-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1498-1505Suppression of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IL-1β Gene Expression by High-Molecular-Weight Adiponectin in RAW264.7 Macrophages Read moreEditor's pick
Although most previous studies in this area used recombinant adiponectin, herein, the author used native high-molecular-weight (HMW) adiponectin purified from human plasma, which is considered the most active form of circulating adiponectin. The current results clearly demonstrate that native HMW adiponectin preferentially inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1β expression but not tumor necrosis factor-α expression by inhibiting the Akt-C/EBPβ inflammatory signaling pathway in macrophages. Furthermore, HMW adiponectin preconditioning is essential for achieving the anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin. Thus, these findings highlight the regulatory mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory function of adiponectin.
-
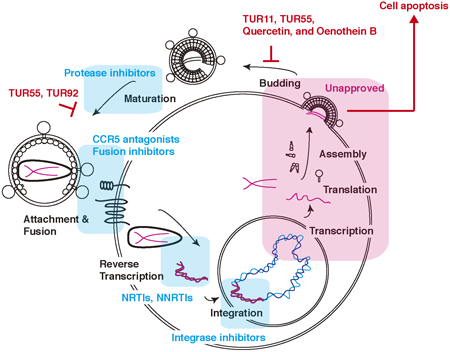
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1535-1547Turkish Plants, Including Quercetin and Oenothein B, Inhibit the HIV-1 Release and Accelerate Cell Apoptosis Read moreEditor's pick
Authors suggest that plant extracts, including quercetin and oenothein B, reduce the amount of virus in the cell supernatants and induce cytotoxicity in HIV-1-infected T cells but not HTLV-1-infected T cells. The large amount of oenothein B were detected in Onagraceae. Thus, the plant extracts might block the HIV-1 release and kill the HIV-1-infected cells. Consequently, the plant extracts from the plant library of Turkey might be suitable candidates to develop novel anti-retroviral drugs that target the late phase of the HIV-1 life cycle.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1583-1591Endothelium-Independent Vasorelaxant Effects of Sudachitin and Demethoxysudachitin, Polymethoxyflavone from the Peel of Citrus sudachi on Isolated Rat Aorta Read moreEditor's pick
Citrus sudachi is a popular fruit in Tokushima Prefecture, Japan, and its peel contains high amounts of polymethoxyflavones with the most abundant being sudachitin (SDC) followed by demethoxysudachitin (DMSDC). The effects of SDC and DMSDC on the cardiovascular system have not been investigated. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of SDC and DMSDC on vascular tonus and to investigate mechanism of action of SDC using aorta preparations isolated from rats. The results demonstrated that SDC and DMSDC cause endothelial-independent relaxation, and that the mechanism of vasorelaxation by SDC is associated with the enhancement of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways.
-
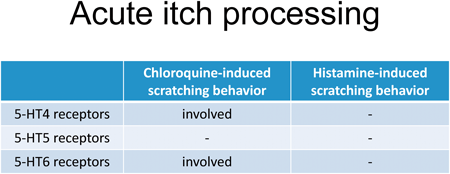
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1601-1608Differential Contribution of 5-HT4, 5-HT5, and 5-HT6 Receptors to Acute Pruriceptive Processing Induced by Chloroquine and Histamine in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Antidepressants, such as milnacipran, a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, and mirtazapine, a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant attenuate the induction of scratching events by chloroquine (CQ) or histamine. However, it remains unclear whether serotonin or noradrenaline is involved in attenuating effects of these antidepressants. Miyahara and colleagues show that 5-HT4 and 5-HT6 receptors are involved in the amelioration of CQ-induced scratches, but not histamine-induced scratches, engendered by the antidepressants. These findings suggest that 5-HT4, 5-HT5, and 5-HT6 receptors play differential roles in acute pruriceptive processing after administration of CQ or histamine.
-
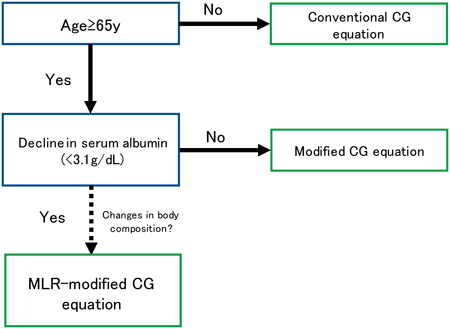
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1609-1618Effects of Body Composition on Renal Function Estimates in Older Patients Read moreEditor's pick
The authors validated the modified Cockcroft-Gault equation, developed previously for aged-oriented cohort, in a newly obtained dataset and found that good renal function estimates were obtained for patients exceeding 65 years of age. Using statistical analysis, estimates for a subset of patients in this cohort were identified to be inadequate and this deviation from estimates was attributed to a decreased albumin level. A multivariate linear regression estimating equation was developed for this region by incorporating body composition parameters. A flow diagram was proposed to select an appropriate renal function estimating equation particularly for older patients.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 1365-1370Comparison of Incidence of Hyponatremia between Linezolid and Vancomycin by Propensity Score Matching Analysis Read moreEditor's pick
Linezolid (LZD) has been reported to cause severe hyponatremia, but infection per se is also a potential cause of hyponatremia by increasing vasopressin secretion. The author compared the incidence and risk of developing hyponatremia between LZD and vancomycin (VCM) using propensity score analysis to demonstrate that hyponatremia is associated with LZD rather than infection. The analysis indicated a significantly higher incidence and 3.7-fold higher risk of developing hyponatremia associated with LZD than with VCM, regardless of patient background characteristics. Regularly monitoring serum sodium and infusing sodium promptly when the level decreases would be required when administering LZD.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 1421-1426Therapeutic Effects of Albumin-Fused BMP7 on 2 Experimental Models of Liver Fibrosis Read moreEditor's pick
Despite the fact that liver fibrosis is an intractable disease with a poor prognosis, effective therapeutic agents are not available. The authors focused on bone morphogenetic factor 7 (BMP7) that inhibits TGF-β signaling. They prepared a long-acting albumin-fused BMP7 (HSA-BMP7) and evaluated its inhibitory effect on liver fibrosis. In the mice with bile duct ligation, HSA-BMP7 administration suppressed the infiltration of inflammatory cells and fibrosis area around the bile duct. In the carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis mice, HSA-BMP7 administration also decreased the hepatic fibrosis. HSA-BMP7 has the potential for serving as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
-
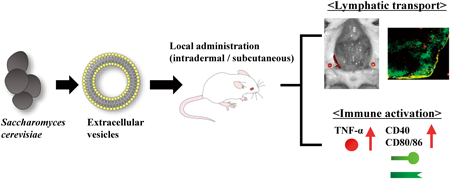
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 1427-1434Lymphatic Transport and Immune Activation Effect by Locally Administered Extracellular Vesicles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae as Biocompatible Vaccine Adjuvants Read moreEditor's pick
The yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an eukaryotic organism that secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs). The authors characterized the biodistribution of locally (intradermally and subcutaneously) administered Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived EVs (S-EVs) and the EV-mediated immune responses to evaluate their potential use as biocompatible vaccine adjuvants. Locally administered S-EVs were delivered to the lymph nodes, mainly reaching the B-cell zone. Furthermore, S-EVs increased the expression of cytokine and costimulatory molecules. Especially, subcutaneously injected S-EVs showed potent adjuvanticity, indicating that subcutaneous administration of S-EVs is the desirable approach for achieving effective immune stimulation. These findings will facilitate the development of novel EV-based immunotherapies.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 1435-1443Osteogenic Effects of KY-054, a Novel Coumarin Derivative on Femur Cortical Bone in Ovariectomized Female Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Osteoporosis is caused by an imbalance between osteoblast bone formation and osteoclast bone resorption, thus is treated with oral and parenteral bone-resorption inhibitors and parenteral bone-formation promoting drugs. The authors demonstrated that KY-054, a novel coumarin derivative, has osteoblast differentiation-promoting activities in mouse and rat mesenchymal stem cells, increasing metaphyseal and diaphyseal cortical bone volume and bone strength parameters without reducing medullary volume by micro-computed tomography in ovariectomized rats. KY-054 is a potential orally active osteogenic anti-osteoporosis drug candidate with a unique mode of action by acceleration of osteoblast differentiation.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 1461-1467Fabrication of 3D-Printed Contact Lens Composed of Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate for Controlled Release of Azithromycin Read moreEditor's pick
Authors fabricated 3D-printed contact lenses composed of polyethylene glycol diacrylate and an antibiotic, azithromycin. The drug-loaded contact lenses were prepared using vat photopolymerization 3D printer, and the effect of second curing on 3D printed object was investigated. The mechanical strength and drug release of contact lens formulation were evaluated in the present study. The 3D printed contact lenses exhibited antimicrobial effect in vitro. The current results suggested that the preparation of antibiotic-loaded contact lenses by 3D printing provides useful information for manufacture of ophthalmic device and personalized therapy.
-
Editor's pick
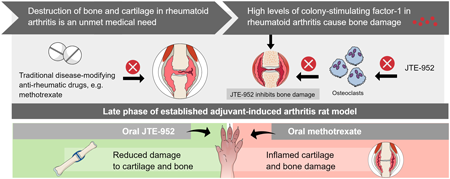
Effectively preventing the structural destruction of joints, particularly bone and cartilage, which progresses due to resistance to conventional anti-inflammatory drugs, is one of the unmet medical needs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study, the authors investigated the therapeutic effects of JTE-952, a novel colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF1R) kinase inhibitor, on methotrexate-resistant joint destruction using a rat model of RA, adjuvant-induced arthritis. Blocking CSF1/CSF1R signaling with JTE-952 did not suppress paw swelling under inflammatory conditions, but it did suppress the destruction of joint structural components, including bone and cartilage, in inflamed joints and may improve subsequent joint dysfunction.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 1240-1248Metallothionein Gene Deficiency Facilitates the Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts into Slow-Twitch Myotubes Read moreEditor's pick
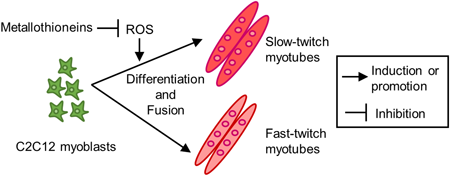
Fast-to-slow fiber transition in skeletal muscle occurs during aging and has been implicated in muscle atrophy in sarcopenia, but the mechanism is unclear. Authors showed that metallothionein 1 and 2 gene knockout (MTKO) using the CRISPR-Cas9 system promoted to myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts, which was accompanied by an increased number of slow-twitch myotubes. The increased slow-type myotubes in MTKO cells was inhibited by an antioxidant N-acetylcysteine, suggesting that MT may be involved in specification of skeletal muscle fiber-type due to its antioxidant capacity. This study may help to elucidate the mechanisms of age-related muscle weakness.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 1296-1303Descriptive Study on a Nationwide Exploratory Questionnaire Survey of Emergency Contraceptive Pills and Their Sexual History and Knowledge in Japan Read moreEditor's pick
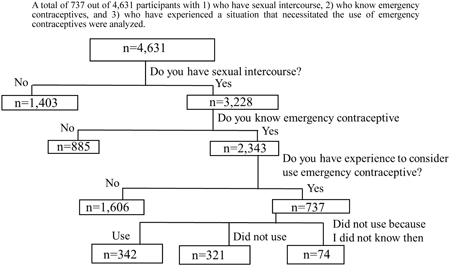
In Japan, the move towards non-prescription emergency contraceptives is under discussion. A nation-wide survey of 4,631 women conducted by the authors revealed that nearly half of them lacked accurate knowledge about emergency contraceptives. Total of 43.6% of women with previous experience needing emergency contraceptives chose not to use them voluntarily. To address this, the authors emphasize the importance of comprehensive sex education, and promoting understanding of emergency contraceptives among women in Japan.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 1310-1315Non-invasive Microneedle Application Increases Ceramide and Natural Moisturizing Factors in a Reconstructed Human Skin Model Read moreEditor's pick
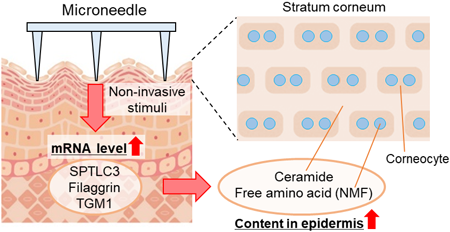
Microneedles are microscopic needle structures with lengths of several hundred micrometers, and have attracted attention as one way to improve skin barrier and moisturizing functions as cosmetic product. However, conventional microneedles are thought to work by penetrating the stratum corneum, which carries the risk of side effects. Therefore, in this study, the authors applied microneedles non-invasively without penetrating the stratum corneum and investigated their effects on the skin. The results showed that microneedles can improve skin barrier and moisturizing functions even when applied non-invasively. This study provides valuable insights for the development of new cosmetic techniques using microneedles.
-
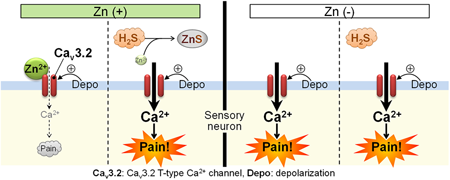
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 1343-1346Dietary Zinc Deficiency Induces Cav3.2-Dependent Nociceptive Hypersensitivity in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
The activity of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels expressed in the sensory neurons is reduced by physiological concentrations of zinc. Sulfides including hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gasotransmitter, enhance the channel activity by removing zinc from Cav3.2, leading to the increased pain sensitivity. Dietary zinc deficiency causes Cav3.2-dependent mechanical allodynia in mice. Exogenously applied sulfides produce Cav3.2-dependent allodynia in the mice fed with normal diet, but do not affect the already developed allodynia in the mice fed with zinc-deficient diet. Thus, the authors suggest that the enhanced Cav3.2 activity participates in the development of pathological pain associated with zinc deficiency.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 8 Pages 1049-1056Inhibitors of the Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Can Ameliorate Bortezomib-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Read moreEditor's pick
Bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy (BIPN), an adverse effect of chemotherapy, can cause patients to suffer from neuropathic pain and lead to drug withdrawal. The authors attempted to explore effective therapeutic targets for BIPN by combining real-world data analysis with in vivo experiments. In the analysis of self-reported adverse event data, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors reduced the incidence of peripheral neuropathy in bortezomib-treated patients. In bortezomib-treated mice, mTOR inhibitors or an inhibitor of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1), a downstream molecule of mTOR complex 1, showed transient analgesic effects. These results suggest that S6K1 may be a therapeutic target for BIPN.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 8 Pages 1065-1071Pharmacist–Urologist Collaborative Management for Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma Receiving Pazopanib Monotherapy Read moreEditor's pick
The authors established an ambulatory care pharmacy practice that enables pharmacist–urologist collaboration for the treatment of patients with urologic cancer taking oral anti-cancer medications. In this manuscript, the authors sought to investigate the usefulness of pharmacist-urologist collaboration, considering the potential confounding factors, for patients with renal cell carcinoma treating pazopanib monotherapy. The results showed that the time to pazopanib discontinuation was significantly prolonged after the implementation of collaborative management by analyzing the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model. These results clearly indicated that the effectiveness of pharmacist-led team care in pharmacotherapies.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 8 Pages 1098-1104Development of Functional Chimeric Nanoparticles by Membrane Fusion of Small Extracellular Vesicles and Drug-Encapsulated Liposomes Read moreEditor's pick
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) have been of interest as a drug delivery system (DDS) for various disease treatments, as they possess some advantages in drug delivery. However, certain issues in drug encapsulation, such as low encapsulation efficiency and poor reproducibility, are needed to be addressed. Herein, a new drug encapsulation approach has been developed which utilizes membrane fusion of sEVs and drug encapsulated liposomes composed of phosphatidylserine via the calcium fusion method. The fused-nanoparticles achieved efficient doxorubicin encapsulation as well as increased cellular uptake of liposomes. The present findings are expected to be applied for encapsulation of other therapeutic modalities into sEVs and development of sEV-like nanoparticles.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 8 Pages 1128-1132Effect of a Single Dose of Oxaliplatin on the Induction of Peripheral Neuropathy in a Rat Model: An in Vivo Electrophysiological Study Read moreEditor's pick
The anticancer drug oxaliplatin (OXA) is associated with peripheral neuropathy as a side effect accompanied by mechanical and cold allodynia. Authors aimed to record and compare the firing of neurons in the deep and superficial layers of the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) in rats treated with a single dose of OXA. Authors found the comparison of neuronal firing frequencies carried out in the present study of a CIPN rat model treated with a single dose of OXA revealed that pain pathology is reflected more strongly by the superficial than by the deeper layer of the SDH.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 7 Pages 907-913Decreased Analgesic Effect of Tramadol in Japanese Patients with CYP2D6 Intermediate Metabolizers after Orthopedic Surgery Read moreEditor's pick
Pharmacogenomic (PGx) testing can predict therapeutic responses or adverse effects based on genetic variants and is expected to be the preemptive precision medicine for patient management. Tramadol is metabolized by CYP2D6 to an active metabolite, which in turn acts as an analgesic. From the retrospective cohort study in Japanese patients with postoperative pain after orthopedic arthroscopic surgery, the authors demonstrated that the analgesic effect in the early postoperative period was depended on CYP2D6 gene polymorphism. These results suggested the clinical utility of preemptive treatment based on the PGx test, which can consider dose adjustment or drug change in advance.