
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Yohei Shimizu2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 405-420
Yohei Shimizu2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 405-420
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLChemoselective reactions can contribute to streamlining synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other functional molecules by avoiding use of protecting groups. In this review, copper catalysts were demonstrated useful for developing two types of chemoselective reactions: C–C bond-forming reactions at an anomeric carbon of unprotected aldoses and difunctionalization reaction of C–C multiple bonds. The “soft” nucleophilic copper species exhibit orthogonal reactivity toward “hard” polar functional groups and preferentially react with “soft” functional groups. The catalysis also controls stereoselectivity and/or regioselectivity to provide value-added products from readily available feedstock compounds.
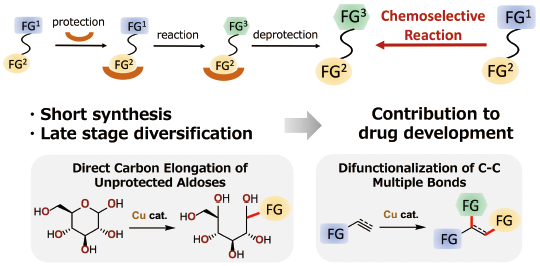 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick“Soft” nature of copper catalysis enabled two types of chemoselective reactions. First, C-C bond forming reactions at an anomeric carbon of unprotected aldoses were developed by taking advantage of orthogonal reactivity between “soft” organocopper species and “hard” polar functional groups, free hydroxy groups. Second, preferential reaction between “soft” copper species and “soft” C-C multiple bonds enabled difunctionalization of the multiple bonds by controlling the reaction order of three reactive species. Well-controlled stereo- and/or regioselectivity of the reactions is another important feature of the copper catalysts.
Download PDF (3251K) Full view HTML
-
Jing Wang, Shengchu Zhang, Kuo Huang, Lang Shi, Qingyong Zhang2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 421-427
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Magnolin (MGL) on inhibition of human breast cancer cells, and explore the underlying molecular mechanisms. The viability of the treated cells was assessed with the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and the proliferation was analyzed in terms of EdU uptake, colony formation, and flow cytometry. The in vitro invasion and migration were determined by the transwell and wound healing assays respectively. The mRNA and protein levels of relevant factors was evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blotting respectively. MGL significantly decreased the viability and promoted apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells, along with reducing EdU incorporation rate as well as the colony forming capacity compared to the untreated control cells. In addition, the in vitro invasion and migration were also significantly inhibited by MGL. Furthermore, MGL suppressed the phosphorylation of MEK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and significantly downregulated the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), the anti-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) and metastasis-associated matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) 2 & 9, and upregulated the cleaved caspases 3 and 9. After ERK was completely inhibited with the small interfering RNA (siRNA), MGL had no effect on these factors, indicating that ERK is essential for MGL action in breast cancer. In conclusion, MGL inhibits proliferation and invasion of and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells through the ERK pathway.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1585K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1585K) Full view HTML -
Si-qi Wang, Xiao Yang, Yong-gang Zhang, En-bo Cai, Xiao-man Zheng, Yan ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 428-435
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
Advance online publication: March 17, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLGinseng (G) and Prepared Rehmannia Root (PRR) are commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine for blood supplementation. This study aimed to study G and PRR with different compatibility ratios changes in chemical composition and inhibition of cyclophosphamide-induced myelosuppression. HPLC was used to determine the chemical constituents of 13 ginsenosides, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF) and verbascoside in different proportions of G-PRR. Balb/c mice were injected intraperitoneally with cyclophosphamide (CTX) to induce bone marrow suppression. The effects of different proportions of G-PRR on peripheral blood, bone marrow nucleated cells, thymus and spleen index of myelosuppressed mice were analyzed. The results showed that the compatibility of G and PRR can promote the dissolution of ginsenosides, and the content of conventional ginsenosides decreased, and the content of rare ginsenosides increased. Different proportions of G-PRR increased the number of peripheral blood and bone marrow nucleated cells in cyclophosphamide-induced bone marrow suppression mice (p < 0.01), increased thymus index (p < 0.01), decreased spleen index (p < 0.01). Different proportions of G-PRR can improve the myelosuppression induced by cyclophosphamide in mice, and the combined effect of G-PRR is better than the single decoction of G and PRR. Among them, G-PRR 2 : 3 and G-PRR 1 : 2 were better than the other groups. These results indicate that different proportion of G-PRR can improve bone marrow suppression, and the combined decoction of G-PRR is better than the separate Decoction in improving bone marrow suppression. This improvement may be related to the changes of the substance basis and active ingredients of G-PRR.
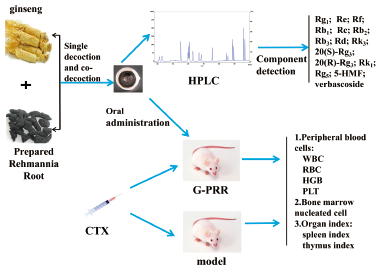 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (917K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (917K) Full view HTML -
 Satoki Aoki, Takako Aboshi, Yoshihito Shiono, Ken-ichi Kimura, Toshihi ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 436-442
Satoki Aoki, Takako Aboshi, Yoshihito Shiono, Ken-ichi Kimura, Toshihi ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 436-442
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSix new sesquiterpenes, tsukiyols A–C, neoilludin C, and 4-O-methylneoilludins A and B, were isolated from the fruiting body of Omphalotus japonicus (Kawam.) Kirchm. & O. K. Mill. Additionally, six known compounds, illudin S, neoilludins A–B, 5-hydroxydichomitol, ergosterolperoxide, and 3β,5α,9α-trihydroxyergosta-7,22-diene-6-one, were also obtained. Their chemical structures were determined with MS, IR, and NMR spectra and the absolute configurations of neoilludins A–C, 4-O-methylneoilludins A, and B were determined with electronic circular dichroism (ECD). Illudin S and 3β,5α,9α-trihydroxyergosta-7,22-diene-6-one showed cytotoxicity against human acute promyelocytic leukemia HL60 cells. Illudin S, 4-O-methylneoilludin A, B, and tsukiyol C showed growth-restoring activity against mutant yeast via Ca2+-signal transduction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickOmphalotus japonicus (Tsukiyotake in japanese) is well-known as a poisonous mushroom in Japan. In this study, the authors isolated six new sesquiterpenes, four known sesquiterpenes and two known steroids from the fruiting body of O. japonicus with column chromatography, solid-phase extraction (SPE), and HPLC. The chemical structures were determined with NMR, MS and IR spectra. Relative configuration was determined with NOE correlations and absolute configuration was determined with ECD calculation. Three new compounds showed growth-restoring activity against mutant yeast via calcium-signal transduction.
Download PDF (621K) Full view HTML -
Tao Wang, Tao Peng, Xiaoxue Wen, Gang Wang, Shuchen Liu, Yunbo Sun, Sh ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 443-446
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCoumarin moiety has garnered momentous attention especially in the design of compounds with significant biological activities. In this work, a series of 3-substituted coumarin derivatives 6a–6l were synthesized and fully characterized. Most of the compounds could obviously inhibit the activity of cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) at the concentration of 10 µM. Besides, 6h and 6l exhibited highest inhibitory effects against COX-2 with inhibition rates of 33.48 and 35.71%, respectively. Detailed structure–activity relationships (SARs) were also discussed. In vivo studies, 6b, 6i and 6l could remarkably repress the xylene-induced ear swelling in mice at the dose of 20 mg/kg. Especially, 6l seemed to be the most effective compound at the dose of 10 mg/kg, displaying favorable anti-inflammatory activity comparable to indomethacin. All of these findings suggested that 6l might be utilized as a candidate for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (521K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (521K) Full view HTML -
Hiroshi Iijima, Katsuki Takebe, Mamoru Suzuki, Hiroko Kobayashi, Tomok ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 447-451
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCatechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) is known as an important drug-target protein in the field of Parkinson’s disease. All clinically approved COMT inhibitors bring a 5-substituted-3-nitrocatechol ring as a pharmacophore, and they bind to COMT with S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and an Mg2+ ion to form a quaternary complex (COMT/SAM/Mg2+/inhibitor). However, structural information about such quaternary complexes is only available for a few inhibitors. Here, a new crystal structure of COMT complexed with nitecapone (5), SAM and Mg2+ is revealed. Comparison of the structures of these complexes indicates that conformation of the catechol binding pocket is almost constant regardless of structure of the inhibitors. The only restriction of the side chain of inhibitors (i.e., the substituent at the 5-position of 3-nitrocatechol) seems to be that it does not make steric repulsion with COMT. However, recent crystallographic and biochemical studies suggest that COMT is a flexible protein, and its conformational flexibility seems crucial for its catalytic process. Based on this information, implications of these quaternary inhibitor complexes were investigated. Met 40 in the α2α3-loop makes atomic contacts with SAM or S-adenosylhomocysteine and the 3-position of the catechol inhibitor. This interaction seems to play a critical role in the affinity of the inhibitor and to stabilize the COMT/SAM/Mg2+/nitrocatechol inhibitor complex by fixing the flexible α2α3-loop.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3024K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3024K) Full view HTML -
 Kazuyuki Kuramoto, Yuki Sawada, Tomohiro Yamada, Takeyuki Nagashima, K ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 452-465
Kazuyuki Kuramoto, Yuki Sawada, Tomohiro Yamada, Takeyuki Nagashima, K ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 452-465
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study reports the synthesis and evaluation of novel indirect AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators. The series of compounds selectively inhibited cell growth in several human breast cancer cell lines by activating AMPK. We performed back-up medicinal chemistry synthetic research on ASP4132, a previously reported as a compound for clinical development that acts as an indirect AMPK activator. This led to the successful identification of 4-({4-[5-({1-[(5-ethoxypyrazin-2-yl)methyl]-4-fluoropiperidin-4-yl}methoxy)-3-methylpyridine-2-carbonyl]piperazin-1-yl}methyl)benzonitrile succinate (27b), a potent, highly aqueous soluble and metabolically stable compound in human hepatocytes. Compound 27b also showed weaker human Ether-a-go-go Related Gene (hERG) inhibitory activity than that of compound 13 and ASP4132. Therefore, 27b was a promising AMPK activator and a second-generation clinical candidate for treatment for human cancer.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes that the synthesis and evaluation of novel indirect adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators. The series of compounds selectively inhibited cell growth in several human breast cancer cell lines by activating AMPK. The back-up medicinal chemistry synthetic research on ASP4132, a previously reported clinical compound that acts as an indirect AMPK activator, led to the successful identification of 27b as a second-generation clinical candidate with promising profiles such as high aqueous solubility and less human Ether-a-go-go Related Gene (hERG) channel inhibitory activity.
Download PDF (1030K) Full view HTML -
 Guoliang Gong, Jianzhao Qi, Ye Lv, Shuai Dong, Chenyu Cao, Ding Li, Ru ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 466-472
Guoliang Gong, Jianzhao Qi, Ye Lv, Shuai Dong, Chenyu Cao, Ding Li, Ru ...2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 466-472
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHistone deacetylases (HDACs) as attractive targets in many diseases therapies has been studied extensively, and its application in cancer research is the most important. Here, we developed a series of derivatives containing natural 2,5-diketopiperazine (DKP) skeleton. Several compounds exhibited distinct HDAC1 inhibitory activities, in particular 2a (IC50 = 405 nM). The selectivity profile for representative 2a indicated that this series of compounds had a preference for HDAC1–3. Additionally, 2a showed the best growth inhibitory activities against K562 and HL-60 tumor cell line with IC50 values of 4.23 and 4.16 µM, respectively. This work may lay the foundation for developing DKP-based HDAC inhibitors as a potential anticancer agent.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe 2, 5-diketopiperazine (DKP) scaffold exists in many natural product families, ranging from fungi and bacteria to the plant kingdom and mammals. Because of the privileged structure and the ability to bind vast receptors, it has become extremely attractive synthetic target for the assembly of natural product-like libraries for drug discovery. In this article, a series of novel derivatives containing DKP skeleton were developed as targeted inhibitors. Several compounds exhibited distinct HDAC1 inhibitory activities and showed antiproliferative activities against K562 and HL-60 tumor cell line.
Download PDF (1717K) Full view HTML -
 Yuki Takechi-Haraya, Yukihiro Goda, Kenichi Izutsu, Kumiko Sakai-Kato2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 473-478
Yuki Takechi-Haraya, Yukihiro Goda, Kenichi Izutsu, Kumiko Sakai-Kato2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 473-478
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe mechanical strength (stiffness) of liposomes affects their cellular uptake efficiency and drug release in drug delivery processes. We recently developed a tip shape evaluation method for improving the precision of liposome stiffness measurement by quantitative imaging (QI)-mode atomic force microscopy (AFM). The present study applied our method to the widely-used AFM instruments equipped for intermittent contact (IC)-mode force curve measurements, and examined instrument-dependent factors that affect the liposome stiffness measurements. We demonstrated that the evaluation of the tip shape for cantilever selection can be applicable to the IC mode as well as the QI mode. With the cantilever selection, the improved precision of the liposome stiffness was obtained when the stiffness of each liposome was determined from the slope in the force-deformation curve by the IC-mode force curve measurement. Further, the stiffness values were found to be similar to that measured by QI-mode measurements. These results indicate that our developed method can be widely used via IC-mode force curve measurements as well as via QI mode. It was also revealed that spatial drift of the cantilever position was instrument-dependent factors which could affect the precision of liposome stiffness measurements in the case of IC-mode force curve measurement. Therefore, in case of stiffness measurement by IC-mode force curve measurement, it is vital to obtain force-deformation curves immediately after imaging a liposome for the precise stiffness measurement of liposomes. These findings will promote the usage of the AFM stiffness measurement method for the characterization of lipid nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickInstrument-dependent factors affecting the precision in the atomic force microscopy stiffness measurement of nanoscale liposomes was examined. The tip shape evaluation method previously developed can be widely used via IC-mode force curve measurements as well as via QI mode. It was also revealed that spatial drift of the cantilever position was instrument-dependent factors which could affect the precision of liposome stiffness measurements in the case of IC-mode force curve measurement. These findings will promote the usage of the AFM stiffness measurement method for the characterization of lipid nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems.
Download PDF (998K) Full view HTML -
Yuta Onuki, Hisanori Nambu, Takayuki Yakura2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 479-486
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialRing-opening cyclization of cyclohexane-1,3-dione-2-spirocyclopropanes using dimethylsulfoxonium methylide proceeded regioselectively to produce 2,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-5H-1-benzopyran-5-ones in good to high yields. The reactions of cycloheptane- and cyclopentane-1,3-dione-2-spirocyclopropanes could construct [7.6]- and [5.6]-fused ring systems. This reaction was also carried out using sulfoxonium ethylide, butylide, and benzylide, resulting in the formation of the corresponding 2,3-trans-disubstituted products in good to high yields, and it was shown that the dimethyl group can act as a dummy substituent. It was found that the 2- and 3-phenyhexahydrobenzopyran-5-ones can be readily converted into 5-hydroxyflavan and 5-hydroxyisoflavan, respectively.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (709K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (709K) Full view HTML
-
Hajime Sato, Mami Yamazaki, Masanobu Uchiyama2020Volume 68Issue 5 Pages 487-490
Published: May 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialPreasperterpenoid A, featuring a 5/7/(3)6/5 pentacyclic structure, is a C25 sesterterpenoid produced by Penicillium verruculosum. The results of density functional calculations on putative biosynthetic carbocation cyclization/rearrangements leading to preasperterpenoid A revealed a highly concerted four-step cyclization mechanism. Interestingly, two secondary carbocation structures were obtained as minima, but appeared almost as shoulders in the energy profile, and may represent essentially transient structures during the highly concerted reaction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (505K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (505K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|