
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hideyuki Ito2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1121-1122
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (189K) Full view HTML
-
Masami Suganuma, Anchalee Rawangkan, Pattama Wongsirisin, Naritaka Kob ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1123-1130
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLOver the past 30 years, research of green tea polyphenols, especially (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), has revealed that consumption of green tea is a practical and effective primary cancer prevention method for the general population. More recently, we believe that green tea polyphenols are beneficial for tertiary cancer prevention using green tea alone or combined with anticancer drugs because EGCG has the potential to inhibit metastatic progression and stemness, and enhance antitumor immunity. In an effort to identify a common underlying mechanism responsible for EGCG’s multifunctional effects on various molecular targets, we studied the biophysical effects of EGCG on cell stiffness using atomic force microscopy. We found that EGCG acts to stiffen the membranes of cancer cells, leading to inhibition of signaling pathways of various receptors. Stiffening of membranes with EGCG inhibited AXL receptor tyrosine kinase, a stimulator of cell softening, motility and stemness, and expression of programmed cell death-ligand 1. This review covers the following: i) primary cancer prevention using EGCG or green tea, ii) tertiary cancer prevention by combining EGCG and anticancer drugs, iii) inhibition of metastasis with EGCG by stiffening the cell membrane, iv) inhibition of AXL receptor tyrosine kinase, a stimulator of cell softening and motility, with EGCG, v) inhibition of stemness properties with EGCG, and vi) EGCG as an alternative chemical immune checkpoint inhibitor. Development of new drugs that enhance stiffening of cancer cell membranes may be an effective strategy for tertiary cancer prevention and treatment.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1429K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1429K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Tanaka, Yosuke Matsuo2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1131-1142
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBlack tea accounts for 70–80% of world tea production, and the polyphenols therein are produced by enzymatic oxidation of four tea catechins during tea fermentation. However, only limited groups of dimeric oxidation products, such as theaflavins, theasinensins, and theacitrins, have been isolated from black tea and chemically characterized. This is largely because of the complexity and heterogeneity of the oxidation products. To determine structures and production mechanisms of uncharacterized black tea polyphenols, in vitro model fermentation experiments using pure catechins and polyphenol oxidase have been applied, and basic oxidation mechanisms have been established. Contemporary methods, such as LC-MS, are also effective to identify catechin oxidation products in black tea. Despite ongoing efforts, almost 60% of the solids in black tea infusion remain uncharacterized. These compounds include the so-called thearubigins, which are a heterogeneous mixture of uncharacterized catechin oxidation products with oligomeric structures. This review summarizes the current knowledge of the production mechanisms of representative black tea polyphenols and presents recent progress in characterization of thearubigins.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1812K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1812K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Ishizu2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1143-1154
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe high-order functions of molecular capture and chiral recognition of tea gallated catechins (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCg) in water were investigated. A solution of equimolar amounts of a variety of heterocyclic compounds and EGCg in water afforded adhesive precipitates containing the heterocyclic compounds and EGCg at a molar ratio of 1 : 1, based on the integrated value of NMR proton signals. The molecular capture abilities of a variety of heterocyclic compounds using EGCg from the aqueous solutions were evaluated with the ratios of the heterocyclic compounds included in the precipitates of EGCg complex to the total heterocyclic compounds used. In the 1H-NMR spectrum of a solution containing cyclo(L-Pro-Gly), cyclo(D-Pro-Gly), and EGCg in a D2O solution, a difference in the chemical shift of the 1H-NMR signal for some protons of the Pro residue was observed. Judging from the crystal structures of the 2 : 2 EGCg complexes of cyclo(L-Pro-Gly), cyclo(D-Pro-Gly), the difference in the chemical shift derived mainly from a magnetic anisotropic shielding effect by the ring current from the B ring of EGCg.In the 1H-NMR spectrum of a solution containing the pharmaceuticals racemic (R,S)-propranolol, (R,S)-diprophylline, (R,S)-proxyphylline and EGCg in D2O, splitting of the 1H-NMR signals of the pharmaceuticals was observed. It was suggested that the pharmaceuticals formed diastereomers of EGCg complexes, as a result chirality of the pharmaceuticals was recognized by EGCg in the D2O solution.
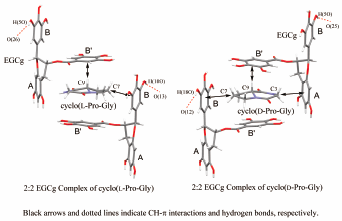 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4138K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4138K) Full view HTML
-
Gyeong Han Jeong, Jae-Hyeon Cho, Cheorun Jo, Seungil Park, Seong Bong ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1155-1162
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA series of novel (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)–phloroglucinol hybrid compounds 1–4 has been successfully synthesized by employing a simple and efficient methodology using a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma irradiation. The new hybrid structures were determined by interpretation of spectroscopic data, with the absolute configurations being established by analysis of the circular dichroism (CD) spectra. The novel hybrids 1 and 2 showed highly improved anti-adipogenic potencies toward both pancreatic lipase and preadipocytes differentiation in 3T3-L1 compared to the original EGCG and phloroglucinol. A novel hybrid 1 represent an interesting subclass of anti-adipogenic candidates that need further research.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1315K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1315K) Full view HTML
-
Jifeng Zheng, Zhiyao Mao, Jianqin Zhang, Liqing Jiang, Ningfu Wang2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1163-1169
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBreast cancer type 1 sensitive protein (BRCA1) is a well-known tumor suppressor and its role in oxidative stress has been confirmed. The purpose of this study is to evaluate whether paeonol has a protective effect on myocardial hypoxia-reoxygenation (A/R) injury, and to explore H9C2 cells through a mechanism-dependent pathway mediated by BRCA1. H9C2 cells were pretreated with paeonol (10 µM) for 18 h before hypoxia was induced to establish a cell model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Use commercial kits to detect antioxidant indicators, including relative oxygen content (ROS) levels, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity, and creatine kinase (CK-MB) and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) activity. The cell viability was analyzed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction method. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to detect BRCA1 mRNA and protein levels. The expression levels of BRCA1, NLRP3 and ACS were determined by Western blotting. In addition, the release of interleukin (IL)-1β (IL-1β), IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was also evaluated by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. The results showed that paeonol (10 µM) can significantly improve the hypoxic A/R damage of H9C2 cells, and the BRCA1 expression of H9C2 cells pretreated with paeonol was significantly increased before A/R damage was induced. BRCA1 is widely known in breast and ovarian cancer. Our data proves that the down-regulation of BRCA1 participates in the decrease of cell viability and the decrease of CK-MB and LDH activities, and protects cells by inhibiting the production of ROS and the activation of Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes and NF-κB. In conclusion, paeonol significantly improved the A/R damage of H9C2 cells induced by hypoxia through the BRCA1/ROS-regulated NLRP3 inflammasome/IL-1β and NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6 pathways. It may be a potential drug against myocardial I/R injury.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1344K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1344K) Full view HTML -
Nakka Niveditha, Munnisa Begum, Duvvala Prathibha, Kalam Sirisha, Pori ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1170-1177
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA series of new C3 heterocyclic-substituted ciprofloxacin derivatives were prepared from ciprofloxacin acid hydrazide as possible chimeric molecules. They were evaluated for their possible in vitro antibacterial (agar cup/bore diffusion method) and antitubercular (Lowenstein–Jensen (LJ) slant method) activities. The results indicated that all the test compounds are highly effective against all the bacterial strains and have shown excellent anti-tubercular activity against normal, multidrug resistant and extensively drug resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. They were found to be more potent antibacterial and antitubercular agents than the standard, ciprofloxacin. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)’s of all the compounds against M. tuberculosis were found to be 0.0625 µg/mL as compared to ciprofloxacin (MIC = 2 to > 8 µg/mL). Molecular docking studies were performed by using AUTODOCK 4.2 on the new ciprofloxacin derivatives at the active site of crystal structure of fluoroquinolones target enzyme Mtb DNA gyrase GyrA N-terminal domain (PDB ID: 3ILW) and also on the active site of crystal structure of chosen heterocyclics target enzyme enoyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) reductase enzyme (PDB ID: 4TZK). Interestingly, almost all the compounds have shown relatively greater binding affinity at both the active sites than ciprofloxacin. Compound 6 exhibited the highest affinity for 3ILW and 4TZK.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1981K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1981K) Full view HTML -
Makiko Fujii, Fuyuko Wada, Natsumi Honda, Keiko Miura, Kaname Hashizak ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1178-1183
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLHydrophobically modified hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HM-HPMC), a polymer in which a small amount of HPMC is stearoxyl substituted, was used as an emulsifier of emulsion-type lotion. A high-pressure homogenizer (microfluidizer) was used. The viscosity of the 1% HM-HPMC aqueous gel decreased after passing through the microfluidizer from 5.5 to 2.7 Pa·s. When liquid paraffin (LP) was used as the oil phase, a stable emulsion was obtained with an LP ratio of 1–40%. The apparent viscosity decreased with LP ratios up to 20%, and then increased with increasing LP concentration. The emulsions with an LP ratio <20% presented a pseudo-viscous flow, similar to that of the diluted polymer solution. HM-HPMC likely adsorbed onto the oil with a stearoxyl group; thus, the interaction between the stearoxyl group, which explained the high viscosity of HM-HPMC, decreased, reducing the viscosity of the emulsion. The LP ratio was 40%, and the emulsion presented a plastic flow, which is typical of concentrated emulsions. The size of the droplet in the emulsion was approximately 1 µm regardless of the LP ratio. When low-viscosity LPs or monoester-type oils such as isopropyl myristate were used, some of the emulsions presented creaming. An emulsion using HM-HPMC as an emulsifier and an appropriate oil homogenized with a microfluidizer is stable, has low viscosity, and can be easily spread on skin.
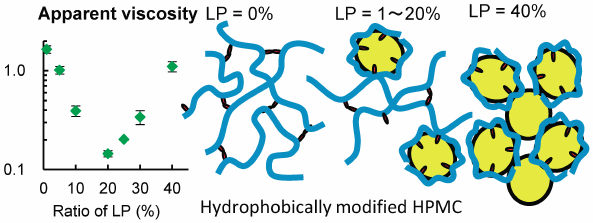 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1323K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1323K) Full view HTML -
 Wenjing Liu, Guangcheng Wang, Zhiyun Peng, Yongjun Li2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1184-1192
Wenjing Liu, Guangcheng Wang, Zhiyun Peng, Yongjun Li2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1184-1192
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: September 26, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA novel series of 4-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-arylpyrimidin-2-amines were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for their anticancer activities. Most of the synthesized compounds exhibited moderate to high antiproliferative activity in comparison to the standard drug cisplatin. Among them, 5i bearing ethoxy at the 4-position of the phenyl was found to be the most active on MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cell lines, with IC50 values of 3.77 ± 0.36 and 3.83 ± 0.26 µM, respectively. Further mechanism study shown that 5i potently inhibited tubulin polymerization, induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and cell apoptosis in MCF-7 cell line. Furthermore, molecular modeling study suggested that 5i probably binds to the colchicine site of tubulin.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickTubulin is an important target for developing anticancer drugs. To discover novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors, the authors designed and synthesized a new series of pyrimidine-based compounds based on the principle of molecular hybrid-based approach. Several compounds exhibited potent anti-tubulin activity and showed antiproliferative activities against MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cell lines. The results indicated that these compounds may have the potential for further development as anticancer agents.
Download PDF (1809K) Full view HTML -
Norio Ogata, Hideaki Tagishi, Motonori Tsuji2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1193-1200
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAnisakiasis is common in countries where raw or incompletely cooked marine fish are consumed. Currently, effective therapeutic methods to treat anisakiasis are unavailable. A recent study found that wood creosote inactivates the movement of Anisakis species. Essential oil of Origanum compactum containing carvacrol and thymol, which are similar to the constituents of wood creosote, was reported to inactivate Anisakis by inhibiting its acetylcholinesterase. We examined whether wood creosote can also inhibit acetylcholinesterase. We examined the effect of components of wood creosote using the same experimental method. A computer simulation experiment (molecular docking) was also performed. Here, we demonstrate that wood creosote inactivated acetylcholinesterase in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.25 mg/mL. Components of wood creosote were also tested individually: 5-methylguaiacol, p-cresol, guaiacol, o-cresol, 2,4-dimethylphenol, m-cresol, phenol and 4-methylguaiacol inactivated the enzyme with an IC50 of 14.0, 5.6, 17.0, 6.3, 3.9, 10.0, 15.2 and 27.2 mM, respectively. The mechanism of acetylcholinesterase inactivation was analyzed using a computer-based molecular docking simulation, which employed a three-dimensional structure of acetylcholinesterase and above phenolic compounds as docking ligands. The simulation indicated that the phenolic compounds bind to the active site of the enzyme, thereby competitively blocking entry of the substrate acetylcholine. These findings suggest that the mechanism for the inactivation of Anisakis movement by wood creosote is due to inhibition of acetylcholinesterase needed for motor neuron activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (11932K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (11932K) Full view HTML -
 Mika Hanashima, Toshiki Matsumura, Yuta Asaji, Tomoyuki Yoshimura, Jun ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1201-1209
Mika Hanashima, Toshiki Matsumura, Yuta Asaji, Tomoyuki Yoshimura, Jun ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1201-1209
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialRegioselectivity for intramolecular Diels–Alder (IMDA) reactions of 6-acetoxy-6-alkenylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ones that were formed by oxidation of 2-alkenylphenols with lead tetraacetate in acetic acid were studied. Bridged regioselectivity was observed in the IMDA reactions of 6-acetoxy-6-alkenylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ones having a dienophile part which could conjugate with an aromatic group. Bridged seven- and eight-membered rings and bicyclo[2.2.2]octane skeletons were constructed by the present IMDA reactions. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations suggested that conjugation of the dienophile with neighboring aromatic groups lowered the highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) energy gap and preceded bridged [4 + 2] adducts.
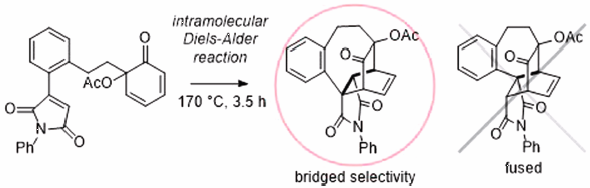 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIntramolecular Diels-Alder (IMDA) reactions are powerful synthetic methods for construction of complex carbon skeletons from relatively simple starting materials. Regioselectivity for producing fused or bridged products by the IMDA reactions is very important for planning a rational synthetic route for target molecules. It has been well known that the IMDA reactions usually provide fused products, while factors for selective formation of bridged products has not been understood well. The authors experimentally found some factors for giving bridged products selectively in IMAD reactions, and they explained the reasons for the observed bridged selectivity by DFT calculations.
Download PDF (815K) Full view HTML -
 Kenji Kikuta, Jan Barta, Yosuke Taniguchi, Shigeki Sasaki2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1210-1219
Kenji Kikuta, Jan Barta, Yosuke Taniguchi, Shigeki Sasaki2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1210-1219
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialN-Acetyl-7-nitroindoline has a characteristic reaction in that its acetyl group is photo-activated to acetylate amines to form amides. In this study, the N-acetyl-7-nitroindoline part was connected to the 2′-deoxyribose part at the 3- or 5-position or to a glycerol unit at the 3-position through an ethylene linker (1, 2, and 3, respectively). They were incorporated into the oligodeoxynucleotides, and their photo-reactivities toward the complementary RNA were evaluated. The acetyl group of 1 was photo-activated to form the deacelylated nitroso derivative without affecting the RNA strand. The photoreaction with 2 suggested acetylation of the RNA strand. In contrast, compound 3 formed the photo-cross-linked adduct with the RNA. These results have shown the potential application of N-acetyl-7-nitroindoline unit in aqueous solutions.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickStimulus-responsive molecules that modify nucleic acids in a site- and base-selective manner play an important role for genomic research. N-Acetyl-7-nitroindoline is a characteristic in that its acetyl group is photo-activated to acetylate amines to form amides. In this study, the N-acetyl-7-nitroindoline part was connected to the 2´-deoxyribose part, which was incorporated into the oligodeoxynucleotide probes, and their photo-reactivities toward the complementary RNA were investigated. One probe was photo-activated to deacetylate to the nitroso derivative. Photo-activation of another probe induced acetylation of the RNA. An interesting finding was the cross-link formation of another probe with the RNA strand.
Download PDF (933K) Full view HTML -
 Tomoyuki Yoshimura, Yuki Umeda, Risako Takahashi, Jun-ichi Matsuo2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1220-1225
Tomoyuki Yoshimura, Yuki Umeda, Risako Takahashi, Jun-ichi Matsuo2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1220-1225
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe nitrolactonization of alkenyl carboxylic acids mediated by Fe(NO3)3·9H2O has been developed. Nitrolactones were obtained in up to 93% yield by treatment of alkenyl carboxylic acids with Fe(NO3)3·9H2O. Mechanistic studies disclosed that the reaction proceeded through a radical intermediate generated from addition of NO2 to alkenyl carboxylic acids.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickNitrogen dioxide has been used as an oxidant and nitrating reagent in organic synthesis. However, its use is limited because it is harmful and hard to handle. Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate has attracted attention as a source of nitrogen dioxide because it is a readily available reagent of low toxicity and cost. This paper describes development of nitrolactonization mediated by iron nitrate as a source of nitrogen dioxide. Nitrolactones obtained by this reaction could lead to useful compounds, such as 1,2-aminoalcohol and amino acid derivatives bearing a tetrasubstituted carbon center.
Download PDF (523K) Full view HTML -
 Masahiro Ueda, Chiaki Komiya, Sayuki Arii, Kohshi Kusumoto, Masaya Den ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1226-1232
Masahiro Ueda, Chiaki Komiya, Sayuki Arii, Kohshi Kusumoto, Masaya Den ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1226-1232
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 07, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLProteins incorporating artificial moieties such as fluorophores and drugs have enjoyed increasing use in chemical biology and drug development research. Preparation of such artificial protein derivatives has relied mainly on native chemical ligation in which peptide/protein thioesters chemoselectively react with N-terminal cysteine (Cys) peptides to afford protein molecules. The protein thioesters derived from expressed proteins represent thioesters that are very useful for the preparation of artificial proteins by native chemical ligation with synthetic peptides with N-terminal Cys. We recently have developed a traceless thioester-producing protocol using carboxypeptidase Y (CPaseY) which is compatible with an expressed protein. The traceless character is ensured by CPaseY-mediated hydrazinolysis of C-terminal Xaa (X)-Cys-proline (Pro)-leucine (Leu)-OH sequence followed by an auto-processing of the Cys-Pro (CP) dipeptide unit, affording the corresponding X-thioester (X-SR). However, hydrazinolysis of the amide bond in the prolyl leucine junction depends significantly on the nature of X. In the case of hydrophobic X residues, the hydrazinolysis overreacts to give several hydrazides while the reaction of hydrophilic X residues proceeds slowly. In this research, we attempted to develop an X-independent CPaseY-mediated protocol and found that the incorporation of a triple CP sequence into the C-terminal end (X-(CP)3-Leu-OH) allows for efficient X-SR formation in a manner that is independent of X.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickPeptide/protein thioesters function as an indispensable synthetic intermediate in Native Chemical Ligation (NCL) that has enjoyed great success in the chemical synthesis of proteins. Facile conversion of recombinant proteins to thioesters allows for the straightforward access to semi-synthetic proteins with chemically synthesized peptides used as an NCL partner. In this paper, the authors developed an efficient thioester-producing protocol. The protocol features the traceless conversion of the CysPro triple repeat–Leu-OH-tagged sequence to the corresponding thioesters by treatment with carboxypeptidase Y in the presence of hydrazine followed by an auto-processing of the CysPro units.
Download PDF (826K) Full view HTML
-
Mika Hosokawa, Kanako Goto, Shota Tanaka, Kumiko Ueda, Seigo Iwakawa, ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1233-1237
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe aim of this study was to investigate appropriate analytical conditions for hydrophilic nucleosides and nucleotides (monophosphates and triphosphates) by HPLC methods using a mixed-mode AX-C18 column with anion-exchange and hydrophobic interactions by quaternary ammonium and C18, respectively, and a reversed-phase pentabromobenzyl (PBr) column with dispersion force and hydrophobic interactions by PBr group. The higher compound polarity led to stronger retention on AX-C18 (triphosphates > monophosphates > nucleosides). AX-C18 demonstrated feasible retention of nucleotides via anion–exchange interaction by increasing the salt and methanol concentrations. In contrast, on PBr, the lower compound polarity led to stronger retention. On PBr, feasible retention of both nucleosides and nucleotides was obtained via dispersion interactions with purine and pyrimidine rings by increasing the methanol concentration. Regarding the pH of phosphate buffer used as the mobile phase, pH 7.0 should be used in measuring nucleoside triphosphates on AX-C18, whereas pH 2.5 is better suited for measuring nucleotides on PBr. In terms of selectivity to highly hydrophilic nucleotides, the mixed-mode AX-C18 column had an advantage over the reverse-phase PBr column. In contrast, PBr column was more versatile than the AX-C18 column. Taken together, HPLC analyses of nucleosides and nucleotides should be carried out by optimizing the interactions between the stationary phase and nucleic acids.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (402K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (402K) Full view HTML -
Misaki Shinoda, Nobuyoshi Morita, Kosaku Tanaka, III, Yoshimitsu Hashi ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 12 Pages 1238-1243
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe reaction of N-(2-{[(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]imino}ethyl)-4-methyl-N-(3-phenylprop-2-yn-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide (6b) with BF3·OEt2 afforded a compound with an unprecedented dodecahydro-4,10 : 5,9-diepoxydipyrrolo[3,4-b:3′,4′-f][1,5]diazocine skeleton (7) after aqueous work-up. The formation mechanism of meso-7 appears to involve dimerization of the hydrated forms (6aS)-C and (6aR)-C of the initial racemic product 9 via cation B generated by facile protonation at the C3a position of 9. Extensive computational studies revealed that the driving force of the facile hydration of 9 is probably release of the ring strain of 9, which arises in part from the bent sp2-hybridized C3a carbon.
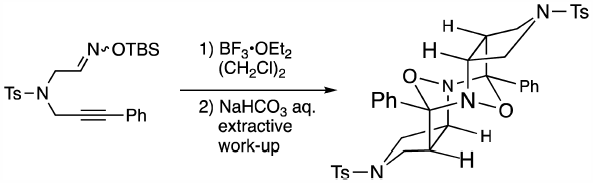 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1258K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1258K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|