
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Xuanhao Li, Xiaobo Wang, Daoxin Hong, Shangyu Zeng, Jinsong Su, Gang F ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 81-87
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
Advance online publication: December 05, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialRhodiola is widely consumed in traditional folk medicine and nutraceuticals. To establish a procedure for the hydrogen (1H)-NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of secondary metabolites from three different Rhodiola species, the variation among three Rhodiola species were studied using 1H-NMR metabolomics combined with multivariate data analysis. Gene expression programming (GEP) was used to generate a formula to distinguish Rhodiola crenulata from two other Rhodiola species. Finally, HPLC was used to demonstrate the results. Same metabolites were compared by quantitative 1H-NMR (qNMR). Three Rhodiola species were clearly discriminated by 1H-NMR fingerprinting involved 22 nuclear magnetic signals of chemical constituents. y = d166 × 2 + C1 + d56 + d236 − d128 × C2 can be used to distinguish R. crenulata from two other Rhodiola species by GEP. The gallic acid concentration in R. crenulata was significantly higher than in the other. Rhodiola species as was the level of salidroside. R. crenulata also exhibited substantially higher levels of α-glucose. The fatty acid level in Rhodiola kirilowii was lower than the other species. These findings demonstrated that 1H-NMR fingerprinting combined with principal component analysis (PCA), partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) and GEP can be used to distinguish different Rhodiola species and these methods were applicable and effective approaches for metabolic analysis, species differentiation, and quality assessment. In addition, gallic acid, salidroside, α-D-glucose, glycine, alanine, caffeic acid and tyrosol and are the discriminators.
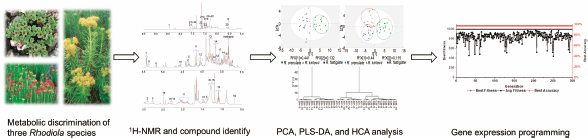 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1050K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1050K) Full view HTML -
Elizabeth Mary Mathew, Sudheer Moorkoth, Pankaj D. Rane, Leslie Lewis, ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 88-95
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML25-Hydroxyvitamin D (25-(OH)D) deficiency is recently been described as one of the multiple factors responsible for pediatric seizures. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D2 are the well-known markers to determine Vitamin D status. In this work we report the development of a sensitive and cost effective HPLC technique for the quantification of the vitamin D metabolites from dried blood spot samples (DBS). The metabolites were extracted using acetonitrile–methanol–0.1% formic acid (60 : 20 : 20 (v/v)) and analyzed on an Acclaim C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm i.d., 3 µm) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The method was linear in the range of 10–80 ng/mL. Limit of detection and limit of quantification (LOQ) of the method were 5 and 10 ng/mL respectively. Extensive stability studies demonstrated the analytes to be stable in stock and matrix with a percent change within the acceptable range of ±15%. Comparison of the newly developed HPLC-DBS method with the reported LC-MS-DBS and electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) methods followed by Bland–Altman analysis demonstrated a bias of 0.08 and −0.14, respectively proving the methods are comparable. Application of the developed method to a pediatric seizure cohort depicted 46.6% of cases as deficient and 26.6% as insufficient for 25-(OH)D. Among deficient cases 8 samples were below 10 ng/mL and exact amount was not calculated since these were below the LOQ levels. The mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) in the remaining 6 deficient cases was 13.22 ± 2.80 ng/mL. The levels in healthy infants were 33.9 ± 6.11 ng/mL. The method can be used routinely for assessing 25-(OH)D deficiency in newborn.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (836K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (836K) Full view HTML -
Shalom P. de O. Assis, Moara T. da Silva, Filipe Torres da Silva, Mire ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 96-105
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPhthalimido-alkyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole derivatives 3a–d and 4a–d were efficiently synthesized using 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction. Anti-inflammatory activity and toxicity studies were performed. The results demonstrated that all the tested compounds reduced carrageenan-induced paw edema and indicated no lethality for toxicity against Artemia salina and acute toxicity in vivo (LD50 up to 1 g kg −1). Furthermore, the structure of phthalimide linked to phenyl group proved to be more active than the compounds containing benzothiazole moiety. Structural modifications such as removal of the phthalimide group and subsequent acetylation, to exemplify a non-cyclic amide, demonstrate that the phthalimide and triazole moieties are important for design of potent candidates with anti-inflammatory drug proprieties. Docking into the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) confirms the importance of the phthalimide and triazole groups in the anti-inflammatory activity. The histopathological studies showed that the compounds 3a–d and 4a–d did not cause serious pathological lesions liver or kidneys.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6223K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6223K) Full view HTML -
Kazuhiro Matsuura, Honami Kojima, Tamami Haraguchi, Miyako Yoshida, Sa ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 106-111
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe purpose of this study was to prepare poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) microspheres (MS) loaded with itraconazole (ITCZ) or miconazole (MCZ) under different evaporation temperatures (25 or 40°C) using an oil-in-water emulsion solvent evaporation method in order to evaluate the initial burst release of drug. Loading efficiencies were comparatively good and the diameters of prepared drug-loaded PLGA MS were around 20 µm in all formulations. The release rates of ITCZ-PLGA MS prepared at 40°C showed a significantly restricted release profile compared with the corresponding ITCZ-PLGA MS prepared at 25°C. This difference in release rate of ITCZ was thought to be caused by the self-healing effect of PLGA, as the glass transition temperature of PLGA is around 40°C. With respect to the MCZ-PLGA MS, the initial burst release was similar in formulations prepared at both 25 and 40°C. Scanning electron microscope results suggested that the initial burst release was due to the localization of MCZ on the surface of MCZ-PLGA MS at higher concentrations. Differential scanning calorimetry measurements suggested complete amorphization of MCZ in MCZ-PLGA MS, whereas crystalline ITCZ was detected in the ITCZ-PLGA MS. This complete amorphization of MCZ is considered to be one of the reasons for the initial burst release.
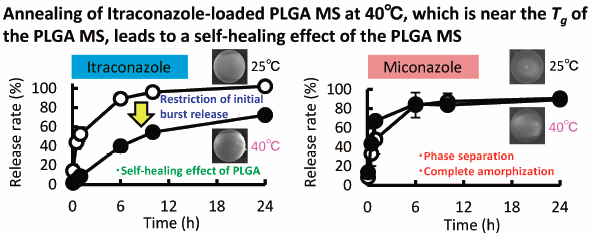 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1334K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1334K) Full view HTML -
 Hidehito Takano, Shinya Uchida, Yasuharu Kashiwagura, Shimako Tanaka, ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 112-119
Hidehito Takano, Shinya Uchida, Yasuharu Kashiwagura, Shimako Tanaka, ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 112-119
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLOrally disintegrating tablets (ODTs), which are administered without water, are beneficial for elderly patients and patients with dysphagia. Masking the unpleasant taste of a drug is an important factor associated with adherence of patients consuming ODTs. We prepared cocoa powder-containing ODTs of bitter-tasting rebamipide (rebamipide chocolet) and evaluated their clinical palatability. We prepared rebamipide ODTs by adding a sweetener and 0, 2.5, 5, and 10% cocoa powder (Ch0-ODTs, Ch2.5-ODTs, Ch5-ODTs, and Ch10-ODTs, respectively). Rebamipide ODTs without cocoa powder and sweetener were used as controls (Cont-ODTs). We performed a gustatory sensation test in 30 healthy adult volunteers. We used the 100-mm visual analog scale (VAS) to evaluate bitterness, sweetness, scent, and overall palatability of the ODTs. The acceptability of each ODT was evaluated on a 5-point scale. Compared to Cont-ODTs, Ch0-ODTs showed no significant improvement in the VAS score for bitterness, scent, and overall palatability during disintegration. However, compared to Cont-ODTs, Ch2.5-ODTs, Ch5-ODTs, and Ch10-ODTs showed an improvement in all items evaluated using the VAS. In particular, Ch2.5-ODTs showed a significant improvement compared to the Cont-ODTs in the VAS score of all items. Evaluation on a 5-point scale indicated that Ch2.5-ODTs and Ch10-ODTs had the highest acceptability. We prepared rebamipide chocolet with excellent palatability properties, which could not be achieved using a sweetener alone, by using the combination of a sweetener and cocoa powder as a new agent for masking bitterness. Our results indicate that cocoa powder may be used as a taste-masking agent in ODTs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick“Chocolet” is an orally disintegrating tablet formulated with cocoa powder to mask the bitterness of drugs. The name “Chocolet” indicates that the formulation combines the good taste of chocolate with the ease of taking of an orally disintegrating tablet. Rebamipide chocolet has been prepared with excellent palatability properties, which could not be achieved using a sweetener alone, by using the combination of a sweetener and cocoa powder as an agent for masking bitterness. “Chocolet” can be used to provide patient-friendly tablets, thus helping to improve medication adherence.
Download PDF (601K) Full view HTML -
Kazunori Inaba, Toshiharu Oie, Hiroko Otake, Takeshi Kotake, Noriaki N ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 120-124
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe evaluation of the dissolution profile of hypnotic drugs is important to promote switching from original products to generic products by removing distrust in generic hypnotics. In this study, we investigated differences in the dissolution profiles between original and generic products (GE-D, GE-S, and GE-T) in commercially available zolpidem tartrate (ZOL) products using the HPLC method using a connected microdialysis probe (microdialysis-HPLC method). Although the degree of hardness and the disintegration time were not different among the original, GE-S, and GE-T, GE-D was 1.4 times harder than the other products. The disintegration time of GE-D was approximately twice as long as that of the original product. Generic products dissolved rapidly as compared with the original product, however, the dissolution rate in the ZOL powder (milled ZOL product) was not different between the original and generic products. Macrogol 6000 (polyethylene glycol (PEG)-6000) was used in the generic products, and this additive was the only PEG difference from the original product. We investigated whether the PEG in the product affected the solubility of ZOL and found that the addition of PEG-4000 or PEG-6000 significantly increased the dissolution rate. These results suggest that the solubility of ZOL may be increased by PEG when the product is disintegrated, resulting in the increased dissolution rate in the generic products. In conclusion, we found that the difference of PEG affected the dissolution profile in the disintegration process using the microdialysis-HPLC method. This finding can help ensure the safety of milled products and the selection of additives.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (586K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (586K) Full view HTML -
Zhi-Gang Sun, Yun-Jie Xu, Jian-Fei Xu, Qi-Xing Liu, Yu-Shun Yang, Hai- ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 125-129
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialBroadened antibacterial activity was introduced to rhodanine derivatives targeting Mycobacterial tuberculosis enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (Mtb InhA) by recruiting feature of xacins to bring DNA Gyrase B inhibitory capability. This is significant for preventing further bacterial injections in the tuberculosis treatment. The most potent compound Cy14 suggested comparable bioactivity (IC50 = 3.18 µM for Mtb InhA; IC50 = 10 nM for DNA Gyrase B) with positive controls. Structure–activity relationship discussion and molecular docking model revealed the significance of rhodanine moiety and derived methoxyl on meta-position, pointing out orientations for future modification.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1119K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1119K) Full view HTML -
 Toshinori Suzuki, Hiroki Ota, Yuma Namba, Toshifumi Fujino2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 130-134
Toshinori Suzuki, Hiroki Ota, Yuma Namba, Toshifumi Fujino2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 130-134
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWhen a neutral solution of a nucleoside mixture was irradiated with UV light having wavelength longer than 300 nm, addition of salicylic acid to the solution greatly accelerated the reaction of thymidine. The UV light irradiation of thymidine solution in the presence of salicylic acid resulted in four major product peaks in HPLC. All the products were identified as isomers of cyclobutane thymidine dimers by MS and NMR. The cyclobutane thymidine dimers were generated from thymidine almost exclusively. UV irradiation with the longer wavelength of 350 nm induced almost no reaction. The results indicate that salicylic acid is a photosensitizer for thymidine dimerization excited by UV light of wavelength 300 to 350 nm.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickWhen a neutral solution of a nucleoside mixture was irradiated with UV light having wavelength longer than 300 nm, addition of salicylic acid to the solution greatly accelerated the reaction of thymidine. The UV light irradiation of thymidine solution in the presence of salicylic acid generated isomers of cyclobutane thymidine dimers almost exclusively. UV irradiation with the longer wavelength of 350 nm induced almost no reaction. The results indicate that salicylic acid is a photosensitizer for thymidine dimerization excited by UV light of wavelength 300 to 350 nm.
Download PDF (447K) Full view HTML -
Yue-Juan Zhang, Xiao-Long Liu, Wen-Ming Wang, Cheng Chen, Mu-Han Zhao, ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 135-142
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSuperbug infection caused by metallo-β-lactamases (MβLs) is a global public health threat. Previous studies reported that the thioesters specifically inhibited the B3 subclass MβL L1. In this work, nine amino acid thioesters 1–9 were synthesized, the activity evaluation revealed that all of these molecules exhibited broad-spectrum inhibitory efficacy against ImiS, IMP-1, NDM-1, and L1, with IC50 values range of 0.02–54.9 µM (except 5 and 7 on NDM-1), and 1 was found to be the best inhibitor with IC50 range of 0.02–16.63 µM. Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) assays showed that thioesters 1, 5 and 9 restored 2–32-fold antibacterial activity of cefazolin and/or imipenem against both Escherichia coli BL21 and DH10B strain expressing ImiS, L1, IMP-1 and NDM-1 (except 5 on NDM-1), and also, thioester 1 increased 2–4-fold antimicrobial activity of cefazolin on two clinical strains Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae producing NDM-1. Stability evaluation indicated that thioester 1 was partially hydrolysed by MβLs to be converted into the mercaptoacetic acid, revealing that the thioester and its hydrolysate mercaptoacetic acid jointly inhibit MβLs. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) monitoring showed that thioester 1 exhibited dose-dependent inhibition on four MβLs tested, and the binding of 1/L1 showed mainly enthalpy driven, while 1/NDM-1 was found to be more entropy driven. Docking studies suggested that 1 bound to Zn(II) ion(s) preferentially via its carboxylate group, while other moieties interacted mostly with the conserved active site residues.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2370K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2370K) Full view HTML -
Noriyasu Hada, Yuna Umeda, Hiromi Kumada, Yoshinori Shimazaki, Kimiaki ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 143-154
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLStereocontrolled syntheses of biotin-labeled oligosaccharide portions containing the non reducing end oligosaccharides of glycosphingolipids from Ascaris suum have been accomplished. Galα1→3GalNAcβ1→OR (1), Galβ1→3Galα1→3GalNAcβ1→OR (2), Galβ1→6Galα1→3GalNAcβ1→OR (3), Galβ1→6(Galβ1→3)Galα1→3GalNAcβ1→OR (4) and GlcNAcβ1→6Galβ1→6(Galβ1→3)Galα1→3GalNAcβ1→OR (5) (R = biotinylated probe) were synthesized by stepwise condensation (1–4) and block synthesis (5) using 5-(methoxycarbonylpentyl) 2-O-benzoyl-3-O-2-napthylmethyl-4,6-O-di-tert-butylsilylene-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-4,6-O-benzylidene-2-deoxy-2-phthalimido-β-D-galactopyranoside (12) as a common precursor. Compound 12 was converted into two kinds of glycosyl acceptors and was condensed with suitable galactosyl donors, respectively.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1330K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1330K) Full view HTML
-
Huijie Liu, Xuejuan Wang, Hanlin Yang, Yan Zhao, Shengping Ji, Hui Ma, ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 155-158
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAminopeptidase N, also known as CD13, is a transmembrance protease with many functions. CD13 is involved in inflammatory diseases and cancers. A convenient and reliable laboratory test method for detecting the suppressing effects of enzyme activity would be useful for study of CD13 inhibitors. Porcine CD13 (pCD13) was traditionally considered an enzyme source but has significant practical disadvantages. pCD13 is not a human source, and the accuracy and reliability of experimental results are greatly reduced. In this study, a modified detection method with K562-CD13 monoclonal cells, a human-derived cell line, was established to detect the suppressing effects of enzyme activity by the CD13 inhibitor. In this method, K562-CD13 monoclonal cells were used as enzyme source and L-leucine p-nitroaniline hydrochloride as substrate. Using CD13 enzyme activity analyses, we found that the ability of the catalytic substrate was weaker in K562 cells than in the other cell lines, and K562-CD13 cells expressed significantly higher levels of CD13 enzyme activity than parental K562 cells. The enzyme activity of CD13 was detected with the new method after ubenimex treatment. The enzyme activity was significantly inhibited by ubenimex in a dose-dependent manner. In summary, this study proposes a sensitive, stable, and objective laboratory method for detecting the inhibitory effect of the CD13 inhibitor.
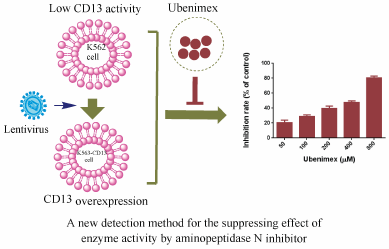 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (829K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (829K) Full view HTML -
Masafumi Okawa, Ryo Akahoshi, Kyoko Kawasaki, Daisuke Nakano, Ryota Ts ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 159-162
Published: February 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTwo new triterpene glycosides, 24-deoxyoxytrogenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)[β-D-glucopyranosyl]-β-D-galactopyranosyl (1→2)-β-D-glucuronopyranoside and sophoradiol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)-β-D-glucuronopyranosyl (1→2)-β-D-glucuronopyranoside with four known glycosides were isolated from a Chinese natural medicine, the roots of Uraria crinita (L.) DESV. Their structures were determined by chemical and spectral methods.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (459K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (459K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|