- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 747-761
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 747-761
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Editor's pickThis review describes the chronotherapeutic strategies based on molecular clock system of chronopharmacokinetic, chronopharmacodynamic and cancer chronopathological factors in the xenobiotic detoxification, transporter, receptor and molecular target. Chronotherapeutic strategies focus on the monitoring of rhythm, overcoming rhythm disruption, manipulation of rhythm, chrono-therapeutic drug monitoring, chrono-drug delivery system and chrono-drug discovery. The screening for small molecules targeting the clock genes is now in progress to stabilize circadian phase and enhance circadian amplitude, thereby consolidating and coordinating circadian organization,. The academic research along with a combination of chemical and biological information is essential to promote the research and development of new modality drug discovery such as clock genes.
Download PDF (7963K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 762-770
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (790K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 771-779
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Advance online publication: March 17, 2021Download PDF (5176K) Full view HTML -
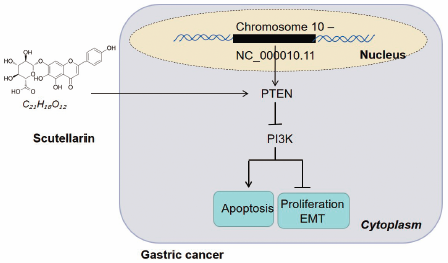
Scutellarin Inhibits the Growth and EMT of Gastric Cancer Cells through Regulating PTEN/PI3K Pathway2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 780-788
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (2963K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 789-797
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 789-797
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
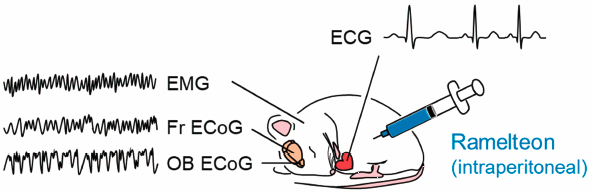
Editor's pickRamelteon, a melatonin receptor agonist, has a sleep-promoting effect by modulating sleep-wake rhythms. To examine the effect of ramelteon on cardiac function, authors simultaneously recorded electrocardiograms, electromyograms, and electrocorticograms in the frontal cortex and the olfactory bulb of unrestrained rats treated with ramelteon. Authors demonstrated that during non-REM sleep, heartrate variability was maintained by ramelteon treatment. Analysis of the electromyograms confirmed that neither microarousal during non-REM sleep nor the occupancy of phasic periods during REM sleep was altered by ramelteon. Thus, authors propose a remedial effect of ramelteon on cardiac activity by keeping the heartrate variability.
Download PDF (2262K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 798-803
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (1104K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 804-815
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 804-815
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Editor's pickNumerous studies have confirmed that the sFlt1/PlGF ratio is a good predictor of the signs and symptoms of Pre-Eclampsia. However, its usefulness is limited to diagnosis after 20 weeks of gestation. To address this issue, in the present study the authors used plasma samples collected at gestational weeks 14-24 weeks from subjects who were subsequently diagnosed as Pre-Eclampsia. By employing SWATH-based proteomics for comprehensive discovery and SRM-based target quantification using in silico peptide selection criteria for validation, the authors were able to identify a 3-protein combination biomarker (AFAM, FINC and SHBG) that can predict effectively during gestational weeks 14-24 whether pregnant women would subsequently develop Pre-Eclampsia.
Download PDF (1549K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 816-821
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (700K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 822-829
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (1781K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 830-837
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 830-837
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Editor's pickCisplatin is an effective anti-cancer drug. A serious major side effect of cisplatin is an acute kidney injury. The authors demonstrated that panduratin A, a bioactive flavonoid, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibition of cell apoptosis. The renoprotective effect of panduratin A is mediated by reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting ERK1/2 and caspase 3 activations. The protective effect of panduratin A did not impair the anti-cancer activity of cisplatin in cancer cells. Panduratin A might be a good candidate agent to alleviate cisplatin’s nephrotoxicity.
Download PDF (3705K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 838-843
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (930K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 844-852
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (2178K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 853-860
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (1590K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 861-868
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Advance online publication: April 08, 2021Download PDF (2300K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 869-874
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 869-874
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Editor's pickInfluenza causes nosocomial outbreaks in healthcare settings. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for healthcare workers is one of the effective strategies for preventing outbreaks of influenza. However, PEP adherence in healthcare workers is rarely analysed. This retrospective questionnaire-based study showed that the adherence to PEP among healthcare workers was low, especially among physicians, and that the primary factor for preventing PEP adherence was misguided self-decision that continuation of PEP was unnecessary. This study emphasized that medication education should be provided to ensure treatment compliance and maximize the therapeutic benefits of PEP when PEP is administered.
Download PDF (573K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 875-883
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (1713K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 884-887
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (1556K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 6 Pages 888-893
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Download PDF (912K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|