
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Koji Morimoto2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1259-1270
Koji Morimoto2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1259-1270
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe biary unit having heteroatom as important scaffolds widely exist in a large number of biologically active compounds and functional organic molecules. Since the cross-coupling is a useful synthetic method for constructing biaryl and heterobiaryl structures, the development of novel cross-coupling methods has been studied intensively. The oxidative biaryl coupling reaction of aromatic compounds having heteroatoms is an attractive method since they do not require the prefunctionalization of arenes. This report describes recent advances in hypervalent iodine(III) induced metal-free synthesis of biaryls having heteroatoms.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe ubiquity of the biaryls with heteroatoms in and on the rings, are of importance in organic chemistry as building blocks of functional compounds, such as bioactive natural products, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Therefore, the cross-couplings can provide powerful tools for the construction of biaryls and the development of a novel coupling method has been intensively studied by synthetic chemists. In the present study, the author demonstrated the metal-free oxidative couplings of two different aromatic C-H bonds in electron-rich arenes for producing biaryls based on new strategies and concepts using hypervalent iodine reagents.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2003K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Tamami Haraguchi, Takayoshi Okuno, Haruka Nishikawa, Honami Kojima, Sa ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1271-1277
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
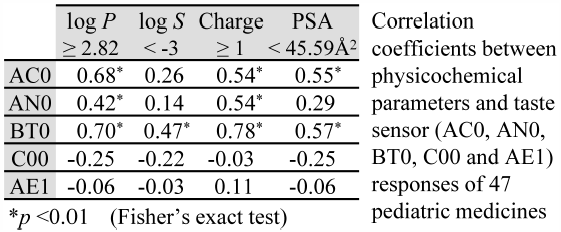
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between response to the bitterness taste sensor and physicochemical parameters of 47 pediatric medicines and to classify these medicines according to the biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS). Forty-seven bitter compounds, most of which were on the WHO model list of essential medicines for children (March 2017), were used in the study. Solutions (0.1 mM) were evaluated by an artificial taste sensor using membranes sensitive to bitterness. On the basis of principal component analysis of taste sensor measurements, chlorpromazine, haloperidol, propranolol, amitriptyline, diphenhydramine were predicted to express the strongest levels of basic bitterness, surpassing that of quinine. Correlation tests between bitter taste sensor outputs and physicochemical properties were then carried out and the compounds classified in terms of their biopharmaceutical properties. High log P values (≥2.82), physiological charge (≥1), low log S values (<−3) and small polar surface area (PSA; <45.59 Å2) were found to correlate significantly with the responses of bitter taste sensors. Forty-one of the 47 compounds could be placed into one of four groups in the BCS, on the basis of dose number (D0), an indicator of solubility which takes into account clinical dosage, and fractional absorption (Fa). For medicines classified in group 4, the factors D0 > 1 and Fa < 0.85 significantly correlated with the responses of the taste sensor for basic bitterness. It was concluded that lipophilicity, physiological charge, solubility, PSA and D0 are the main factors affecting the bitterness of pediatric medicines.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (511K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (511K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shuichi Mori, Nozomi Tsuemoto, Tomoya Kasagawa, Eiichi Nakano, Shinya ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1278-1283
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe progesterone receptor (PR) plays an important role in various physiological processes, especially in the female reproductive system, and abnormalities of PR function are associated with several diseases, including some types of cancer. Non-steroidal PR ligands are of interest as candidate drugs for treatment of PR-related diseases without the serious adverse effects that may be caused by steroidal ligands. For the development of non-steroidal PR ligands, both a hydrophobic backbone and a polar functional group corresponding to the 3-carbonyl group of progesterone, which interacts with Gln725 and Arg766 of the PR-ligand binding domain, are critically important. We previously showed that carborane is a useful hydrophobic pharmacophore for PR antagonists, and in this work, we introduced the pentafluorosulfanyl (SF5) group as a novel polar functional group of carborane-based non-steroidal PR antagonists. All the synthesized SF5-containing carborane derivatives exhibited PR-antagonistic activity at micromolar or submicromolar concentration. Among them, compounds 11 are potent progesterone antagonists with submicromolar IC50 values.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (514K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (514K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Honami Kojima, Tamami Haraguchi, Saeri Ikegami, Haruka Nishikawa, Miya ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1284-1292
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe purpose of the study was to prepare a poly-γ-glutamic acid hydrogel (PGA gel), to evaluate physicochemical properties, its ease of swallowing using texture profile analysis (TPA) and its taste-masking effects on amlodipine besylate (AML) using the artificial taste sensor and human gustatory sensation testing. Using TPA, 0.5 and 1.0% (w/v) PGA gels in the absence of drug were within the range of acceptability for use in people with difficulty swallowing according to permission criteria published by the Japanese Consumers Affairs Agency. The elution of AML from prepared PGA gels was complete within an hour and the gel did not appear to influence the bioavailability of AML. The sensor output of the basic bitterness sensor AN0 in response to AML mixed with 0.5 and 1.0% PGA gels was suppressed to a significantly greater degree than AML mixed with 0.5 and 1.0% agar. In human gustatory sensation testing, 0.5 and 1.0% PGA gels containing AML showed a potent bitterness-suppressing effect. Finally, 1H-NMR spectroscopic analysis was carried out to examine the mechanism of bitterness suppression when AML was mixed with PGA gel. The signals of the proton nearest to the nitrogen atom of AML shifted clearly upfield, suggesting an interaction between the amino group of AML and the carboxyl group of PGA gel. In conclusion, PGA gel is expected to be a useful excipient in formulations of AML, not only increasing ease of swallowing but also masking the bitterness of the basic drug.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1465K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1465K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Iliana González-Hernández, Francisca Palomares-Alonso, José Becerril-V ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1293-1300
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLBased on our previous research on cysticidal drugs, we report the synthesis and evaluation of three new benzimidazole derivatives. In these compounds, the amido group was used as a bioisosteric replacement of the ester group. The molecular docking on β-tubulin revealed that the derivatives interacted through hydrogen bonding with N165, E198 and V236. All compounds showed in vitro activity against Taenia crassiceps cysts. Among them, benzimidazole 3 was found to be the most potent of the series (EC50 0.86 µM). This compound also exhibited the highest probability of binding and the lowest binding free energy score and was therefore selected for in vivo evaluation. Results indicated that the efficacy of compound 3 was comparable to that of the reference drug, albendazole (50.39 vs. 47.16% parasite reduction). Animals treated with compound 3 seemed to tolerate this benzimidazole well, with no changes in behavior, or food and water consumption. These findings are consistent with the in silico prediction results, which indicated low toxicity risks. The pharmacokinetic study showed that the half-life and mean residence time (6.06 and 11.9 h, respectively) were long after oral administration. Together, these results indicate that this new benzimidazole derivative represents a promising structure with cysticidal activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3797K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3797K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Yujiro Kameyama, Maki Matsuhama, Chie Mizumaru, Rieko Saito, Tsuyoshi ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1301-1313
Yujiro Kameyama, Maki Matsuhama, Chie Mizumaru, Rieko Saito, Tsuyoshi ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1301-1313
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録A pharmacopoeia’s core mission is to protect public health by creating and making available public standards to help ensure the quality of drugs. In recent years, pharmacopoeias around the world have harmonized their standards in the present context of globalized drug supply chains and markets. For example, the Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group has worked to harmonize excipient monographs and general chapters. In addition, the International Meeting of World Pharmacopoeias has been held by the WHO to discuss information exchange and international collaboration, among other topics. To contribute further to the protection of public health in the globalized drug market, we conducted a comparative study of the pharmacopoeias in Japan, Europe, and the United States. We aimed to examine current differences among the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, the European Pharmacopoeia, and the United States Pharmacopeia–National Formulary and to identify areas that require further collaboration among the three pharmacopoeias. In this study, we analyzed monographs and general chapters listed in the three pharmacopoeias. We identified the features of the monographs and general chapters listed in each pharmacopoeia, as well as differences across the pharmacopoeias. Moreover, on the basis of our findings, we suggest standards that require further collaboration among the pharmacopoeias in certain preferred areas. The comparison data produced by this study are expected to be used to develop strategies for future revisions of pharmacopoeias around the world.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickPharmacopoeias have provided public standards to help ensure the quality of drugs. As of 2018, pharmacopoeias exist in 56 countries and 3 regions. These pharmacopoeias have contributed to the quality assurance of drug substances and products by providing common standards for users in each region/country. As drug markets and supply chain is globalizing, the independent standards in each pharmacopoeia increase users’ burden of having to perform analytical procedures in different ways and using different acceptance criteria to satisfy pharmacopoeia requirements that vary across regions. To contribute to the further convergence of pharmacopoeial standards, the authors conducted a comparative study of the pharmacopoeias in Japan, Europe, and the United States.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1863K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Heba Kamal Abd El-Mawgoud2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1314-1323
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLCondensation of rhodanine (1) with pyrazol-3(2H)-one derivatives (2a–f) gave 5-substituted-2-thioxo-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives (3a–f). Reaction of compound (1) with 2-arylmethylidene-malononitrile (4a–d) yielded the unexpected derivatives (5a–d). The latter compounds were subjected to cyclization reactions with malononitrile under different basic conditions, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and/or thiourea to furnish the fused thiazole derivatives (6a–d) and (8–10a–d). Coupling of (1) with diazotized aromatic amines (11a–c) in pyridine afforded the arylhydrazones (12a–c). Fusion of latter compounds with malononitrile afforded the thiazolopyridazine derivatives (13a–c). The structures of the newly synthesized compounds were elucidated via spectral data and elemental analyses. The in-vitro cytotoxic activity of compounds (3a–f) against the cell line MCF-7 was evaluated. Also, the synthesized products were investigated for their antibacterial and antifungal activities against six standard organisms including the G+ bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, G− bacteria, Escherichia coli and Proteus vulgaris in addition to fungi, Candida albicans and Aspergillus flavus.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (687K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (687K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ziad Omran, Ashraf N. Abdalla, Munjed M. Ibrahim, Mohammad A. Hossain, ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1324-1327
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/09/28ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Phenanthroindolizidines are naturally occurring alkaloids mainly isolated from different species of Asclepiadaceae. These alkaloids are characterized by an excellent anticancer activity against a very wide range of cancerous cell lines including those who are multi drug resistant. Nevertheless, phenanthroindolizidines are associated with sever neurotoxicity that prevented any candidate from this family to pass the clinical trials. A number of boron-based analogues of (R)-6-O-desmethylantofine have been synthesised. Their physochemical properties were evaluated, same as their in-vitro antiproliferative activity. The pinacol boronate ester derivative (3) showed interesting cytotoxicity against a panel of cancerous cell lines attested by a cancer cell growth-inhibitory potency (GI50) as low as 30 nM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (382K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (382K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shuji Ohsaki, Ryosuke Mitani, Saki Fujiwara, Hideya Nakamura, Satoru W ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1328-1336
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
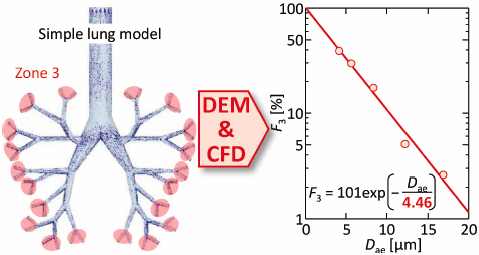
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDry powder inhalation (DPI) has attracted much attention as a treatment for respiratory diseases owing to the large effective absorption area in a human respiratory system. Understanding the drug particle motion in the respiratory system and the deposition behavior is necessary to improve the efficiency of DPI. We conducted computer simulations using a model coupling a discrete element method and a computational fluid dynamics method (DEM–CFD) to evaluate the particle deposition in human respiratory system. A simple artificial respiratory model was developed, which numerically investigated the effect of particle properties and inhalation patterns on the particle deposition behavior. The DEM–CFD simulations demonstrated that the smaller- and lower-density particles showed higher reachability into the simple respiratory model, and the particle arrival ratio to the deep region strongly depended on the aerodynamic diameter. The particle arrival ratio can be described as an exponential function of the aerodynamic diameter. Furthermore, the exponential relationship between the particle reachability into the depth of the simple respiratory model and the aerodynamic diameter predicted the particle aerodynamic diameter based on the required reachability. The particle shape also had an impact on the particle deposition behavior. The rod-like particles with a larger aspect ratio indicated higher reachability into the depth of the simple respiratory model. This was attributed to the high velocity motion of the particles whose long axis was in the direction of the deep region.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3537K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3537K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Susumu Kawakami, Erika Miura, Ayaka Nobe, Masanori Inagaki, Motohiro N ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1337-1346
Susumu Kawakami, Erika Miura, Ayaka Nobe, Masanori Inagaki, Motohiro N ...2019 年 67 巻 12 号 p. 1337-1346
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The 1-BuOH-soluble fraction of the methanol (MeOH) extract of Diospyros maritima was separated by chromatographic techniques to give three new oleanane-type and one new ursane-type triterpene glucoside, named ebenamariosides A–D (1–4); two megastigmanes were also isolated. The structures of triterpene glucosides was elucidated with extensive investigation by one and two dimensional NMR spectroscopy and the structures were confirmed by partial enzymatic hydrolyses to give the corresponding mono-glucosides and aglycones. The structures of the megastigmanes, including their absolute stereochemistries, were elucidated by spectroscopic evidence and by the modified Mosher’s method. Two megastigmanes were chemically correlated and their absolute structures were unambiguously determined. The cytotoxicity of the triterpene glucosides and their degradation products were assayed. They did not show any significant activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickFour new triterpene glucosides and two megastigmanes were isolated from the leaves of Diospyros maritima. The structures of triterpene glucosides were elucidated by a sequential hydrolysis of glycosidic and ester bonds using different enzymes to give partial hydrolyzed intermediates and finally aglycones. Hydrolysis of 28-O-ester bonded glucose by a crude glucosidase may give a new tool in triterpene chemistry. Two new megastigmanes were also isolated and their structures were unambiguously elucidated using the modified Mosher's method and two megastigmanes were chemically correlated by NaBH4 reduction of the ketonic one.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1074K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|