- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 361
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 361
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
Editor's pickCutting-edge contributions from invited poster presentations providing significant research works in the fifth International Symposium for Medicinal Sciences (ISMS) in the 139th Chiba annual meeting in 2019 are assembled for the Current Topics section in this issue of the Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.
PDF形式でダウンロード (150K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 362-365
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (576K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 366-374
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (831K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 375-383
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1050K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 384-392
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/02PDF形式でダウンロード (690K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 393-398
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/05PDF形式でダウンロード (790K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 399-403
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (674K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 404-408
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (492K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 409-417
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/24PDF形式でダウンロード (2994K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 418-423
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/20PDF形式でダウンロード (563K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 424-431
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/14PDF形式でダウンロード (2062K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 432-439
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/26PDF形式でダウンロード (1868K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 440-449
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2536K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 450-457
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 450-457
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
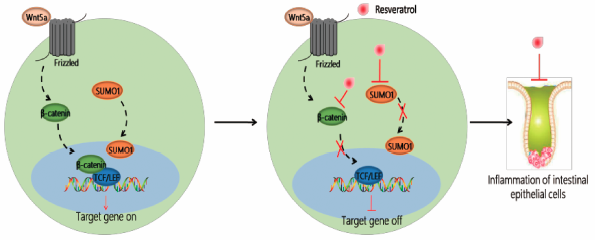
Editor's pickMao et al. found that resveratrol can significantly inhibit the expression of SUMO1. They demonstrate that resveratrol alleviates inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in mice by inhibiting the expression of SUMO1 molecule, and by modulating the activation of wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Clinical analysis also proves that the expression of SUMO1 and β-catenin molecules increased with the worsening of the disease, which also provides a new method for clinical diagnosis and treatment of IBD.
PDF形式でダウンロード (11179K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 458-462
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 458-462
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/18Editor's pickEdoxaban is an oral anticoagulant used for preventing and treating stroke or systemic embolism. Bleeding is the most common complication associated with anticoagulants. In particular, severe bleeding is assumed to be related to mortality in patients treated with anticoagulation therapy. However, few studies have examined the risk factors for bleeding in Japanese patients receiving edoxaban. The article by Takase et al. revealed that a low baseline hemoglobin level was a significant risk factor for major and clinically relevant bleeding in Japanese patients receiving edoxaban.
PDF形式でダウンロード (315K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 463-473
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2404K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 474-479
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (430K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 480-487
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1963K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 488-492
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (324K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 493-502
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1584K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 503-508
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1768K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 509-515
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2758K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 516-525
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 516-525
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/21Editor's pickThe article by Tanaka et al. proposed a novel mechanism of radioresistance and candidate for use as radiosensitizers in radiation therapy of melanoma. A2B receptor was involved in radioresistance via DNA damage response in B16 cells. A2B receptor antagonist enhances tumor growth-inhibitory effect by gamma-ray and shows radiosensitizing effect in vivo. These findings proposed that A2B receptor contributes to radioresistance, and could be a new target for the development of agents to increase the efficacy of radiotherapy.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1750K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 526-532
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2468K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 533-539
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (4740K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 540-545
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 540-545
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/27Editor's pickCD81 is important for regulating biological processes such as B cell receptor signaling and B cell differentiation. However, little is known about degradation mechanism of CD81. Hosokawa et al. demonstrated that CD81 on the cell surface is degraded by lysosome via K63- and K29-linked poly-ubiquitination. The poly-ubiquitinated CD81 is translocated from the cell surface into endosomes and is degraded by lysosomes. This is the first report showing that the lysosomal degradation of CD81 requires poly-ubiquitination and clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2973K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 546-549
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (483K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 550-553
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (429K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 554-557
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/01/07PDF形式でダウンロード (430K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 558-564
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2548K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 565-568
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/12/18PDF形式でダウンロード (481K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 3 号 p. 569-573
発行日: 2020/03/01
公開日: 2020/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (646K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|