
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Hidetoshi Arakawa2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1099-1112
Hidetoshi Arakawa2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1099-1112
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLOne important aspect of analytical chemistry research in the pharmaceutical sciences is the development of diagnostic and therapeutic analyses for disease, and the development of analytical methods for elucidating the causes of disease. I have been focusing on developing a highly sensitive method for measuring trace amounts of specific components in biological samples. This research can be roughly divided into three approaches: the use of immunoassays and DNA hybridization as methods utilizing specific affinities, the use of capillary electrophoresis as a highly sensitive and rapid separation method, and the use of chemiluminescence and bioluminescence reactions. The components being measured are compounds such as hormones, tumor markers, drugs, reactive oxygen species and genes in biological samples for the purpose of developing therapies for the prevention and treatment of diseases.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickAnalytical methods for disease diagnosis require high sensitivity and specific methods. For neonatal mass screening of congenital metabolic disorders, a 3 mm diameter disc of dried filter paper blood obtained from one drop of newborn blood is used, and one disc contains about 4 μL of blood. Diagnosis is performed by measuring hormones and genes in this disc. In hormone analysis, chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay was developed. In genetic analysis, pyrophosphate generated by PCR amplification reaction or DNA fragment as amplification product was analyzed by luciferase bioluminescence method and capillary electrophoresis, respectively. In addition, identification of reactive oxygen species generated from natural medicines and antianginal drugs and their physiological action mechanism are described.
PDF形式でダウンロード (6794K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Kwang-su Park, Kyungha Yoo, Mi Kyoung Kim, Woong Jung, Yoon Kyung Choi ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1113-1116
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
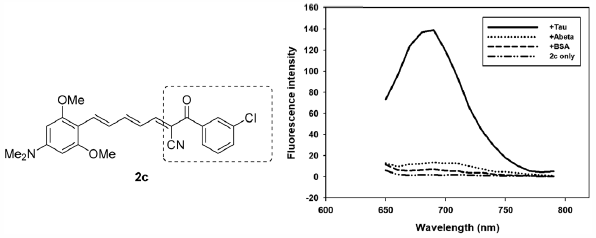
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDevelopment of a novel, tau-selective near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) probe was attempted by combining the 3,5-dimethoxy-N,N-dimethylaniline-4-yl moiety with an α-cyanoacetophenone via hexatrienyl π-linker. In particular, for structure–activity relationship study of the α-cyanoacetophenones, a chlorine substituent was introduced to the aromatic ring to give a series of compounds (2a–2d). Among those, compound 2c with meta-chloro aryl substituent was identified as a tau-selective NIRF probe: selectivity for tau over amyloid β (Aβ) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) was estimated to be 10.3 and 19.5 fold, respectively. The mechanism for tau-selectivity of 2c was found to be based on the specific recognition of the microenviroment of tau fibrils, which was endowed by its molecular rotor-like properties. The tau-selective NIRF probe 2c was also able to stain tau fibrils in tau-green fluorescent protein (GFP)-transgenic human neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y cells).
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (881K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (881K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Rafat Milad Mohareb, Nermeen Saeed Abbas, Rehab Ali Ibrahim2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1117-1131
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe reaction of cyclohexan-1,4-dione with elemental sulfur and any of the 2-cyano-N-arylacetamide derivatives 2a–c gave the 2-amino-4,5-dihydrobenzo[b]thiophen-6(7H)-one derivatives 3a–c to be used in some heterocyclization reactions. The multicomponent reactions of any of compounds 3a–c with aromatic aldehydes 6a–c and either of malononitrile or ethylcyanoacetate gave the 5,9-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-f]chromene derivatives 9a–r, respectively. The anti-proliferative evaluation of the newly synthesized compounds against the six cancer cell lines A549, HT-29, MKN-45, U87MG, SMMC-7721 and H460 showed that the nine compounds 3c, 5c, 9e, 9h, 9i, 9j, 9l, 9q, 11e and 13e with highest cytotoxcity. Toxicity of these compounds against shrimp larvae revealed that compounds 3c, 9j, 9q, and 13e showed no toxicity against the tested organisms. The c-Met kinase inhibition of the most potent compounds showed that compounds 9j, 9q, 10e, 12e and 13e have the highest activities. Compounds 9j, 9l, 9q and 11e showed high activity towards tyrosine kinases. Moreover, compounds 9j, 9q and 13e showed the highest inhibitor activity towards Pim-1 kinase.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (674K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (674K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Chitosan-Acrylic Polymeric Nanoparticles with Dynamic Covalent Bonds. Synthesis and Stimuli BehaviorHerman Palacio, Felipe Otálvaro, Luis Fernando Giraldo, Gilles Ponchel ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1132-1143
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/10/12ジャーナル フリー HTML
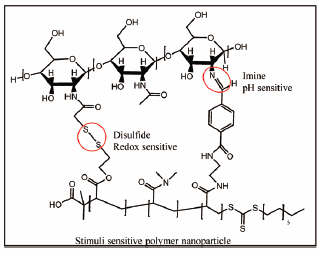
電子付録Drug delivery represents one of the most important research fields within the pharmaceutical industry. Different strategies are reported every day in a dynamic search for carriers with the ability to transport drugs across the body, avoiding or decreasing toxic issues and improving therapeutic activity. One of the most interesting strategies currently under research is the development of drug delivery systems sensitive to different stimuli, due to the high potential attributed to the selective delivery of the payload. In this work, a stimuli-sensitive nanocarrier was built with a bifunctional acrylic polymer, linked by imine and disulfide bonds to thiolate chitosan, the latter being a biopolymer widely known in the field of tissue engineering and drug delivery by its biodegradability and biocompatibility. These polymer nanoparticles were exposed to different changes in pH and redox potential, which are environments commonly found inside cancer cells. The results proof the ability of the nanoparticles to keep the original structure when either changes in pH or redox potential were applied individually. However, when both stimuli were applied simultaneously, a disassembly of the nanoparticles was evident. These special characteristics make these nanoparticles suitable nanocarriers with potential for the selective delivery of anticancer drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2377K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2377K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Ko Morishita, Yoshimichi Shoji, Shunkichi Tanaka, Masaki Fukui, Yuma I ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1144-1160
Ko Morishita, Yoshimichi Shoji, Shunkichi Tanaka, Masaki Fukui, Yuma I ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1144-1160
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLA novel series of benzoylsulfonamide derivatives were synthesized and biologically evaluated. Among them, 4-(biphenyl-4-ylmethylsulfanylmethyl)-N-(hexane-1-sulfonyl)benzamide (compound 18K) was identified as a protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitor with potent and selective inhibitory activity against PTP1B (IC50=0.25 µM). Compound 18K functioned as a non-competitive inhibitor and bound to the allosteric site of PTP1B. It also showed high oral absorption in mice (the maximum drug concentration (Cmax)=45.5 µM at 30 mg/kg), rats (Cmax=53.6 µM at 30 mg/kg), and beagles (Cmax=37.8 µM at 10 mg/kg), and significantly reduced plasma glucose levels at 30 mg/kg/d (per os (p.o.)) for one week with no side effects in db/db mice. In conclusion, the substituted benzoylsulfonamide was shown to be a novel scaffold of a non-competitive and allosteric PTP1B inhibitor, and compound 18K has potential as an efficacious and safe anti-diabetic drug as well as a useful tool for investigations of the physiological and pathophysiological effects of allosteric PTP1B inhibition.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickA novel series of benzoylsulfonamide derivatives were synthesized and biologically evaluated. Among them, compound 18K was shown to inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) activity potently and non-competitively (IC50=0.25 μM). Molecular dynamics simulation demonstrated that 18K binds to the allosteric site of PTP1B. Compound 18K showed high oral absorption in mice, rats, and beagles, and markedly reduced plasma glucose levels, TG levels, and HOMA values with no side effects at 30 mg/kg (p.o.) for one week in db/db mice. In conclusion, the substituted benzoylsulfonamide is a novel scaffold of non-competitive allosteric PTP1B inhibitors, and compound 18K is a promising candidate for an efficacious and safe anti-diabetic drug with anti-obesity effects.
PDF形式でダウンロード (3514K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Taiki Kohiki, Yusuke Nishikawa, Tsubasa Inokuma, Akira Shigenaga, Akir ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1161-1166
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLA synthetic platform for chlorpromazine (CPZ) oligomers, which could be generated via photo-reaction of CPZ, is essential to promote their biological and structural studies. In this paper, the first synthetic platform for CPZ oligomers is described. A photo-irradiation experiment of CPZ to confirm whether the structure of the CPZ dimer generated by the photo-irradiation was identical to that prepared by our synthetic method is also reported.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (619K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (619K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Chihiro Tsukano, Satoshi Suetsugu, Nobusuke Muto, Yoshiji Takemoto2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1167-1174
Chihiro Tsukano, Satoshi Suetsugu, Nobusuke Muto, Yoshiji Takemoto2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1167-1174
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Tetrahydrobiphenylene consists of cyclobutene fused with benzene and cyclohexene rings. In this paper, a direct method for synthesizing tetrahydrobiphenylenes based on a palladium (Pd)(0)-catalyzed C(sp2)–H functionalization was investigated. The developed method was applied to the synthesis of several tetrahydrobiphenylenes having an oxygen functionality at the ring juncture. The derivatization of a tetrahydrobiphenylene is also reported.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThis paper describes the development of a synthetic method for tetrahydrobiphenylenes and derivatives based on a palladium(0)-catalyzed C(sp2)−H functionalization. This is a new direct method for accessing partially hydrogenated biphenylenes. The derivatization of a tetrahydrobiphenylene is also reported.
PDF形式でダウンロード (712K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Shouichi Hosaka, Yuji Tokunaga2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1175-1178
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe powder properties of two 1,4-dihydropyridine type compounds, manidipine dihydrochloride (Man) and benidipine hydrochloride (Ben), which possess similar physicochemical properties, were compared through thermal and mechanical analyses. Man and Ben were compressed with lactose monohydrate (Lac) and magnesium stearate (Mgst) at different compression forces. As an index, we focused on the onset temperatures of Lac dehydration during thermal analysis and plotted them against compression forces to evaluate the differences in powder properties between Man and Ben. To discuss in detail, the Lac ratio was selected as a formulation factor and compression speed as a process factor, which would be influenced to the onset temperature or its profile. It could be represented that Man was more adherent than Ben through thermal analysis by changing these critical factors, which were consistent with the results obtained through mechanical analysis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (313K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (313K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tae In Kim, Bora Shin, Geum Jin Kim, Hyukjae Choi, Chong Soon Lee, Mi ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1179-1184
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/09/26ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Three new compounds, a sesquilignan (1) and two glucosylated phenylpropanoids (2, 3), and seven known compounds (4–10), were isolated from the fruits of Illicium verum HOOK. FIL. (Illiciaceae). The structures of 1–3 were determined based on one and two dimensional (1D- and 2D-) NMR data and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra analyses. Compounds 3, 5, 6, and 8–10 exhibited potent inhibitory activities against topoisomerase II with IC50 values of 54.6, 25.5, 17.9, 12.1, 0.3 and 1.0 µM, respectively, compared to etoposide, the positive control, with an IC50 of 43.8 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (742K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (742K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shin-ichi Hirashima, Takafumi Narushima, Masahiro Kawada, Kosuke Nakas ...2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1185-1190
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
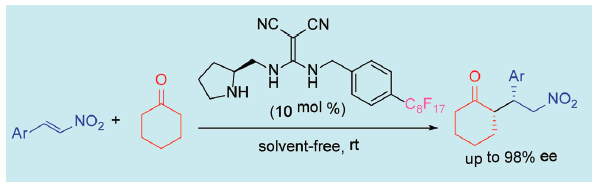
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe novel fluorous organocatalyst bearing a diaminomethylenemalononitrile motif is prepared. The fluorous organocatalyst efficiently promotes asymmetric conjugate additions of ketones to nitroalkenes and results in high yields of these addition products with excellent enantioselectivities under solvent-free conditions.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (517K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (517K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ryuichiro Suzuki, Shu Kan, Yoshiaki Sugita, Yoshiaki Shirataki2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1191-1194
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLA novel p-coumaroyl dimethyl malate (1) was isolated from the Pandanus amaryllifolius leaf in addition to three known analogs of p-coumaroyl dimethyl malate (2–4), and their structures were elucidated by analysis of the spectroscopic data. The p-coumaroyl malate derivatives were isolated as a mixture of E and Z isomers. To determine the cause of isomerization, the p-coumaroyl malate isolated in this study was synthesized. We concluded that the Z isomer might be an artifact generated from the E isomer through purification steps.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (401K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (401K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yuki Sakai, Yukiko Asakura, Mitsuhiro Morita, Takashi Takahashi2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1195-1198
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/09/27ジャーナル フリー HTMLHydroxy β-methyl fatty acid ethyl esters bearing different carbon chain lengths and varying hydroxyl group positions were successfully synthesized from symmetric diols. These fatty acid derivatives are useful intermediates of chemical probes for metabolic analyses of fatty acid.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (350K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (350K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tsutomu Warashina, Toshio Miyase2017 年 65 巻 12 号 p. 1199-1204
発行日: 2017/12/01
公開日: 2017/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The MeOH extract from dried whole Sedum bulbiferum MAKINO (Crassulaceae) plants yielded 34 compounds, including six new flavonoid glycosides and 28 known compounds. The structures of new compounds were established using NMR, Mass spectroscopic analysis and chemical evidence.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (560K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (560K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|