent and desorption time), a statistical technique response surface methodology (RSM) was employed. The limit of detection and the linear dynamic range for the proposed method were 10 μg L−1, and 33.5 – 500 μg L−1, respectively. The adsorbent showed a high capacity (110.2 mg g−1) and the method allowed obtaining a preconcentration factor of 67. The inter- and intra-day relative standard deviations for a solution of 100 μg L−1 (n = 5) were found to be 4.8 – 6.2%. The developed method was successfully applied for the determination of U(VI) in water samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (927K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (927K) -
Heng WANG, Liangpo LIU, Syed Ali Musstjab Akber Shah EQANI, Heqing SHE ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 777-781
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo quantitatively measure trace levels of bisphenol A (BPA) in infant urine, a simply improved high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)–tandem mass-spectrometry method was developed and validated. In the present work, a ZORBAX SB-C18 column (2.1 × 30 mm, 3.5 μm) was used for trapping and isolating BPA from the HPLC mobile phase. The result showed that the trapping column can provide effective separation from the background BPA to the sample BPA. This method has a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.048 μg/L, spiked recoveries 85.4% (0.50 – 10.0 μg/L), and relative standard deviations of 1.8 – 15.9%. By using its low-LOD advantage, we firstly reported that Chinese infants (n = 48 with age <6 months) have been ubiquitously exposed to BPA (detection frequency of 93%) with an median level of 0.13 μg/L (ranging from below LOD to 5.04 μg/L). View full abstractDownload PDF (691K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (691K) -
Chao HU, Xiang Juan KONG, Ru Qin YU, Ting Ting CHEN, Xia CHUArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 783-788
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel fluorescence sensing platform for ultrasensitive detection of S1 nuclease activity has been constructed based on MnO2 nanosheets and FAM labeled single-stranded DNA (FAM-ssDNA). In this system, MnO2 nanosheets were found to have different adsorbent ability toward ssDNA and mono- or oligonucleotide fragments. FAM-ssDNA could adsorb on MnO2 nanosheets and resulted in significant fluorescence quenching through fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), while mono- or oligonucleotide fragments could not adsorb on MnO2 nanosheets and still retained strong fluorescence emission. With the addition of S1 nuclease, FAM-ssDNA was cleaved into mono- or oligonucleotide fragments, which were not able to adsorb on MnO2 nanosheets and the fluorescence signal was never quenched. The different fluorescence intensity allowed for examination of S1 nuclease activity. The developed method can detect S1 nuclease activity in the range of 0 – 20 U mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.05 U mL−1. Benefits of the system include less time-consuming processes and more simple design compared to other endonuclease assays. Satisfactory performance for S1 nuclease in complex samples has been successfully demonstrated with the system. The developed assay could potentially provide a new platform in bioimaging and clinical diagnosis. View full abstractDownload PDF (1093K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1093K) -
Si-qin-gao-wa HAN, Lin BAO, Mei-Ling ZHANG, Xiang LIN, Wu-Li-Ji HASIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 789-792
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDiazepam injection was detected based on a droplet surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) platform, which overcomes the disadvantages of the poor uniformity and time-consuming sample treatment process of the conventional “drop and dry” detection strategy. The Raman peak positions of diazepam injection were determined and identified, they are mainly located in the 689, 1002, 1170 and 1598 cm−1, etc. Different concentrations of diazepam injection were detected. It was found that the intensity of 1002 cm−1 increases linearly with concentration in the range from 0.05 to 10 μg/mL and the linear correlation coefficient is 0.988. The limit of detection can reach 0.05 μg/mL. The SERS method is easy, fast and efficient. The results are accurate and reliable. It has favorable application potential in the detection of diazepam injection. View full abstractDownload PDF (806K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (806K) -
Yan WANG, Bin-Bin HUANG, Wan-Lin DAI, Bin XU, Tian-Liang WU, Jia-Ping ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 793-799
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA sensitive capsaicin sensor was constructed based on a poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) functionalized graphite modified screen printed electrode (PSS-Grp/SPE) in this study. The PSS-Grp and poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) functionalized graphite (PDDA-Grp) were easily synthesized by interacting Grp with PSS and PDDA through sonication, and resulted in negative and with positive charges on the surface, respectively. The prepared PSS-Grp and PDDA-Grp were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy (UV-vis). The electrochemical performance of PSS-Grp in a 50 μM capsaicin solution presented a current density of 33 μA cm−2, which was much higher than the PDDA-Grp of 1.5 μA cm−2. Our study showed that capsaicin could interact better with strong negative charges on the PSS-Grp/SPE surface to give a higher electrochemical response. The direct electrochemical sensing of capsaicin was achieved at PSS-Grp/SPE using differential pulse stripping voltammetry (DPSV) under the optimized conditions. View full abstractDownload PDF (2354K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2354K) -
Trisna K. SARI, Jiye JIN, Rahmiana ZEIN, Edison MUNAFArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 801-806
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV) for the determination of trace amounts of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) at a graphite/styrene-acrylonitrile (Graphite-SAN) copolymer composite electrode is described. This method involves a preconcentration step whereby the trace Cr(VI) was cathodically reduced to Cr(III) on an electrode surface in an acetate buffer (pH 5), followed by an anodic stripping technique with a square-wave voltammetric mode. It has been shown that the analytical sensitivity is significantly improved at the Graphite-SAN copolymer composite electrode in comparison with the conventional glassy carbon electrode, due to the strong interaction between Cr(III) and the nitrile end group of the SAN copolymer. The SWASV response was characterized with respect to the pH, deposition potential, possible interferences, etc. Under the optimal conditions, the stripping peak height linearly increased with the concentration of Cr(VI) in a range from 0 to 150 ng mL−1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.997, and a detection limit of 4.2 ng mL−1 was achieved based on signal-to-noise ratio of about 3. The Graphite-SAN composite electrode exhibited some interesting advantages, such as high mechanical rigid, easy surface renewable, higher sensitivity and better peak resolution in comparison with the results at conventional glassy carbon electrodes. They have been applied to the determination of Cr(VI) in real water samples with satisfactory recoveries.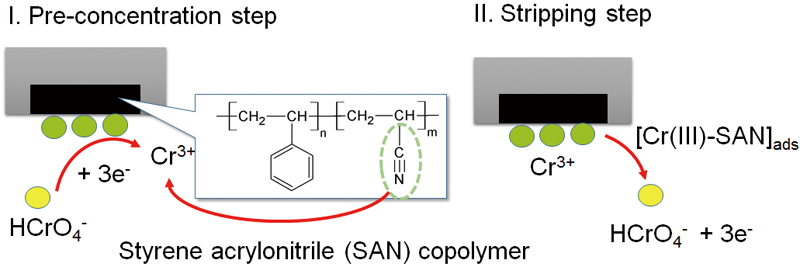 View full abstractDownload PDF (999K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (999K) -
Nil OZBEK, Gulcin Torunoglu TURAN, Bahire Filiz SENKAL, Suleyman AKMANArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 807-811
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, at first the synthesis of 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate-ethylene glycole dimethacrylate co-polymer beads and its modification with tris(2-aminoethyl) amine is described. Characterization of the polymer was done by FTIR and SEM. The functional co-polymer was filled in a disposable pipet tip and tightly connected to a 50-mL syringe for the separation and the enrichment of lead and cadmium prior to their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The sample and then the eluate were subsequently drawn and discharged to retain and desorb lead and cadmium by means of the syringe, respectively. Both analytes were quantitatively retained at pH 4 and eluted using 3.0 mol L−1 of HNO3 at flow rates of approximately 10 mL min−1. Under the optimum conditions, the enrichment factors of up to 50-fold both elements could be obtained by drawing and discharging 250 mL (5 × 50 mL) of the sample, and then 5 mL of the eluent. The recoveries were >90%. The limits of detection (3σ; N = 10 of blank) for Pb and Cd were 0.0034 and 0.0016 mg L−1 for a 50-fold enrichment, respectively. The analyte concentrations in a certified waste water reference agreed within the certified values in the 95% confidence range. View full abstractDownload PDF (647K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (647K) -
Tomoya IWATA, Hirohisa NAGATANI, Toshiyuki OSAKAIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 813-819
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe fluorescence behaviors of potential-sensitive dyes including anionic DiBAC4(3) (denoted by dye A), DiSBAC2(3) (dye B), and zwitterionic di-4-ANEPPS (dye C) were studied in oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions. In this study, the equilibrium Galvani potential difference (ΔOWφeq) of the O/W-emulsion droplets was controlled by changing the ratio of the concentrations of electrolytes added to the O (=1,2-dichloroethane) and W phases. When using an adequate combination of the dyes, i.e., B and C, we could observe that the ratio of their fluorescence peak intensities was changed from 1.08 to 1.38, depending on the change of (ΔOWφeq from 26 to 73 mV. It is desirable to apply this method to study the potential-dependent ion or electron-transfer reactions occurring at vesicles or liposomes, and also to biomembranes. View full abstractDownload PDF (1241K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1241K) -
Young-Min KIM, Jae Woo KIM, Hye Mi MOON, Min-Jin LEE, Akihiko HOSAKA, ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 821-824
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAnalysis of a residual solvent in polymeric materials has become an important issue due to the increased regulations and standards for its use. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) is a solvent widely used in many industries and restricted as one of the chemicals under EU REACH regulations due to its potential harmful effects. In this study, thermal desorption–gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (TD-GC/MS) is applied for the quantitative analysis of NMP with the use of a polymer-coated sample cup. By using the polymer-coated sample cup, the vaporization of NMP was prevented during waiting time before TD-GC/MS analysis. The calibration curve for the TD method showed good linearity (correlation coefficient, r2 = 0.9998) and precision values (below 5.3% RSD). NMP recovery rates in different polymer matrices (PS, PMMA and PVC) were in the range of 98.8 to 106.6% with RSD values below 5.0%. The quantification result (600 mg NMP/kg PVC) for the blind NMP carrying sample in a PVC matrix by TD-GC/MS was higher than that (532 mg NMP/kg PVC) by solvent extraction-GC/MS method. View full abstractDownload PDF (502K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (502K) -
Hisashi SATOH, Yuji MIYAZAKI, Shou TANIUCHI, Mamoru OSHIKI, Rathnayake ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 825-830
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn ionophore-doped sensing membrane phosphate (PO4) microsensor based on bis(dibromophenylstannyl)methane (Bis microsensor) is described. The Bis microsensor showed a Nernstian response. The response of the Bis microsensor was log-linear down to a monohydrogen phosphate ion (HPO42−) concentration of 0.5 μM (corresponding to 1.0 μM of orthophosphate at pH 7.2), whereas the detection limit of PO4-microsensors based on trialkyl/aryltin chloride was 50 μM of HPO42−. The Bis microsensor showed excellent selectivity for HPO42− against nitrite, nitrate, chloride, bicarbonate and sulfate, as compared with PO4 microsensors based on trialkyl/aryltin chloride. Dissolved oxygen, which is known to interfere with the response of a previously developed cobalt-based potentiometric solid-state PO4 microsensor, had no effect on the response of the ionophore-doped sensing membrane-type microsensors described herein. Only OH− (i.e., pH) interfered with the ionophore-doped sensing membrane-type microsensors. View full abstractDownload PDF (663K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (663K) -
M. Lutfi FIRDAUS, Ikka FITRIANI, Santhy WYANTUTI, Yeni W. HARTATI, Ren ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 831-837
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNovel green-chemistry synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) is introduced as a low-cost, rapid and easy-to-use analytical method for mercury ion detection. Aqueous fruit extract of water apple (Syzygium aqueum) was used for the first time as bioreductant to synthesize stable AgNPs. The prepared AgNPs have a yellowish-brown color with a surface plasmon resonance peak at 420 nm. The addition of Hg(II) ions then changes the AgNPs color to colorless. The color change was in proportion to the concentration of Hg(II) ions. The presence of other metal ions in the system was also evaluated. The proposed method shows good selectivity and sensitivity towards Hg(II) ions. Using UV-visible spectrophotometry, the detection limit of the developed method was 8.5 × 10−7 M. The proposed method has been successfully applied for determination of Hg(II) ions in tap and lake water samples with precision better than 5%. View full abstractDownload PDF (1593K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1593K) -
Hong-qi XIA, Yuki KITAZUMI, Osamu SHIRAI, Kenji KANOArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 839-844
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNon-catalytic direct electron transfer (DET) signal of Compound I of horseradish peroxidase (POD) was first detected at 0.7 V on POD/carbon nanotube mixture-modified electrodes. Excellent performance of DET-type bioelectrocatalysis was achieved with POD immobilized with glutaraldehyde on Ketjen Black (KB)-modified electrodes for H2O2 reduction with an onset potential of 0.65 V (vs. Ag | AgCl | sat. KCl) without any electrode surface modification. The POD-immobilized KB electrode was found to be suitable for detecting H2O2 with a low detection limit (0.1 μM at S/N = 3) at –0.1 V. By co-immobilizing glucose oxidase (GOD) and POD on the KB-modified electrode, a bienzyme electrode was constructed to couple the oxidase reaction of GOD with the DET-type bioelectrocatalytic reduction of H2O2 by POD. The amperometric detection of glucose was performed with a high sensitivity (0.33 ± 0.01 μA cm−2 μM−1) and a low detection limit (2 μM at S/N = 3). View full abstractDownload PDF (810K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (810K) -
Yukina MATSUI, Katsumi HAMAMOTO, Yuki KITAZUMI, Osamu SHIRAI, Kenji KA ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 845-851
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe performed numerical simulations on an extremely fast, mediated, electron transfer-type bioelectrocatalytic reaction using a microband electrode. The simulations under fast-enzyme-kinetics conditions predicted that the decrement of the current density by increaseing the microband thickness would effectively improve the upper limit of detection. These predictions were accurate for an ultrathin-ring with thickness of 100 nm and gold leaf with thickness of 10 μm electrodes, acting as novel amperometric glucose sensors with FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase. The gold leaf electrode provided pseudo-steady-state currents which were proportional to the glucose concentration up to a concentration of 20 times higher than the mediator concentration. View full abstractDownload PDF (1109K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1109K) -
Kosuke HARA, Taka-aki YANO, Kota SUZUKI, Masaaki HIRAYAMA, Tomohiro HA ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 853-858
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialLocal crystalline structures of LiCoO2 nanothin film cathodes in a lithium ion battery have been spectroscopically elucidated through confocal Raman imaging analysis at high spatial resolution of several hundred nanometers. A significant difference in the crystalline structure is found between the nanometric thin films and bulk powders. Thermally induced local decomposition of LiCoO2 into an impurity phase on the films has also been revealed along with the mechanism of the temperature-triggered decomposition process. Moreover, frequency-based Raman imaging enables us to locally probe spatial separation between stoichiometric (LiCoO2) and non-stoichiometric (Li1-xCoO2, 0 < x < 1) crystal phases on the thin films. Such local crystalline analysis is a promising approach to provide new insights into the degradation mechanism of lithium-ion batteries, which would result in improving the performance of thin film-based lithium ion batteries. View full abstractDownload PDF (1069K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1069K)
Notes
-
Yuya HASEGAWA, Yasutada SUZUKI, Susumu KAWAKUBOArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 859-862
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn on-site determination method for trace arsenic has been developed by collecting it as molybdenum blue (MB) in the presence of tetradecyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride on a mixed cellulose ester membrane filter and by measuring reflection absorbance (RA) of MB on the filter using a laboratory-made palm-top size reflection-absorbance colorimeter with a red light-emitting diode. The value of RA was proportional to the amount of arsenic up to 0.5 μg with a detection limit of 0.01 μg. The proposed method was successfully applied to soil extract and hot-spring water samples.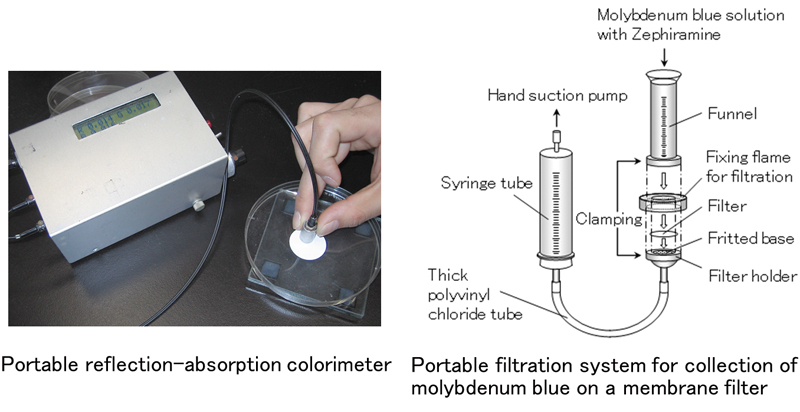 View full abstractDownload PDF (604K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (604K) -
Maya KAMAO, Yoshihisa HIROTA, Yoshitomo SUHARA, Naoko TSUGAWA, Kimie N ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 863-867
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis study aimed to develop a menadione (MD) determination method employing liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) using a pseudo multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) technique, wherein two quadrupoles are used to monitor the same ion. Detection limits of 40 and 2 pg were obtained for MD and its deuterium-labeled form, respectively, whereas MD intra- and inter-assay coefficient of variation values were determined as 5.4 – 8.2%, with the corresponding recoveries equaling 90.5 – 109.6%. The developed method enables determination of MD in urine, plasma, cell extract, and culture media, demonstrating that pseudo multiple reaction monitoring can achieve quantification of compounds forming no suitable product ions, such as MD. View full abstractDownload PDF (1291K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1291K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017 Volume 33 Issue 7 Pages 869
Published: July 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (3080K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|