
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yayoi Kawano, Ayano Imamura, Tomoe Nakamura, Mio Akaishi, Mitsutoshi S ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1659-1665
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
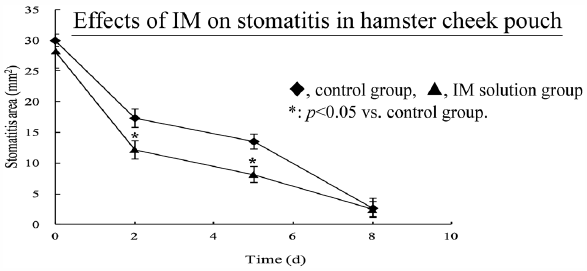
Advance online publication: September 15, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe stomatitis caused by anticancer agents and radiation therapy deteriorates patient QOL, potentially causing eating disorders as a result of pain. Although gargling and ointments can be used in the treatment of stomatitis, patients must spit out mouthwash after use, while ointment application requires a finger to be inserted into the oral cavity. In contrast, sprays eliminate these potential compliance problems. Therefore, we developed a stomatitis spray that remains on the oral mucosa. It has been reported that irsogladine maleate (IM) is effective against stomatitis via oral administration. IM is water insoluble; thus, it was dissolved with various cyclodextrins (CDs). Furthermore, we examined combination with gum ghatti (GG), a mucoadhesive polymer. The interaction between mucin and GG was examined by Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation monitoring. We found that GG exhibited mucoadhesion. Furthermore, we examined the healing effects of IM on stomatitis in a stomatitis model hamster. We found that stomatitis healed after direct application of IM. However, the model used in this experiment is not based on stomatitis caused by anticancer agents. Further study is therefore necessary.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1225K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1225K) Full view HTML -
Gan Siaw Chin, Hiroaki Todo, Wesam Radhi Kadhum, Mariani Abdul Hamid, ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1666-1673
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
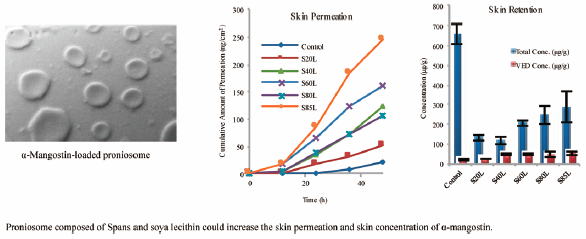
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe current investigation evaluated the potential of proniosome as a carrier to enhance skin permeation and skin retention of a highly lipophilic compound, α-mangostin. α-Mangostin proniosomes were prepared using the coacervation phase seperation method. Upon hydration, α-mangostin loaded niosomes were characterized for size, polydispersity index (PDI), entrapment efficiency (EE) and ζ-potential. The in vitro permeation experiments with dermis-split Yucatan Micropig (YMP) skin revealed that proniosomes composed of Spans, soya lecithin and cholesterol were able to enhance the skin permeation of α-mangostin with a factor range from 1.8- to 8.0-fold as compared to the control suspension. Furthermore, incorporation of soya lecithin in the proniosomal formulation significantly enhanced the viable epidermis/dermis (VED) concentration of α-mangostin. All the proniosomal formulations (except for S20L) had significantly (p<0.05) enhanced deposition of α-mangostin in the VED layer with a factor range from 2.5- to 2.9-fold as compared to the control suspension. Since addition of Spans and soya lecithin in water improved the solubility of α-mangostin, this would be related to the enhancement of skin permeation and skin concentration of α-mangostin. The choice of non-ionic surfactant in proniosomes is an important factor governing the skin permeation and skin retention of α-mangostin. These results suggested that proniosomes can be utilized as a carrier for highly lipophilic compound like α-mangostin for topical application.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3789K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3789K) Full view HTML -
Ken-ichi Izutsu, Hiroyuki Yoshida, Hiroko Shibata, Yukihiro Goda2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1674-1680
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe objective of this study was to elucidate the mixing state of proteins and amino acid excipients concentrated in the amorphous non-ice region of frozen solutions. Thermal analysis of frozen aqueous solutions was performed in heating scans before and after a heat treatment. Frozen aqueous solutions containing a protein (e.g., recombinant human albumin, gelatin) or a polysaccharide (dextran) and an amino acid excipient (e.g., L-arginine, L-arginine hydrochloride, L-arginine monophosphate, sodium L-glutamate) at varied mass ratios showed single or double Tg′ (glass transition temperature of maximally freeze-concentrated solutes). Some mixture frozen solutions rich in the polymers maintained the single Tg′ of the freeze-concentrated amorphous solute–mixture phase. In contrast, amino acid-rich mixture frozen solutions revealed two Tg′s that suggested transition of concentrated non-crystalline solute–mixture phase and excipient-dominant phase. Post-freeze heat treatment induced splitting of the Tg′ in some intermediate mass ratio mixture solutions. The mixing state of proteins and amino acids varied depending on their structure, salt types, mass ratio, composition of co-solutes (e.g., NaCl) and thermal history. Information on the varied mixing states should be valuable for the rational use of amino acid excipients in lyophilized protein pharmaceuticals.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (843K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (843K) Full view HTML -
Yusuke Amino, Yoshinobu Takino, Megumi Kaneko, Fumie Ookura, Mai Yamam ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1681-1691
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
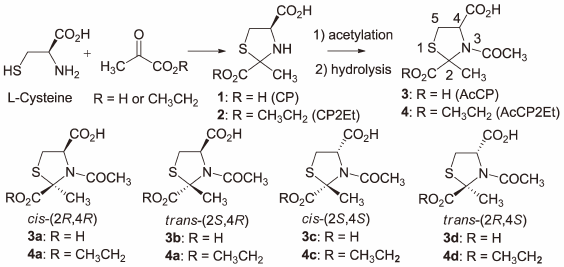
Supplementary materialIn the pathway of melanin biosynthesis, cysteine (Cys) is utilized for the synthesis of pheomelanin. Accordingly, Cys is considered to suppress the formation of brown–black eumelanin. Although attempts have been made to utilize Cys and its derivatives as skin-whitening agents, their instability and odor hinders their application as a cosmetic agent. Herein, N-acetyl-2-methylthiazolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid ethyl ester (AcCP2Et) was proposed as a candidate for a stable and prolonged-release derivative of Cys to inhibit dopachrome formation after its degradation in melanocytes. It was synthesized by acetylation of 2-methylthiazolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid 2-ethyl ester (CP2Et), the condensation derivative of Cys and ethyl pyruvate. AcCP2Et suppressed melanogenesis in melanocytes in vitro, was stable in phosphate buffer at 70°C for five days, and exhibited far less odor than CP2Et. Therefore, AcCP2Et was validated to be a useful deriative of Cys for application as a skin-whitening agent. AcCP2Et comprises four stereoisomers; thus characterization of each stereoisomer was required. The stereochemistry of AcCP2Et was confirmed via a single-crystal X-ray structure analysis of N-acetyl-2-methylthiazolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid (AcCP) derived from AcCP2Et. In the synthesis of AcCP2Et, the acetylation of CP2Et proceeded with epimerization at C4 to give trans-isomers when excess acetyl chloride and an organic amine was used, whereas it proceeded while retaining the original (R) configuration at C4 to give the cis- and trans-isomer when an equivalent of acetyl chloride with an inorganic base was used. These results indicate that the formation of an intermolecular mixed acid anhydride is responsible for the isomerization at the C4 asymmetric center.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1194K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1194K) Full view HTML -
 Shunichi Utsumi, Tomohiro Nakamura, Yasuko Obata, Noboru Ohta, Kozo Ta ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1692-1697
Shunichi Utsumi, Tomohiro Nakamura, Yasuko Obata, Noboru Ohta, Kozo Ta ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1692-1697
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPermeation enhancers are required to deliver drugs through the skin efficiently and maintain effective blood concentrations. Studies of the barrier function of the stratum corneum using l-menthol, a monocyclic monoterpene widely used in medicines and foods, have revealed an interaction between characteristic intercellular lipid structures in the stratum corneum and permeation enhancers. The variety of permeation enhancers that can be used to contribute to transdermal delivery systems beyond l-menthol is increasing. In this study, we focused on nerolidol and levulinic acid and investigated their influence on stratum corneum lipid structures. Nerolidol, a sesquiterpene, has been reported to enhance the permeation of various drugs. Levulinic acid is reported to enhance the permeability of buprenorphine and is used as a component of the buprenorphine® patch. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction and attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform IR spectroscopy measurements revealed that nerolidol disturbs the rigidly arranged lipid structure and increases lipid fluidity. Levulinic acid had a smaller effect on stratum corneum lipid structures, but did increase lipid fluidity when co-administered with nerolidol or heat. We found that nerolidol has an effect on stratum corneum lipids similar to that of l-menthol, and levulinic acid had an effect similar to that of oleic acid.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn this study, the authors focused on two permeation enhancers: nerolidol and levulinic acid to clarify the mechanism of action of permeation enhancers on lipids structures. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction revealed that nerolidol strongly affected the orthorhombic and hexagonal structures, whereas levulinic acid had little effect on the lateral packing structures.
Download PDF (848K) Full view HTML -
Yasunori Miyazaki, Kozo Takayama, Tomonobu Uchino, Yoshiyuki Kagawa2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1698-1706
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLScientific approaches for dispensation are important for the quality and efficacy of drug treatments. Therefore, for the dispensation of powdered medicines, we have developed a powder blending method using a planetary centrifugal mixer (PCM) to replace the empirical manual method involving a mortar and pestle. The aim of this study was to optimize the formulation of pharmaceutical diluents for dispensing powdered medicines, using PCM. The diluents, composed of powdered lactose, crystalline lactose, and corn starch were assigned to a {3,2}-Simplex Lattice design. Then, the designed diluents were blended with model powders, such as carbazochrome sodium sulfonate powder, rifampicin capsule contents, and crushed sulfasarazine tablets, at ratios of 1 : 4, 1 : 1, and 4 : 1 using PCM at 800 rpm for 60 s at a 20% filling rate. The mixtures were examined for content uniformity relative standard deviation (RSD) and flowability angle of repose (AOR). Response surface methodology was applied to optimize the formulation with the smallest RSD and AOR, and then the design space of desired diluents was estimated. On the basis of the design space, crystalline lactose, the mixture of lactose powder and crystalline lactose at a ratio of 1 : 4, and the mixture of corn starch and crystalline lactose at a ratio of 1 : 4, were suitable diluents for the powdered formulation, the content of the capsules, and the crushed tablets, respectively. The selected diluents were successfully applied to other model medicines showing a sufficient RSD and AOR. This technique could contribute to the development of scientific approaches for dispensation.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3734K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3734K) Full view HTML -
Phan Van Kiem, Le Canh Viet Cuong, Bui Huu Tai, Nguyen Xuan Nhiem, Hoa ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1707-1712
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
Advance online publication: September 29, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTwo new lignans (7S,7′R,8S,8′R)-3,3′-dimethoxy-7,7′-epoxylignan-4,4′,9-triol 4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (1) and 9-O-formylaviculin (2) together with other thirteen known secondary metabolites were isolated from the leaves of Antidesma hainanensis. Their chemical structures were determined using NMR, electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopic methods, and as well as by comparison with those reported in the literature. Neuro-inflammatory activity of isolated compounds was evaluated by their inhibition on nitric oxide (NO) production in activated BV2 microglial cells. At concentration of 40 µM, compounds 1–3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 14, and 15 exhibited inhibitory effects over 50%, suggesting that they could be potential candidate drugs for the cure of neuro-inflammation. In addition, compounds 1, 8, 14, and 15 significantly inhibited 16.23, 27.76, 21.23, and 29.44% NO production at diluted concentration as low as 2.5 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (606K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (606K) Full view HTML -
Ippei Suzuki, Hiroki Kubota, Takashi Ohtsuki, Chiye Tatebe, Atsuko Tad ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1713-1719
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
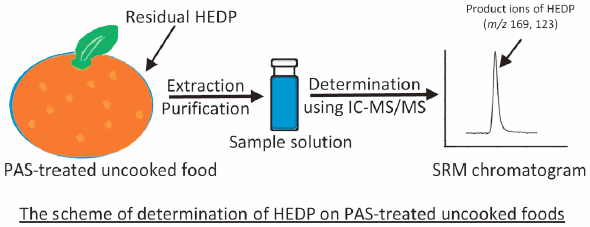
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA rapid, sensitive, and specific analytical method for the determination of 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP) on uncooked foods after treatment with a peracetic acid–based sanitizer (PAS) was developed. The method involves simple sample preparation steps and analysis using ion chromatography (IC) coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The quantification limits of HEDP on uncooked foods are 0.007 mg/kg for vegetables and fruits and 0.2 mg/kg for meats. The recovery and relative standard deviation (RSD) of HEDP analyses of uncooked foods ranged from 73.9 to 103.8% and 1.9 to 12.6%, respectively. The method’s accuracy and precision were evaluated by inter-day recovery tests. The recovery for all samples ranged from 93.6 to 101.2%, and the within-laboratory repeatability and reproducibility were evaluated based on RSD values, which were less than 6.9 and 11.5%, respectively. Analyses of PAS-treated fruits and vegetables using the developed method indicated levels of HEDP ranging from 0.008 to 0.351 mg/kg. Therefore, the results of the present study suggest that the proposed method is an accurate, precise, and reliable way to determine residual HEDP levels on PAS-treated uncooked foods.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (698K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (698K) Full view HTML -
Jennifer Chia Wee Fern, Hideya Nakamura, Satoru Watano2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1720-1725
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe aim of this study is to develop a novel milling system using supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) for the improvement of dissolution characteristics of water-poorly soluble drugs. SC-CO2 possesses high potential in the application of nanotechnology, due to the attractive properties of SC-CO2 fluid such as cheap, inert and non-polluting. In addition, SC-CO2 has density comparable to a liquid, viscosity similar to a gas, and high diffusion capacity. Most of all, carbon dioxide exists as gas in room temperature and pressure, which enables the removal of fluid instantaneously. In this study, a novel method of milling using SC-CO2 was proposed to produce fine-drug particles. SC-CO2 milling was conducted and its performance was compared with the ones by various milling methods such as jet milling, dry milling and wet milling. A comparison on the effect of each milling medium on its milling performance, drug size distribution, and particle morphology was conducted. Operating variables of the SC-CO2 milling system were also investigated to clarify the factors affecting the milling properties and to improve drug release characteristics of water-poorly soluble drugs.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1799K) Full view HTML -
Kazuhiro Higuchi, Hideki Hikita, Asumi Murayama, Daichi Yuri, Natsu Ko ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1726-1738
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLArg-Gly-Asp (RGD) mimics were synthesized and their anti-platelet activity was evaluated. A concise method was developed for the synthesis of the target compounds from dehydroepiandrosterone and Wieland–Miescher and Hajos–Parrish ketones, which are suitable for readily available platform. Among the synthesized compounds, the perhydronaphthalene framework with a 3-(4-piperidinyl)propoxyl structure 3e possessed the highest anti-aggregative activity. The IC50 values of 3e were 0.91 mM (ADP initiation) and 0.54 mM (collagen initiation).
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1047K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1047K) Full view HTML -
Katsuhiko Yamamoto, Taro Kojima, Masatoshi Karashima, Yukihiro Ikeda2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1739-1746
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
Advance online publication: October 12, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo judge the developability and analyze functional mechanism of co-amorphouses, we investigated the physicochemical properties of co-amorphouses and compare the properties with the co-crystals having the same drug and counters. Co-amorphous compounds are a novel approach to improve the physicochemical properties of drugs. A co-amorphous is in an amorphous solid state allowing non-ionic interactions between drug molecules and counter molecules. The co-amorphous compounds composed of itraconazole (ITZ) with the organic carboxyl acid, fumaric acid (FA) or L-tartaric acid (TA), were prepared by mechanical grinding. Potential interactions within ITZ-FA co-amorphous were assessed by Raman spectroscopy. ITZ-FA co-amorphous was not crystallized as the co-crystal or as a single ITZ crystal, suggesting that the amorphous state, like the amorphous solid dispersion, was physically stable and that ITZ-FA co-amorphous was also chemically stable. In contrast, no clear interactions were observed within ITZ-TA co-amorphous, and the co-amorphous was physically stable but chemically unstable. The solubility of the co-amorphous state was much higher than those of ITZ crystal and the co-crystals and was almost identical to that of amorphous ITZ. A co-amorphous compound like ITZ-FA co-amorphous might be feasible to implement in the development of solid drug products and bring some merits compared to the co-crystals, and the function is governed by the interaction between a drug and a counter. The co-amorphous approach may be an effective strategy for drug development and can contribute to the production of novel drugs with improved functions.
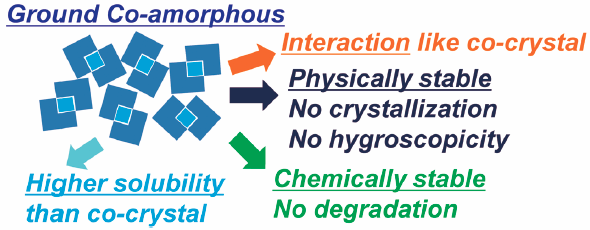 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1077K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1077K) Full view HTML -
Mostafa Mohammed Ghorab, Mansour Sulaiman Alsaid, Yassin Mohammed Niss ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1747-1754
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNovel sulfonamides 3–19 with a biologically active 3,4-dimethoxyphenyl moiety were designed and synthesized. The structures of the synthesized compounds were established using elemental analyses, IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR spectral data and mass spectroscopy. All the synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro anticancer activity against four cancer cell lines, namely human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2), human medulloblastoma (Daoy), human cervical cancer (HeLa), and human colon cancer (HT-29), by using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and dasatinib as the reference drug. Among the tested derivatives, compounds 4, 10, 16, and 19 showed good activity as cytotoxic agents. The most active derivatives were evaluated for their ability to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-2. Compounds Z-4-(3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-oxoprop-1-enylamino)-N-(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide 10 and Z-4-(3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-oxoprop-1-enylamino)-N-(1H-indazol-6-yl)-benzenesulfonamide 19 were more active as VEGFR-2 inhibitors than dasatinib. Molecular docking of the most active derivatives on the active site of VEGFR-2 revealed that compound 19 exhibited favorable and promising results.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1171K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1171K) Full view HTML -
Zi-Li Ren, Jing Zhang, Hai-dong Li, Ming-Jie Chu, Li-Song Zhang, Xiao- ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1755-1762
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
Advance online publication: October 01, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAcetylcholinesterase (AChE) is a key enzyme which present in the central nervous system of living organisms. Organophosphorus pesticides (OPs) that serve as insecticides are AChE inhibitors which have been used widely in agriculture. A series of novel OPs containing pyrazole moiety have been designed and synthesized. The biological evaluation indicated compound 4e appeared 81% larvicidal activity against Plutella xylostella at the concentration of 0.1 mg/L and the inhibition of AChE by compound 4e was distinctly enhanced with the increasing doses. Molecular docking of compound 4e into the three dimensional X-ray structure of the Drosophila melanogaster AChE (DmAChE, PDB code: 1QO9) was carried out utilizating the Discovery Studio (DS), the binding model revealed that the title structure was tightly embedded in the binding sites of DmAChE. Therefore, we suggest that compound 4e may serve as a novel AChE inhibitor that can be utilized as a new insecticidal drug.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1583K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1583K) Full view HTML
-
Hisanori Nambu, Naoki Ono, Wataru Hirota, Masahiro Fukumoto, Takayuki ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1763-1768
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn efficient and practical synthesis of 2′,3′-nonsubstituted cyclohexane-1,3-dione-2-spirocyclopropanes using a sulfonium salt was achieved. The reaction of 1,3-cyclohexanediones and (2-bromoethyl)diphenylsulfonium trifluoromethanesulfonate with powdered K2CO3 in EtOAc at room temperature (r.t.) provided the corresponding spirocyclopropanes in high yields. The synthetic method was also applied to 1,3-cyclopentanedione, 1,3-cycloheptanedione, 1,3-indanedione, acyclic 1,3-diones, ethyl acetoacetate, and Meldrum’s acid.
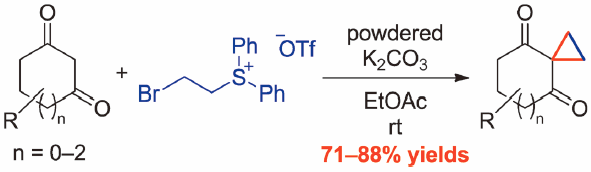 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (675K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (675K) Full view HTML -
Nobuko Mibu, Kazumi Yokomizo, Kana Murakami, Yurika Ono, Masato Ishima ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1769-1780
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe report the preparation of new tripodal receptor-type C3- and CS-symmetrical molecules constructed on a tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (TAEA) template. Both the anti-herpes simplex virus type 1 (anti-HSV-1) activity and cytotoxic activity of synthesized receptor-type derivatives were evaluated in order to find a characteristic structural feature for these bioactivities of compounds. Among the compounds of synthesized symmetrical TAEA-related derivatives, compound 13k showed high anti-HSV-1 activity (50% effective concentration (EC50)=16.7 µM) and low cytotoxicity (50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50)=>200 µM). The presence of a hydrogen bond donor proton in the molecule is thought to be an important structural factor for expressing potential anti-HSV-1 activities.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (942K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (942K) Full view HTML -
Takaaki Sakai, Shin-ichi Hirashima, Kosuke Nakashima, Chie Maeda, Akih ...2016 Volume 64 Issue 12 Pages 1781-1784
Published: December 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDiaminomethylenemalononitrile organocatalysts promote the asymmetric chlorination of simple cyclic β-keto esters such as methyl, ethyl, and benzyl esters of 1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indene-2-carboxylic acid. This affords the corresponding chiral α-chlorinated carbonyl products in excellent yields with high enantioselectivities.
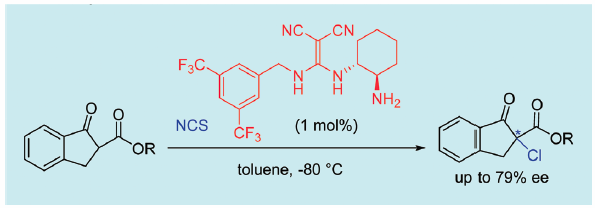 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (486K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (486K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|