
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Katsuyoshi Matsunami2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 467-468
Katsuyoshi Matsunami2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 467-468
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEditor's pickPhotographs of tropical and subtropical plants of Madagascar, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia and Okinawa, Japan by courtesy of the authors. And some chemical structures of new compounds isolated from these plants are shown. Upper left: Macaranga tanarius and a prenylflavanone, Upper middle: Senna siamea, Upper right: Croton tonkinensis and an ent-Kaurane diterpene, Middle left: Rhinacanthus nasutus, Central middle: Baobab; Adansonia grandidieri, Middle right: Impatiens balsamina, Lower left: Artemisia roxburghiana and X-ray crystallography of a guaianolide, Lower middle: Justicia gendarusa, Lower right: Croton cascarilloides and a plausible biosynthetic pathway of new skeletons.
Download PDF (175K) Full view HTML
-
Yumin Dai, Yixi Liu, L. Harinantenaina Rakotondraibe2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 469-482
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMadagascar’s rain forests and tropical dry forests are home to numerous endemic plant species and the island is considered a biodiversity hotspot. About 80% of the Madagascan (Malagasy) population relies on traditional medicines that have been proven to contain a variety of biologically active compounds. In the search for bioactive compounds from Madagascan biodiversity, we accessed and collected most of the literature dealing with the isolation, structure elucidation, and biological activities of organic small molecules originating from Madagascan plants and marine organisms. Since we published the first review of this work in 2009 (Curr. Med. Chem., 17, 2010, Hou and Harinantenaina), the present paper covers the isolation, structures, and bioactivity of 182 new secondary metabolites isolated from Malagasy higher plants and marine organisms in the last seven years (2009–2017).
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1910K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1910K) Full view HTML -
Muhammad Ajmal Shah, James E. Keach, Pharkphoom Panichayupakaranant2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 483-492
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDiabetes mellitus is the seventh leading cause of death globally. Ninety percent of the diabetic population suffers from type-2 diabetes, which still needs an effective, safe and economical oral hypoglycemic therapy. Plants are rich sources of various therapeutic molecules. More than 400 medicinal plants of interesting phytochemical diversity have been reported for their antidiabetic potential. Naphthoquinones are a group of phytochemicals, which have a wide range of pharmacological potential, including antidiabetic activity. Naphthoquinones exert their antidiabetic effects through various mechanisms such as the inhibition of α-glucosidase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, increased glucose uptake in myocytes and adipocytes via glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) and GLUT2 translocations, enhanced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) ligand activity, and by normalizing carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes in the liver. Moreover, naphthoquinone inhibits adipogenesis by both upstream and downstream regulation to control obesity, which is one of the important risk factors for diabetes. Naturally occurring naphthoquinones, as well as their plant sources, are therefore of interest for exploring their antidiabetic potential. The present review aims to overview the antidiabetic potential of naphthoquinones and their plant resources in Thailand.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (995K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (995K) Full view HTML -
Phan Minh Giang, Hideaki Otsuka2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 493-505
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe study of natural products introduces interesting new bioorganic structures and potential candidates for the drug discovery stage in the development of innovative drugs. Vietnam enjoys a broad biodiversity of native plant species, microorganisms, marine organisms, and a long tradition of using herbal remedies. Thus, the study of medicinal plants in determining the basis of their efficacy and safety is an important task for modern researchers in Vietnam. The present review covers literature on new compounds elucidated from the systematic study of medicinal plants within some popular genera in Vietnam, as well as their significant biological activities.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1406K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1406K) Full view HTML -
Retno Widyowati, Mangestuti Agil2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 506-518
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis article reviews the chemical constituents and bioactivities of several Indonesian plants typically used in Jamu prescriptions in Indonesia. Jamu is Indonesia traditional medicine: it consists of either a single ingredient or a mixture of several medicinal plants. One plant family always used in Jamu is Zingiberaceae (ginger), such as Curcuma domestica/C. longa, C. xanthorrhizae, C. heyneana, C. zedoaria, C. aeruginosa, Zingiber aromaticum, Alpinia galanga. We also report other commonly used plant families such as Justicia gendarussa and Cassia siamea, whose activities have been extensively explored by our department.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1207K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1207K) Full view HTML -
Katsuyoshi Matsunami, Hideaki Otsuka2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 519-526
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe Okinawa Islands are a crescent-shaped archipelago and their natural forests hold a huge variety of unique subtropical plants with relatively high endemism. We have performed phytochemical study on Okinawan subtropical plants for many years. In this review, we describe our recent research progress on the isolation of new compounds and their various bioactivities.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2130K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2130K) Full view HTML
-
 Jiakun Long, Yang Wang, Chen Xu, Tingting Liu, Gengli Duan, Yingjia Yu2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 527-534
Jiakun Long, Yang Wang, Chen Xu, Tingting Liu, Gengli Duan, Yingjia Yu2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 527-534
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
Advance online publication: March 02, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLUncaria rhynchophylla is woody climber plant distributed mainly in China and Japan, the stems and hooks of which can be collected as “Gou-Teng” for the treatment of hyperpyrexia, epilepsy and preeclampsia. Fudan University first manufactured KHR98, the extract of Uncaria rhynchophylla. In order to study the active components and structural information of KHR98, we established a HPLC coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF)-MS method for rapid analysis of alkaloids. In qualitative analysis, a total of eight compounds, including four known alkaloids and four unknown components, were detected and identified. The fragmentation behaviors, such as the fragment ion information and the fragmentation pathways of the eight components were summarized simultaneously, and the concentration of the above components was determined by HPLC-MS method. The quantitative method was proved to be reproducible, precise and accurate. This study shed light on the standardization and quality control of the KHR98 and provided a foundation for the further research on pharmacology, follow-up clinical research and New Drug Applications.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe authors established a HPLC-Q-TOF-MS method for rapid analysis of alkaloids in KHR98 (the extract of Uncaria rhynchophylla). A total of eight compounds, including four known alkaloids and four unknown components, were detected and identified. The structural information and fragmentation pathways of eight components were interpreted. A precise and sensitive HPLC-MS method was validated to simultaneously determine these substances. This study shed light on the standardization and quality control of the KHR98 and provided a foundation for the further research on pharmacology, follow-up clinical research and New Drug Applications.
Download PDF (1324K) Full view HTML -
Manman Li, Yanping Chen, Pengfei Zhang, Ling Zhang, Ri Zhou, Yan Xu, H ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 535-540
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
Advance online publication: March 07, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
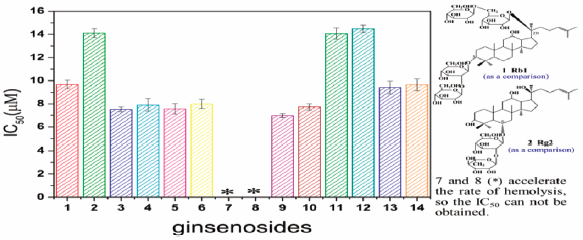
Supplementary materialTwelve pseudo-ginsenosides were synthesized under a mild condition, via a simple three-step called acetylation, elimination-addition and saponification. The inhibitory effects of these twelve pseudo-ginsenosides were screened on the hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes caused by 2,2′-azobis (2-amidinopropane hydrochloride) (AAPH). It was found that the IC50 values followed the sequence of (20Z) pseudo-protopanaxatriol (pseudo-PPT)<(20Z) pseudo-protopanaxadiol (pseudo-PPD)<(20Z) pseudo-Rh2<(20E) pseudo-PPT<(20E) pseudo-PPD<(20E) pseudo-Rh2<(20Z) pseudo-Rg2<(20E) pseudo-Rg2<Rb1<(20Z) pseudo-Rh1<Rg2<(20E) pseudo-Rh1. These compounds can be divided into three groups: accelerate the hemolysis group (7, 8), weak group (2, 11, 12) and strong group (others). Moreover, we also find that most of the Z configuration has better antioxidative activity than E configuration and the number and type of sugar moieties to the ring of triterpene dammarane influence the antioxidative activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1473K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1473K) Full view HTML -
Yoshihiro Hayashi, Atsushi Kosugi, Takahiro Miura, Kozo Takayama, Yosh ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 541-547
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe influence of granule size on simulation parameters and residual shear stress in tablets was determined by combining the finite element method (FEM) into the design of experiments (DoE). Lactose granules were prepared using a wet granulation method with a high-shear mixer and sorted into small and large granules using sieves. To simulate the tableting process using the FEM, parameters simulating each granule were optimized using a DoE and a response surface method (RSM). The compaction behavior of each granule simulated by FEM was in reasonable agreement with the experimental findings. Higher coefficients of friction between powder and die/punch (μ) and lower by internal friction angle (αy) were generated in the case of small granules, respectively. RSM revealed that die wall force was affected by αy. On the other hand, the pressure transmissibility rate of punches value was affected not only by the αy value, but also by μ. The FEM revealed that the residual shear stress was greater for small granules than for large granules. These results suggest that the inner structure of a tablet comprising small granules was less homogeneous than that comprising large granules. To evaluate the contribution of the simulation parameters to residual stress, these parameters were assigned to the fractional factorial design and an ANOVA was applied. The result indicated that μ was the critical factor influencing residual shear stress. This study demonstrates the importance of combining simulation and statistical analysis to gain a deeper understanding of the tableting process.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2996K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2996K) Full view HTML -
 Masashi Horibe, Ryoichi Sonoda, Satoru Watano2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 548-553
Masashi Horibe, Ryoichi Sonoda, Satoru Watano2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 548-553
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA method for scale-up of a lubricant mixing process in a V-type blender was proposed. Magnesium stearate was used for the lubricant, and the lubricant mixing experiment was conducted using three scales of V-type blenders (1.45, 21 and 130 L) under the same fill level and Froude (Fr) number. However, the properties of lubricated mixtures and tablets could not correspond with the mixing time or the total revolution number. To find the optimum scale-up factor, discrete element method (DEM) simulations of three scales of V-type blender mixing were conducted, and the total travel distance of particles under the different scales was calculated. The properties of the lubricated mixture and tablets obtained from the scale-up experiment were well correlated with the mixing time determined by the total travel distance. It was found that a scale-up simulation based on the travel distance of particles is valid for the lubricant mixing scale-up processes.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn this study, scale-up experiments of the lubricant mixing processes were conducted for V-type blenders under the same condition of fill level and Froude number. Three scales of V-type blender were used for the scale-up experiment. However, the physical properties of them were not corresponded either mixing time or number of revolution. Thus, the DEM simulations of three scales of V-type blender mixing were conducted to find the scale-up factor. As a result, it was found that a scale-up simulation based on the travel distance of particles is valid for lubricant mixing scale-up processes.
Download PDF (1091K) Full view HTML -
Tomoko Otsuka, Yosuke Kuroiwa, Kazunari Sato, Kazunari Yamashita, Tada ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 554-561
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe properties of wet mass, which indicate the progress of high shear granulation processes, usually have an effect on final product properties, such as tablet dissolution. The mixer torque rheometer (MTR) is a useful tool for quantitatively measuring the ‘kneading state’ of wet mass and detecting differences in granules. However, there have been no studies of the relationship between the MTR torque and the final product properties to date. In this study, we measured the MTR torque of wet granules at different kneading states, which were prepared by changing the granulation conditions. We then evaluated the relationship between the MTR torque and the dissolution rate of the final product properties. The amperage of the high shear granulator is usually monitored during granulation, but we could not detect a difference in the kneading state through the amperage. However, using MTR torque we were able to quantify the difference of the wet mass. Moreover, MTR torque showed a high correlation with dissolution, compared with the correlations with other intermediate properties, such as granules particle size and tablet hardness. These other properties are affected by following processes and are not properties that directly relate to the kneading state. Thus, MTR torque is a property of wet mass after granulation, and it can be used to directly evaluate differences of the kneading state, and as a result, dissolution. These results indicate the importance of controlling the kneading state, i.e., the progress of granulation, and the utility of MTR for detecting differences in wet mass.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1516K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1516K) Full view HTML -
 Hideyuki Konishi, Tomoyuki Sekino, Kei Manabe2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 562-567
Hideyuki Konishi, Tomoyuki Sekino, Kei Manabe2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 562-567
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
Advance online publication: February 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA practical Pd-catalyzed carbonylation of (hetero)aryl bromides using a crystalline carbon monoxide (CO) surrogate, 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl formate (TCPF), was developed. This reaction proceeds without the slow addition technique that was previously required and with a low catalyst loading (1 mol%). The utility of this Pd-catalyzed external-CO-free carbonylation using TCPF was demonstrated in the synthesis of a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickA practical Pd-catalyzed carbonylation of (hetero)aryl bromides using a crystalline carbon monoxide (CO) surrogate, 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl formate (TCPF), was developed. This reaction proceeds without the slow addition technique that was previously required and with a low catalyst loading (1 mol%) on a gram scale. The utility of this Pd-catalyzed external-CO-free carbonylation using TCPF was demonstrated in the synthesis of a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
Download PDF (534K) Full view HTML -
Hiroki Fukushima, Daisuke Ikegami, Chiaki Kuroda, Kenichi Kobayashi2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 568-574
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSurfactant-type protonic acid-promoted intramolecular cyclization of functionalized allylsilanes was studied in water for the synthesis of α-methylene-γ-lactone compounds. ω-Formyl-β-(acetoxymethyl)allylsilane afforded carbocyclic compounds in good yields, while the cyclization product was not obtained from the corresponding β-ethoxycarbonyl derivative. It was found that (Z)-β-(acetoxymethyl)allylsilane predominantly afforded the cis-product, while (E)-β-(acetoxymethyl)allylsilane afforded both cis- and trans-products at a ratio of almost 1 : 1. The stereoselectivity of the cyclization reaction was almost the same as a protonic acid-promoted reaction in CH2Cl2 and was explained by an interaction between the C(Si)–C(alkene) bond and the carbonyl moiety. The cyclization products were converted to α-methylene-γ-lactone compounds.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (659K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (659K) Full view HTML -
 Hiroyuki Kobayashi, Takashi Misawa, Makoto Oba, Naoya Hirata, Yasunari ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 575-580
Hiroyuki Kobayashi, Takashi Misawa, Makoto Oba, Naoya Hirata, Yasunari ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 575-580
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe designed and synthesized a series of cell-penetrating peptides containing cationic proline derivatives (ProGu) that exhibited responsive changes in their secondary structures to the cellular environment. Effects of the peptide length and steric arrangement of the side chain in cationic proline derivatives [Pro4SGu and Pro4RGu] on their secondary structures and cell membrane permeability were investigated. Moreover, peptides 3 and 8 exhibited efficient intracellular delivery of plasmid DNA.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe authors designed and synthesized a series of cell-penetrating peptides containing cationic proline derivatives (ProGu) that exhibited responsive changes in their secondary structures to the cellular environment. Effects of the peptide length and steric arrangement of the side chain in cationic proline derivatives [Pro4SGu and Pro4RGu] on their secondary structures and cell membrane permeability were investigated. Moreover, peptides 3 and 8 exhibited efficient intracellular delivery of plasmid DNA. These results indicate that the peptides containing cationic proline derivatives could be a useful tool to deliver the hydrophilic biomolecules into the cells.
Download PDF (956K) Full view HTML
-
Takuya Izawa, Koji Nakayama, Noritaka Uchida, Kazuhiro Nojima2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 581-584
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
Advance online publication: February 22, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDehydroacetic acid (1) was found to induce photoisomerization, converting aldrin (3) and dieldrin (4) into photoaldrin (5) and photodieldrin (6), respectively, not only when irradiated with artificial light at wavelengths longer than 290 nm in air but also when exposed to sunlight in air. By contrast, sodium dehydroacetate (2) induced both photoisomerization, primarily converting 3 to 5 and photoepoxidation, partially forming 6. Thus, because 2 is usually used as a water-soluble antiseptic, photo-erethism might occur due to the isomerization and epoxidation properties of this compound. The difference between the photoreactivity of 1 and that of 2 might be attributed to the spin density of the odd electron on the carbon atom in the respective radicals that were formed after photo-excited 1 and 2 caused H-abstraction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (933K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (933K) Full view HTML -
Fumihiko Ogata, Takehiro Nakamura, Naohito Kawasaki2018 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 585-588
Published: May 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, the degradation of methylene blue (MB) and acid orange II (ORII) by the Fenton reaction was improved by using HCl and HNO3. In addition, the effects of pH, temperature, concentration of Fenton’s reagent, and adjustment reagent of solution pH on the decoloration were evaluated. The results showed that the optimal pH for decoloration of MB and ORII was 2.5 and that the decoloration of MB and ORII increased with higher temperature and concentration of Fenton’s reagent. Moreover, the decoloration in the Fenton-reaction process with HCl and HNO3 was greater than the decoloration with H2SO4 by approximately 4.3–5.6 and 1.7–5.6 times for MB and 3.2–3.6 and 4.6–7.2 times for ORII compared to with H2SO4. These results indicated that Fenton-reaction with HCl and HNO3 could be useful for the degradation technology of dyes compared to generally Fenton-reactions.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (844K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (844K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|