
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Chao Wang2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 683-693
Chao Wang2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 683-693
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
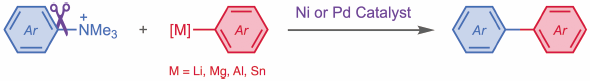
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this review, we summarize our recent progress on functionalization of the ammonium C–N bond through a transition-metal-catalysed cross-coupling process. By synergistic utilization of computational and experimental methods, we have successfully developed several new C–N bond cleavage protocols and established new reaction mechanisms. These findings provide new possibilities for transforming naturally abundant chemicals into useful functional molecules in an efficient and selective manner.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickAmine groups occur widely in many naturally abundant chemicals and artificial functional molecules. Efficient C–N bond conversion methods suitable for late-stage functionalization would greatly expand their synthetic utility. However, transformation of C–N bond is generally difficult, due to the high stability. Ammonium salt is an ideal pre-activation form for amine, since it can be obtained quantitatively from amine via simple protocol. In this review, synthetic transformations through ammonium C–N bond cleavage developed by the author’s group are summarised, describing a new trend for utilization of amine in organic synthesis.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1949K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Huibo Lei, Xinyu Wang, Yuhao Zhang, Taofang Cheng, Rui Mi, Xike Xu, Xi ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 694-712
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLHerba Cistanche, known as Rou Cong Rong in Chinese, is a very valuable Chinese herbal medicine that has been recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Rou Cong Rong has been extensively used in clinical practice in traditional herbal formulations and has also been widely used as a health food supplement for a long time in Asian countries such as China and Japan. There are many bioactive compounds in Rou Cong Rong, the most important of which are phenylethanoid glycosides. This article summarizes the up-to-date information regarding the phytochemistry, pharmacology, processing, toxicity and safety of Rou Cong Rong to reveal its pharmacodynamic basis and potential therapeutic effects, which could be of great value for its use in future research.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1714K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1714K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Masanori Imai, Koichi Kato, Yoshihiro Yamaguchi, Mikako Fujita, Masami ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 713-716
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録With the aim of shedding some light on the still scarcely investigated mechanism of transformation of imines in metal complexes, this study describes the investigation of the hydrogen–deuterium (H/D) exchange reaction of a bis[2-(pyridylmethylidene)-1-(2-pyridylmethylamine]iron(II) complex ([Fe(PMAP)2]2+), following our previous work on a low-spin iron(II) complex bearing two molecules of S-2-pyridylmethylidene-1-(2-pyridyl)ethylamine. This complex has been proven to undergo successive transiminations in acetonitrile, yielding a bis[1-(2-pyridyl)ethylidene-2-pyridylmethylamine]iron(II) complex. In the analogous [Fe(PMAP)2]2+ complex, a 1,3-hydrogen rearrangement occurs in a 10% deuterium oxide-acetonitrile-d3 (D2O–CD3CN) solution. The H/D exchange reaction of [Fe(PMAP)2]2+ was examined in the presence of various concentrations of 2,6-dimethylpyridine as a base in a 10% D2O–CD3CN solution at 45 °C, and the reaction mechanism was investigated.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (959K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (959K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Ze Zhang, Kun Han, Chunying Wang, Chengyan Sun, Ning Jia2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 717-725
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disease with high incidence among old people. Dioscin is a product extracted from natural herbs, which has multiple pharmacological activities. In this study, we investigated the potential effects of disocin on amyloid-β peptide (Aβ1–42) oligomers-treated HT22 cells. Aβ1–42 oligomers induced great neurotoxicity to HT22 cells as examined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The results of terminal deoxynucleoitidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate biotin nich end labeling (TUNEL) staining and flow cytometry indicated that Aβ1–42 oligomers led to increased apoptosis and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in HT22 cells. However, dioscin could remarkably inhibit the neurotoxicity induced by Aβ1–42 oligomers, as well as decrease the apoptosis and ROS generation. Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3) staining and quantification indicated that dioscin upregulated the expression of neuroprotective SIRT3. Moreover, dioscin induced the formation of autophagosomes and autolysosomes in HT22 cells. Dioscin also enhanced the levels of Beclin-1 and LC3-II while decreased the level of p62. These results suggested that dioscin could activate autophagy in HT22 cells. It was also found that knocking down SIRT3 resulted in the downregulation of Beclin-1, LC3-II and the aggregation of p62, suggesting that SIRT3 was an important regulator in autophagy. Furthermore, we found that knocking down SIRT3 or inhibiting autophagy suppressed the protective effects of dioscin on Aβ1–42 oligomers-induced neurotoxicity, apoptosis and ROS generation. These results revealed that SIRT3 and autophagy functioned together in the neuroprotective mechanisms of dioscin. Therefore, dioscin might be a promising drug to protect against Aβ1–42 oligomers-induced neurotoxicity and reduce neuron damage or death in AD.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2303K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2303K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ryosuke Mitani, Shuji Ohsaki, Hideya Nakamura, Satoru Watano2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 726-736
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
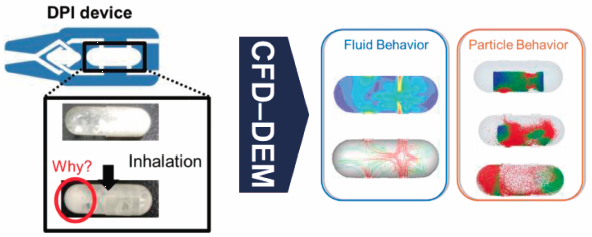
電子付録This study investigated the particle adhesion mechanism in a capsule of dry powder inhaler (DPI) based on a combined computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD–DEM) approach. In this study, the Johnson–Kendall–Roberts (JKR) theory was selected as the adhesion force model. The simulation results corroborated the experimental results—numerous particles remained on the outlet side of the capsule, while a few particles remained on the inlet side. In the computer simulation, the modeled particles were placed in a capsule. They were quickly dispersed to both sides of the capsule, by air fed from one side of the capsule, and delivered from the air inlet side to the outlet side of the capsule. It was confirmed that vortex flows were seen at the outlet side of the capsule, which, however, were not seen at the inlet side. Numerous collisions were observed at the outlet side, while very few collisions were observed at the inlet side. These results suggested that the vortex flows were crucial to reduce the amount of residual particles in the capsule. The original capsule was then modified to enhance the vortex flow in the area, where many particles were found remaining. The modified capsule reduced the number of residual particles compared to the original capsule. This investigation suggests that the CFD–DEM approach can be a great tool for understanding the particle adhesion mechanism and improving the delivery efficiency of DPIs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5256K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5256K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kazuki Watanabe, Yusuke Kawashima, Chisato Mukai, Tatsuya Takagi, Yuki ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 737-741
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Cycloaddition catalyzed by transition metals such as rhodium (I) is an important way to synthesize functionalized molecules in medicinal chemistry. When the reagent has a saturated ring containing more than five carbons (or heavy atoms), the reaction can progress when the compound has an allenyl group, but not for a vinyl group. Here, we constructed two computational models for allenylcyclopentane-alkyne and vinylcyclopentane-alkyne, and obtained their reaction pathways using density functional theory (DFT). From the reaction pathways, we confirmed that the former model has a much lower reaction energy than the latter. We also found that the molecular orbitals of the transition state structure at the rate-controlling step contribute significantly to the difference in reactivity between the two models.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (788K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (788K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Fatma Abd El-Fattah Ragab, Enas Ibrahim Mohammed, Gehad A. Abdel Jalee ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 742-752
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Five new series of hydroxybenzofuranyl-pyrazolyl chalcones 3a,b, hydroxyphenyl-pyrazolyl chalcones 6a–c and their corresponding pyrazolylpyrazolines 4a, d, 7a–c and 8a–f have been synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 inhibitory activity. All the synthesized compounds exhibited dual COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitory activity with obvious selectivity against COX-2. The pyrazolylpyrazolines 4a–d and 8a–f bearing two vicinal aryl moieties in the pyrazoline nucleus showed more selectivity towards COX-2. Within these two series, derivatives 4c, d and 8d–f bearing the benzenesulfonamide group were the most selective. Compounds 4a–d and 8a–f were further subjected to in vivo anti-inflammatory screening, ulcerogenic liability and showed good anti-inflammatory activity with no ulcerogenic effect. In addition compounds 4c and 8d as examples showed prostaglandin (PG)E2 inhibition % 44.23 and 51.4 respectively, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) inhibition % 33.48 and 41.41 respectively and gastroprotective effect in ethanol induced rodent gastric ulcer model. In addition, to explore the binding mode and selectivity of our compounds, 8d and celecoxib were docked into the active site of COX-1 and COX-2. It was found that compound 8d exhibited a binding pattern and interactions similar to that of celecoxib with COX-2 active site, while bitter manner of interaction than celecoxib to COX-1 active site.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1225K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1225K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Kazuki Miura, Chihiro Onodera, Motonari Takagi, Ryosuke Koyama, Takako ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 753-761
Kazuki Miura, Chihiro Onodera, Motonari Takagi, Ryosuke Koyama, Takako ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 753-761
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The genes GLB1 and GALC encode GLB1 isoform 1 and galactocerebrosidase, respectively, which exhibit β-galactosidase activity in human lysosomes. GLB1 isoform 1 has been reported to play roles in rare lysosomal storage diseases. Further, its β-galactosidase activity is the most widely used biomarker of senescent and aging cells; hence, it is called senescence-associated β-galactosidase. Galactocerebrosidase plays roles in Krabbe disease. We previously reported a novel β-galactosidase activity in the Golgi apparatus of human cells; however, the protein responsible for this activity could not be identified. Inhibitor-derived chemical probes can serve as powerful tools to identify the responsible protein. In this study, we first constructed a cell-based high-throughput screening (HTS) system for Golgi β-galactosidase inhibitors, and then screened inhibitors from two compound libraries using the HTS system, in vitro assay, and cytotoxicity assay. An isoflavone derivative was identified among the final Golgi β-galactosidase inhibitor compound hits. Molecular docking simulations were performed to redesign the isoflavone derivative into a more potent inhibitor, and six designed derivatives were then synthesized. One of the derivatives, ARM07, exhibited potent inhibitory activity against β-galactosidase, with an IC50 value of 14.8 µM and competitive inhibition with Ki value of 13.3 µM. Furthermore, the in vitro and cellular inhibitory activities of ARM07 exceeded those of deoxygalactonojirimycin. ARM07 may contribute to the development of affinity-based chemical probes to identify the protein responsible for the newly discovered Golgi β-galactosidase activity. The therapeutic relevance of ARM07 against lysosomal storage diseases and its effect on senescent cells should be evaluated further.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe authors previously reported novel β-galactosidase activity in the human Golgi apparatus and predicted the precursor GLB1 isoform 1 as the enzyme responsible for this activity. GLB1 isoform 1 is involved in lysosomal storage diseases and widely used as a biomarker of cellular senescence. Inhibitor-derived chemical probes may serve as powerful tools for identifying the enzyme. In this study, the authors screened inhibitors from two compound libraries. One of the obtained inhibitors showed increased inhibitory activity following redesigning using molecular docking simulations. This inhibitor may be useful for developing chemical probes to identify the enzyme discovered by the authors.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1500K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Koji Karasawa, Masatoshi Takakura, Saori Kato, Momoha Akatsuka, Masaru ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 762-765
Koji Karasawa, Masatoshi Takakura, Saori Kato, Momoha Akatsuka, Masaru ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 762-765
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The excellent antibacterial activity of manuka honey has been well-documented and is often evaluated according to the unique manuka factor (UMF) index. UMF is determined by an assay based on a bacterial culture, which is time-consuming and does not allow for quantitative analysis. This study developed a simple and rapid method for UMF evaluation using fluorescence fingerprints, principal component analysis (PCA), and partial least squares (PLS) regression. Manuka honey samples were diluted four times with water and fluorescence was observed at three wavelength combinations, namely 260–300 (excitation; ex) to 370 (emission; em) nm, 340 (ex) to 480 nm (em), and 440 (ex) to 520 nm (em), that are mainly attributed to lepteridine, leptosperin, 2-methoxybenzoic acid, and N-methyl phenazinium. Analyzing fluorescence fingerprints using PCA and PLS regression provided a reliable evaluation of the UMF in manuka honey and could be used to differentiate between manufacturers.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickHoney produced from manuka in New Zealand has exceptionally high antibacterial activity and is approved as a medicine for wound care. In this paper, authors developed a simple and rapid evaluation method for the antibacterial activity of manuka honey by using a fluorescence fingerprint (excitation and emission matrix). Three distinct wavelength combinations of fluorescence were obtained from the honey samples. A correlation between the fingerprint and the antibacterial activity was indicated by a multivariate analysis, and authors succeeded in the evaluation of the activity from the fingerprint. Furthermore, some chemicals (leptosperin and leptosperin) were indicated as antibacterial compounds in the honey.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2274K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kazuaki Taguchi, Victor Tuan Giam Chuang, Mai Hashimoto, Mayuki Nakaya ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 766-772
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLLactoferrin (Lf) nanoparticles have been developed as a carrier of drugs and gene. Two main methods, desolvation technique and emulsification method, for preparation of protein nanoparticles have been reported so far, but most of the previous reports of Lf nanoparticles preparation are limited to emulsification method. In this study, we investigated the optimal conditions by desolvation technique for the preparation of glutaraldehyde-crosslinked bovine Lf (bLf) nanoparticles within the size range of 100–200 nm, and evaluated their properties as a carrier for oral and intravenous drug delivery. The experimental results of dynamic light scattering and Transmission Electron Microscope suggested that glutaraldehyde-crosslinked bLf nanoparticles with 150 nm in size could be produced by addition of 2-propanol as the desolvating solvent into the bLf solution adjusted to pH 6, followed by crosslinking with glutaraldehyde. These cross-linked bLf nanoparticles were found to be compatible to blood components and resistant against rapid degradation by pepsin. Thus, cross-linked bLf nanoparticles prepared by desolvation technique can be applied as a drug carrier for intravenous administration and oral delivery.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1822K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1822K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Materu Yuyama, Takeshi Ito, Yumiko Arai, Yuki Kadowaki, Natsumi Iiyama ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 773-778
Materu Yuyama, Takeshi Ito, Yumiko Arai, Yuki Kadowaki, Natsumi Iiyama ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 773-778
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
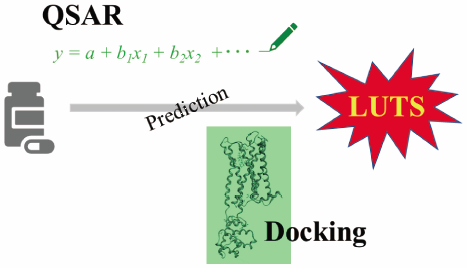
電子付録Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) induced by anticholinergic drug action impair the QOL of patients and are associated with a poor prognosis. Therefore, it is expedient to develop methods of predicting the anticholinergic side effects of drugs, which we aimed to achieve in this study using a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) and docking study with molecular operations environment (MOE; Molecular Simulation Informatics Systems [MOLSIS], Inc.) In the QSAR simulation, the QSAR model built using the partial least squares regression (PLS) and genetic algorithm-multiple linear regression (GA-MLR) methods showed remarkable coefficient of determination (R2) and XR2 values. In the docking study, a specific relationship was identified between the adjusted docking score (-S) and bioactivity (pKi) values. In conclusion, the methods developed could be useful for in silico risk assessment of LUTS, and plans are potentially applicable to numerous drugs with anticholinergic activity that induce serious side effects, limiting their use.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThere are a lot of medicines having anticholinergic actions as side effect. However, it is sometimes difficult to examine side effect only in clinical studies because of various limitations. Therefore, the authors tried to predict anticholinergic activity on the basis of compound’s structures by quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) and docking study. These methods might be helpful for risk assessment of anticholinergic side effects.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1510K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Gerard Lee See, Florencio Arce Jr., Shoko Itakura, Hiroaki Todo, Kenji ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 779-783
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLTranilast, a lipophilic drug with various ophthalmic applications, was used as a model drug to establish the possibility of delivering lipophilic drugs through the eyelid skin. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution studies were conducted employing three application methods (topical application onto eyelid skin, eye drops, and intravenous injection in rats) to broaden the significance of delivering drugs through the eyelids. A two-compartment open model analysis was used for intravenous route while a non-compartmental evaluation was used for topical applications to estimate the pharmacokinetic parameters. Eyelid skin application, eye drops, and intravenous administration had mean residence times (MRTs) of 8.07, 1.79, and 3.25 h in the eyeball and 10.8, 1.29, and 2.97 h in the conjunctiva, correspondingly. In the eyeball, topical application of tranilast onto the eyelids corresponded to a 4.5- and 2.5-fold higher MRT compared with eye drops and intravenous administration, respectively. An 8.4- or 3.6-fold higher MRT was observed in the conjunctiva after topical application compared with eye drops or intravenous administration, respectively. This indicated a gradual penetration of tranilast into the eyeball and conjunctiva, subsequently a slow elimination from these target tissues.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (439K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (439K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Satoru Tamura, Akihito Miyoshi, Tomikazu Kawano, Toshihiro Horii, Sawa ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 784-790
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
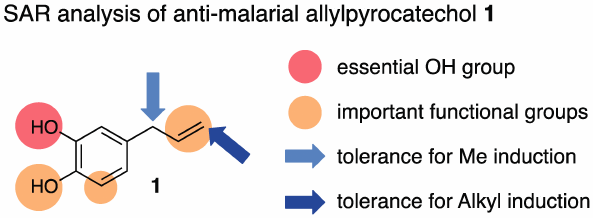
電子付録Malaria disease remains a serious worldwide health problem. In South-East Asia, one of the malaria infection “hot-spots,” medicinal plants such as Piper betle have traditionally been used for the treatment of malaria, and allylpyrocatechol (1), a constituent of P. betle, has been shown to exhibit anti-malarial activities. In this study, we verified that 1 showed in vivo anti-malarial activity through not only intraperitoneal (i.p.) but also peroral (p.o.) administration. Additionally, some analogs of 1 were synthesized and the structure–activity relationship was analyzed to disclose the crucial sub-structures for the potent activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (591K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (591K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Kumiko Sakai-Kato, Yuki Takechi-Haraya, Tsukasa Chida, Manami Okazaki, ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 791-796
Kumiko Sakai-Kato, Yuki Takechi-Haraya, Tsukasa Chida, Manami Okazaki, ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 791-796
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Because of the complexity of nanomedicines, analysis of their morphology and size has attracted considerable attention both from researchers and regulatory agencies. The atomic force microscope (AFM) has emerged as a powerful tool because it can provide detailed morphological characteristics of nanoparticles both in the air and in aqueous medium. However, to our knowledge, AFM methods for nanomedicines have yet to be standardized or be listed in any pharmacopeias. To assess the applicability of standardization of AFM, in this study, we aimed to identify robust conditions for assessing the morphology and size of nanoparticles based on a polystyrene nanoparticle certified reference material standard. The spring constant of the cantilever did not affect the size of the nanoparticles but needed to be optimized depending on the measurement conditions. The size analysis method of the obtained images affected the results of the analyzed size values. The results analyzed by cross-sectional line profiling were independent of the measurement conditions and gave similar results to those from dynamic light scattering. It was indicated that approximately 100 particles are required for a representative measurement. Under the optimized conditions, there were no significant inter-instrument differences in the analyzed size values of polystyrene nanoparticles both in air and under aqueous conditions.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickBecause of the complexity of nanomedicines, analysis of their morphology and size has attracted considerable attention. The atomic force microscope (AFM) has emerged as a powerful tool for providing detailed morphological characteristics of nanoparticles. To assess the applicability of standardization of AFM as an analytical methodology of nanomedicines, in this study, authors identified robust conditions for assessing the morphology and size of nanoparticles based on a polystyrene nanoparticle certified reference material standard. Under the optimized conditions, there were no significant inter-instrument differences in the analyzed size values of polystyrene nanoparticles both in air and under aqueous conditions.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1312K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Genichiro Tsuji, Masaaki Yusa, Sayaka Masada, Hidetomo Yokoo, Junko Ho ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 797-801
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/05/21ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe side effects of kwao keur dietary supplements (obtained from the tuberous root of Pueraria mirifica) have recently been reported by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan. To control the quality of kwao keur products, its ingredients need to be maintained by characteristic marker compounds, such as miroestrol, deoxymiroestrol, and kwakhurin (KWA). In this study, we described the facile synthesis of KWA, a marker compound of P. mirifica. Our revised synthetic method produced KWA with shorter steps and higher yield than the reported method. Furthermore, the absolute purity of KWA was determined by quantitative NMR analysis for standardization as a reagent, and its purity was 92.62 ± 0.12%.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (651K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (651K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Yoshihito Shimizu, Masatoshi Taga, Yoshimitsu Takahashi, Iku Tada, Fum ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 802-805
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe dosages of drugs in newborn infants are small. Small dose necessitate consideration of the loss of drug when administered via feeding tube. In this study, we conducted a tube administration test for seven kinds of antiepileptic drugs and two kinds of potassium supplements using a neonatal feeding tube and investigated the drug loss using the collection rate. We also studied the differences in collection rates among different dosage forms and drugs to determine the more suitable dosage forms and drugs. We investigated three dosage forms: powder, fine granules or dry syrup (powdery form) drugs, powdery form drugs that have been pulverized (pulverized powdery forms), and pulverized tablets. Additionally, we investigated two potassium supplements to determine which was more suitable: potassium L-aspartate and potassium gluconate. For topiramate, only the powdery form caused tube obstructions; the collection rates of the pulverized powdery form and pulverized tablets were > 90%. All antiepileptic drugs other than topiramate that were tested had collection rates of about > 90%. Considering stability and pharmacokinetics, the more suitable dosage form for topiramate is pulverized tablets, whereas the more suitable dosage form for other antiepileptic drugs is powdery form. Collection rate of potassium gluconate was higher than that of potassium L-aspartate. The current study, which indicates that potassium gluconate powdery form is the more suitable drug, presents the more suitable dosage form and drug for administration via feeding tube to newborn infants. These results show that it is essential to evaluate passage through the tube using the collection rate.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (282K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (282K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yasuhiro Mie, Kyoka Takahashi, Ryo Torii, Shen Jingkai, Takumi Tanaka, ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 806-809
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/05/26ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe direct electron transfer between human cytoglobin (Cygb) and the electrode surface, which would allow manipulating the oxidation states of the heme iron in Cygb, was first observed by immobilizing Cygb on a nanoporous gold (NPG) electrode via a carboxy-terminated alkanethiol. The voltammetric performances of the wild type and mutated Cygb-immobilized NPG electrodes were evaluated in the absence or presence of potential substrates. The obtained results demonstrated that the usefulness of the proposed method in understanding the function of Cygb in molecular basis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (666K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (666K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masahiro Kimura, Kumiko Kosuge, Yui Ko, Nodoka Kurosaki, Noriko Tagawa ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 810-813
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/05/22ジャーナル フリー HTMLSalusin-β is an endogenous bioactive peptide that was identified in a human full-length enriched cDNA library using bioinformatics analyses. In our previous study, we found that synthetic salusin-β exhibits antibacterial activity against only Gram-positive microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus NBRC 12732. Salusin-β has an ability to depolarize the cytoplasmic membrane of this bacterium, and this phenomenon may be linked to the antibacterial activity of this peptide. A cell-penetrating peptide (CPP), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 transactivator of transcription (Tat) (49–57) is a short cationic peptide that can traverse cell membranes. In this report, synthetic peptide conjugates of salusin-β and HIV-1 Tat(49–57) showed potent antibacterial activities against both Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus NBRC 12732 and Gram-negative Escherichia coli NBRC 12734. The synthetic peptides also depolarized the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli NBRC 12734 as well as Staphylococcus aureus NBRC 12732. These results suggested that HIV-1 Tat(49–57) is a protein transduction domain or CPP that changes the interaction mode between salusin-β and the cell membrane of Escherichia coli NBRC 12734. By binding to HIV-1 Tat(49–57), salusin-β showed a broad antibacterial spectrum regardless of whether the target was a Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacterium.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (832K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (832K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Serika Teshima, Yukiko Yamashita-Higuchi, Sachiko Sugimoto, Katsuyoshi ...2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 814-817
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録From the leaves of Zanthoxylum ailanthoides, four new phenolic glucosides, termed zanthosides A–D (1–4), were isolated. Their structures were elucidated by means of spectroscopic evidence. Zanthoside A was enzymatically hydrolyzed and thus the aglycone obtained was found to be (1′S,2′R)-(−)-trans-decursidinol, isolated from Angelica decursiva.
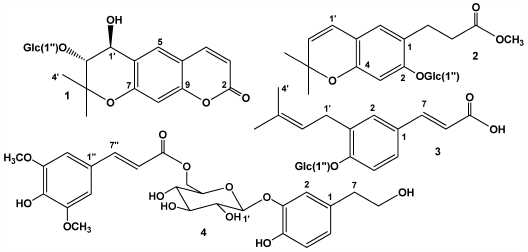 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (384K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (384K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tomoyo Kamei, Tamiko Takahashi, Hiroyuki Teramae, Jyunichi Koyanagi2020 年 68 巻 8 号 p. 818-821
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録1-Fluoroindan-1-carboxyic acid (FICA) derivatives containing a monosubstituted benzene ring (1b–e) were synthesized as their methyl esters and their potential as chiral derivatizing agents (CDAs) were assessed by both 19F- and 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Introduction of a substituent at the 4-position in the benzene ring caused a 1.2–2 fold increase in ΔδF values when compared with that of FICA. This increase was investigated using a correlation model for 19F-NMR and by the order of the stability of the synperiplanar (sp) and antiperiplanar (ap) conformers of the (R,S) and (S,S) diastereomers from the Gibbs’ free energy at 298.15 K.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1424K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1424K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|