-
Editor's pick
An administration plan for vancomycin in bedridden elderly patients has not been established. This study evaluated the prediction accuracy of the Bayesian-derived area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of vancomycin using creatinine-based equations for estimating kidney function in such patients. In this paper, the authors showed that the Bayesian approach using the estimated creatinine clearance calculated by substituting the serum creatinine level + 0.2 into the Cockcroft-Gault equation has the highest prediction accuracy for the AUC in bedridden elderly patients. These results may contribute to improving the efficacy and safety of vancomycin in such patients.
-
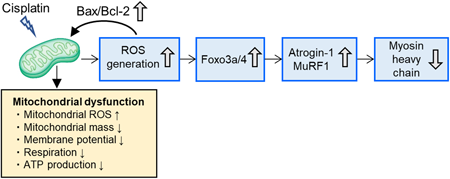
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 6 Pages 780-792Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Cisplatin-Induced Myotube Atrophy Read moreEditor's pick
Recently, chemotherapy-induced secondary sarcopenia has emerged as an important clinical issue; however, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, the authors focused on the possible involvement of mitochondrial disturbances in cisplatin-induced muscle atrophy using a cellular model. They concluded that mitochondrial dysfunction and the resultant generation of excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS), but not energy disruption, play a central role in cisplatin-induced C2C12 myotube atrophy. These results suggest that mitochondrial protection and/or ROS scavenging may be promising strategies for preventing muscle atrophy associated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 576-582The Effects of Sacran, a Sulfated Polysaccharide, on Gut Microbiota Using Chronic Kidney Disease Model Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Sacran, a type of new sulfated polysaccharide, is a biomaterial with excellent water solubility and safety, and is expected to be used in pharmaceuticals of the future. In the present study, sacran suppressed oxidative stress and inhibited the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Sacran also had a multifaceted effect on the progression of CKD by altering the mix of intestinal microflora as a prebiotic in addition to the above effects. Thus, sacran is expected to have an effective nephroprotective effect especially when oxidative stress initially appears at the early stage of renal failure.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 614-624PI3K/AKT1 Signaling Pathway Mediates Sinomenine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Apoptosis: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study Read moreEditor's pick
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most frequent cancers. Sinomenine (SIN) is a compound derived from Sinomenium acutum. Authors’ investigations have found that SIN suppressed SK-Hep-1 cells’ proliferation, enhanced the collapse of potential of the mitochondrial membrane, triggered cell apoptosis, down-regulated PI3K p85α, AKT1, BCL-2, Pro-Caspase 9, Pro-Caspase 3 expressions, and up-regulated Cleaved Caspase 9 and Cleaved Caspase 3 expressions. In addition, insulin-like growth factor-1 could reverse the high apoptosis of SK-Hep-1 cells induced by SIN. Therefore, authors revealed that inhibition of PI3K/AKT1 signaling cascade by SIN induced hepatocellular carcinoma cells apoptosis.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 635-642Chronic Volume Overload Caused by Abdominal Aorto-Venocaval Shunt Provides Arrhythmogenic Substrates in the Rat Atrium Read moreEditor's pick
Atrial enlargement often provides arrhythmogenic substrates, leading to the induction of atrial fibrillation. The authors examined the anatomical, molecular biological, and electrophysiological characteristics of remodeled atria in rats with 8- and 12-week of aorto-venocaval shunt (AVS). It is noteworthy that marked electrophysiological changes were detected only in the AVS-12W rat despite obvious increments in atrial and ventricular tissue weights and altered gene expression in the AVS-8W rat, which suggests that the electrical remodeling observed in the atrium is preceded by structural remodeling after AVS surgery. These findings provide important information on experimental evidence regarding the timing of generation of arrhythmogenic substrate in the atria.
-
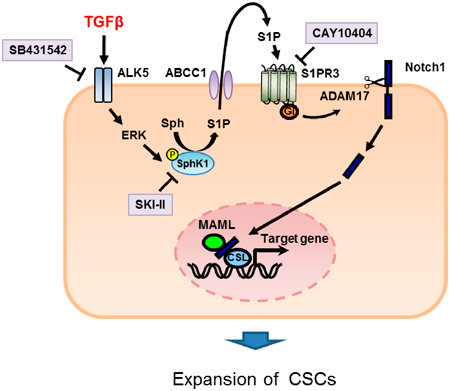
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 649-658Transforming Growth Factor Beta Promotes the Expansion of Cancer Stem Cells via S1PR3 by Ligand-Independent Notch Activation Read moreEditor's pick
Breast cancer are originated from cancer stem cells (CSCs), which contribute to drug resistance and recurrence. The authors examined the effects of transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) signaling on proliferation of breast CSCs. TGFβ induced the proliferation of CSCs via phosphorylation of sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) via a Smad-independent manner and subsequent production of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). Moreover, Notch pathway was involved in the S1P response via S1P receptor 3. These results suggest that TGFβ-SphK1-S1P-Notch signaling pathway is a novel therapeutic target in breast cancer.
-
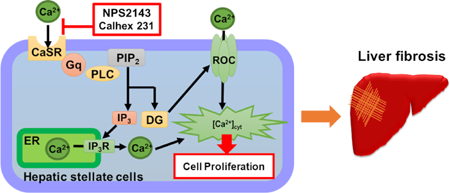
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 664-667Ca2+ Signaling and Proliferation via Ca2+-Sensing Receptors in Human Hepatic Stellate LX-2 Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are a key player in the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis including cirrhosis. The development of hepatic fibrosis is associated with enhanced calcium signaling in HSCs. However, the regulatory mechanism of calcium signaling in HSCs is largely unknown. In addition, there is no specific therapeutic drug for hepatic fibrosis currently. This report reveals that calcium-sensing receptors are expressed in human HSCs and function in the regulation of calcium signaling and cell proliferation. These findings help to elucidate the molecular mechanism of hepatic fibrosis and develop a potential therapeutic target for hepatic fibrosis.
-
Editor's pick
Organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) and multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 and 2-K (MATE1/2-K) are critically involved in renal secretion, pharmacokinetics (PK), and toxicity of cationic drugs. Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) at OCT2 and/or MATE1/2-K have been shown to result in clinical impacts on PK, therapeutic efficacy and are probably involved in the renal accumulation of drugs. In this work, an overview of OCT2 and MATE1/2-K is presented. The primary structure, membrane location, functional properties, and clinical impact of OCT2 and MATE1/2-K are described. In addition, clinical aspects of DDIs in OCT2 and MATE1/2-K and their involvement in drug nephrotoxicity are compiled.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 4 Pages 394-396Simultaneous Screening of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants Using High-Resolution Melting Analysis Read moreEditor's pick
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant has multiple receptor-binding domain (RBD) mutations. Some of these mutations can increase infectivity and reduce antibody affinity. In this study, the authors successfully developed a rapid screening assay to simultaneously identify RBD mutations in the Omicron and Delta variants using high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis. As this HRM-based genotyping assay does not require sequence-specific probes, unlike the TaqMan probe assay, it is easy to perform and cost-effective. This simple method may contribute to the rapid identification and prevention of the potential widespread infection of SARS-CoV-2 variants.
-
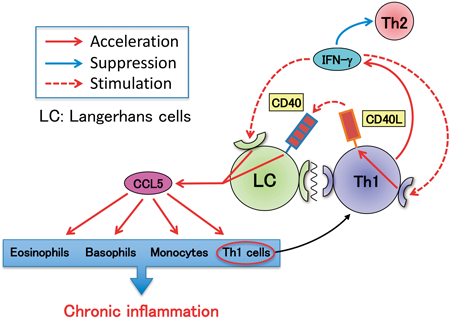
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 4 Pages 491-496Influence of the Th1 Cytokine Environment on CCL5 Production from Langerhans Cells Read moreEditor's pick
It has long been known that the chronic skin lesions of atopic dermatitis (AD) patients show increased amounts of Th1 cells in addition to Th2 cells. However, it has remained unclear whether these Th1 cells actually participate in the exacerbation of skin inflammation. In this paper, the authors showed that Langerhans cells (LCs) augmented CCL5 production by responding to Th1 cytokine, IFN-g while presenting antigen to Th cells, and that this augmentation of CCL5 production would contribute to infiltration of eosinophils and other Th1 cells into skin lesions, followed by expansion of chronic inflammation in the skin.
-
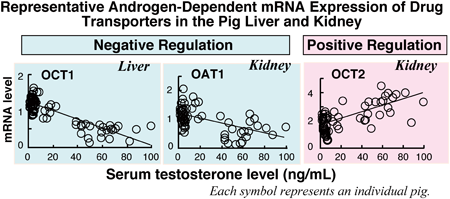
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 4 Pages 508-516Sex, Organ, and Breed Differences in the mRNA Expression of Drug Transporters in the Liver and Kidney of Pigs Read moreEditor's pick
Breed and organ-dependent sex differences in the mRNA amounts of several drug transporters in the liver and kidney were found in pigs. In Meishan pigs, the sex differences in the amounts of hepatic MDR1, OATP1B3, and OCT1 mRNAs and in those of renal MRP2, OAT1, OAT2, OAT3, and OCT2 mRNAs were found. However, no such sex differences were observed in Landrace pigs. Furthermore, additional experiments using castrated and/or testosterone propionate-treated pigs suggested that breed-dependent sex differences in the gene expression of drug transporters, especially hepatic OCT1 and renal OAT1, were primarily due to the difference in serum testosterone concentration.
-
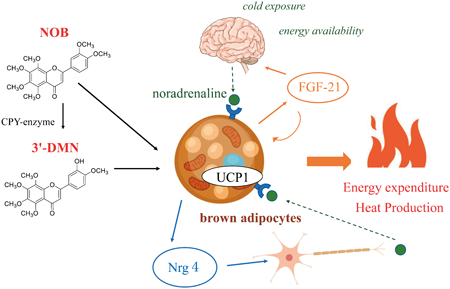
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 4 Pages 528-533Nobiletin and 3′-Demethyl Nobiletin Activate Brown Adipocytes upon β-Adrenergic Stimulation Read moreEditor's pick
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) specifically regulates energy expenditure via heat production. Hence, BAT may have the potential to combat obesity in humans. The activity of BAT is directly regulated by β-adrenergic stimulation. In this study, the authors report the effects of Nobiletin (NOB), a natural polymethoxylated flavone present in citrus fruits, on BAT activation using β-adrenergic agonists. NOB can enhance the thermogenic functions of brown adipocytes and promote brown adipokine secretion due to enhanced β-adrenergic stimulation. NOB could be a promising candidate for activating BAT under β-adrenergic stimulation and preventing the onset of obesity.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 3 Pages 323-332Infliximab Treatment Persistence among Japanese Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Retrospective Japanese Claims Data Study Read moreEditor's pick
This report reveals that the persistence rates of infliximab therapy differed across chronic inflammatory diseases in real-world practice. Although infliximab has contributed to the treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and rheumatoid arthritis, loss of response to long-term therapy has been a major problem. The authors described the persistence rates of infliximab therapy using the Japanese claims data to estimate its long-term effectiveness. Factors associated with the longer persistence were identified in each disease group. These results could facilitate the proper use of infliximab for persistent successful treatment.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 3 Pages 339-353Betulin Attenuates TGF-β1- and PGE2-Mediated Inhibition of NK Cell Activity to Suppress Tumor Progression and Metastasis in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
This study reveals that a natural compound, betulin, inhibits the growth of B16 melanoma by enhancing natural killer cell activity through attenuating transforming growth factor (TGF)-b1- and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-induced immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. No report has shown such compounds that target TGF-b1- and PGE2-induced immunosuppressive activities so far. Additionally, it is intriguing that the mechanism-of-action of betulin differs from that of TGF-b1 type I receptor kinase inhibitors. Targeting TGF-b1 activity is a promising strategy for cancer therapy. Findings of this study provide new insight to develop drugs for immune checkpoint therapy in an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 3 Pages 354-359Activation of Host Immune Cells by Probiotic-Derived Extracellular Vesicles via TLR2-Mediated Signaling Pathways Read moreEditor's pick
Live microorganisms with positive effects on the host are known as probiotics. Probiotics secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) that activate immune response. The authors investigated the involvement of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and its downstream signaling of immune cells in cytokines production elicited by EVs from probiotics. TLR2 is a key molecule in EV-mediated immune activation. Furthermore, JNK/MAPK as well as NF-κB signaling pathways play important roles in cytokines production from EV-treated immune cells. These findings offer a promising perspective for the understanding of the host biological function induced by probiotic-derived EVs, which is helpful for developing an EV-based immunotherapeutic system.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 3 Pages 360-363Fosphenytoin Alleviates Herpes Simplex Virus Infection-Induced Provoked and Spontaneous Pain-Like Behaviors in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Spontaneous pain in acute herpes zoster (HZ) is severe, autonomous and inescapable, which makes the patient very uncomfortable. In this study, the authors demonstrated that intravenous injection of fosphenytoin (fPHT), a water-soluble prodrug of phenytoin, suppressed spontaneous pain-related behavior in mice model of acute HZ induced by cutaneous infection with herpes simplex virus type-1. The suppressive effects were more potent than diclofenac or pregabalin. Intravenous fPHT may become a viable option for an acute HZ pain, especially for spontaneous pain.
-
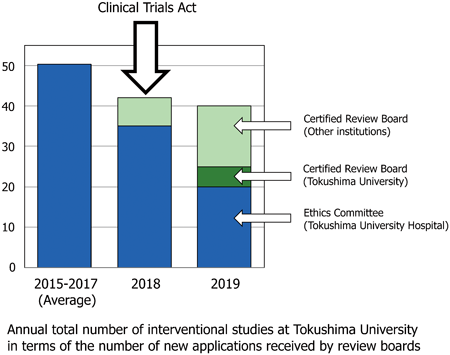
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 3 Pages 374-377Trends in Investigator-Initiated Clinical Studies at a University Hospital after Enforcement of the 2018 Clinical Trials Act in Japan Read moreEditor's pick
The Clinical Trials Act was enforced in 2018 with the aim of ensuring public trust in clinical research. The authors examined the activity of interventional research before and after the enforcement of the law, using the number of applications to the ethics committees as an indicator at a university hospital with a certified review board. It was found that the number of applications tended to decrease with the enforcement of the law. Possible way to promote clinical studies in the new Clinical Trials Act era should be further examined.
-
Editor's pick
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) from tumor cells has multiple roles, including tumor invasion, tumor proliferation, and tumor immunity. In this paper, the author focused on the role of TGF-β against tumor immunity and summarized the potential of anti-tumor immunity by using anti-TGF-β antibody or chemical components with immune checkpoint inhibitors and chimeric antigen receptor cells. Furthermore, the molecular mechanisms by which TGF-β controlled tumor immunity were described in this review.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 2 Pages 162-168RSK-Mediated Non-canonical Activation of EphA2 by Tamoxifen Read moreEditor's pick
The authors have previously demonstrated that non-canonical phosphorylation of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase is catalyzed by ribosomal S6 kinases (RSKs), downstream kinases of the MEK-ERK pathway, and promotes migratory potentials of cancer cells. The article by Yonehara et al. demonstrated that tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator used to treat breast cancers, induces the rapid phosphorylation of EphA2 by RSK in an ER-independent manner. In addition, tamoxifen significantly enhances the migration of ER-negative breast cancer cells possibly via the activation of RSK-EphA2 axis. These results provide novel insights into the tumor-promoting activity of tamoxifen.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 2 Pages 194-199Effective Anticancer Therapy by Combination of Nanoparticles Encapsulating Chemotherapeutic Agents and Weak Electric Current Read moreEditor's pick
Ameliorating the intratumor delivery of nanoparticles (NPs) is challenging. This study applied weak electric current (WEC) onto the tumor surface to improve the intratumor delivery of I.V. administrated Doxorubicin (DOX) encapsulated NPs. Interestingly, WEC markedly increased NPs accumulation into the tumor. Consequently, WEC/DOX-NPs combination significantly suppressed tumor growth compared to DOX-NPs alone. Mechanistically, WEC-mediated opening of intercellular adhesion in tumor is suggested to employ the increased intratumor accumulation of DOX-NPs utilizing enhanced permeability and retention effect. Therefore, a combined application of WEC and NPs containing chemotherapeutic agents will be useful for effective anticancer therapy.