
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Hao Zhang, Lulu Zhang, Lu Yang, Quanyu Zhou, Xuan Zhang, Wanli Xing, K ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 237-245
Hao Zhang, Lulu Zhang, Lu Yang, Quanyu Zhou, Xuan Zhang, Wanli Xing, K ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 237-245
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAs a background sampling site in western Japan, the Kanazawa University Wajima Air Monitoring Station (KUWAMS) continuously observes the air pollutants, including PM1, PM2.5, organic carbon (OC) and element carbon (EC). Data for September 2019 to April 2020 were compared with data for September 2018 to April 2019. The mean concentrations of both PM1 and PM2.5 were 4.10 µg/m3 (47%) and 5.82 µg/m3 (33%) lower, respectively in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) period (January to April) than in the same period in 2019. Notably, the average concentrations of both classes of particulate matter (PM) in the COVID-19 period were the lowest for that period in all years since 2016. OC and EC also considerably lower (by 69 and 63%, respectively) during the COVID-19 period than during the same period in 2019. All pollutants were then started to increase after the resumption of the work in 2020. The pollutant variations correspond to the measure implemented during the COVID-19 period, including the nationwide lockdown and work resumption. Furthermore, the reductions in the ratios PM1/PM2.5 and OC/EC during COVID-19 period indicate lighter pollution and fewer emission sources. This analysis of the changes in the pollutant concentrations during the epidemic and non-epidemic periods illustrates the significance of the dominant pollution emissions at KUWAMS and the impact of pollution from China that undergoes long-range transport to KUWAMS.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickTo evaluate the impact of air pollutants long-range transported from the Asian continent on the atmospheric environment in Japan, a background site in the top of Noto peninsula, the Kanazawa University Wajima Air Monitoring Station (KUWAMS), has been used for continuous observation since 2004. Among the numerous reports on air pollution during the COVID-19 pandemic, this article proves for the first time that the implementation of the lockdown policy in China reduced both the air pollution in domestic China and that involved in the long-range transport to KUWAMS, including fine (PM2.5) and ultrafine particulates (PM1.0), Organic Carbon (OC) and Element Carbon (EC).
Download PDF (1678K) Full view HTML -
Seiji Tanaka, Michiho Ito2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 246-252
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe terrestrial plants, Isodon japonicus (Burm. f.) H. Hara and Isodon trichocarpus (Maxim.) Kudô (Labiatae), are native to Japan. Different parts of these plants have been used as a traditional bitter stomachic, under the name Isodon herb (Enmei-so). Ent-kaurane diterpenoids are the major constituents of Isodon herb that contribute to the herb’s medicinal properties. However, large variability with respect to the composition of these diterpenoids limits the suitability of Isodon herb as a pharmaceutical ingredient. Thus, an investigation of the factors that affect its chemical composition is required. In this study, the DNA-barcoding method, using internal transcribed spacer sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA, was applied to cultivated and commercial samples of Isodon herb. Further, each such sample was separated into leaves, stems, and flowers and analyzed for diterpenoid content by HPLC. Moreover, the diterpenoid content in coarsely cut and powdered samples was evaluated. Results confirmed that the source species of these samples was I. japonicus or I. trichocarpus. The three major diterpenoids in Isodon herb were enmein, oridonin, and ponicidin. The diterpenoid content was affected by milling process. Moreover, the diterpenoid content was greatly affected by the ratio between leaves and stems in each sample. Thus, to accurately quantify the diterpenoids in Isodon herb, the use specific conditions such as drying using mild temperature conditions and avoiding milling of the samples might be necessary. This may help in regulating variations in the herb’s composition, in turn, providing better quality and a safe herbal product for pharmaceutical use.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (594K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (594K) Full view HTML -
Wanthani Paengsri, Napapha Promsawan, Apiwat Baramee2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 253-257
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
Advance online publication: January 08, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA series of 3-substituted-2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives with a variety of side chains were successfully synthesized by Mannich reaction of 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (lawsone) with selected amines and aldehydes. All substances (1–16) were evaluated for in-vitro antimalarial activity against strains of Plasmodium falciparum by microculture radioisotope technique. Bioassay data revealed that ten derivatives (1–8, 11 and 13) displayed significantly good activity with values of IC50 ranging from 0.77 to 4.05 µg/mL. The best biological profile (IC50 = 0.77 µg/mL) was observed in compound 1, possessing a n-butyl substituted aminomethyl group. Experimental results support the potential use of our active Mannich components as promising antimalarial agents in the fight against malaria infections and multidrug resistance problems.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (422K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (422K) Full view HTML -
Koichi Saito, Mai Yokota, Sachi Saito, Rie Ito2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 258-264
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe degradation behavior of eight benzodiazepines (BZPs): alprazolam, etizolam, diazepam, triazolam, nitrazepam (NZP), flunitrazepam (FNZ), bromazepam, and lorazepam, in artificial gastric juice was monitored by a LC/photodiode array detector (PDA) to estimate their pharmacokinetics in the stomach. For drugs that were degradable, such physicochemical parameters as reaction rate constant were measured to evaluate the effect of storage conditions on drug degradability, such as whether the degradation proceeds faster by increasing storage temperature, or whether the degradation reaction is reversible by adjusting pH. As a result, it was confirmed that although the eight BZPs degraded in artificial gastric juice, most of them could be restored when pH was increased, and the restoration rates differed depending on the pH and the type of BZP. As for NZP, an Arrhenius plot was drawn to obtain the physicochemical parameters, such as activation energy and activation entropy involved in the degradation reaction, and the reaction kinetics was discussed. In addition, two substances were confirmed as the degradation products of NZP in artificial gastric juice: one was a reversible degradation product (A) (intermediate) and the other was an irreversible degradation product (B) (final degradation product). The intermediate was identified as 2-amino-N-(2-benzoyl-4-nitrophenyl)-acetamide, and the final degradation product was 2-amino-5-nitrobenzophenone. Therefore, when detecting NZP in human stomach contents, such as during judicial dissection, it would be prudent to target NZP as well as the intermediate (A) and the final degradation product (B).
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1190K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1190K) Full view HTML -
Ryota Morimoto, Takumi Matsumoto, Mayuri Minote, Masayuki Yanagisawa, ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 265-270
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialPeptide drug leads possess unusual structural features that allow them to exert their unique biological activities and ideal physicochemical properties. In particular, these peptides often have D-amino acids, and therefore the absolute configurations of the component amino acids have to be elucidated during the structural determination of newly isolated peptide drug leads. Recently, we developed the highly sensitive labeling reagents D/L-FDVDA and D/L-FDLDA for the structural determination of the component amino acids in peptides. In an LC-MS-based structural study of peptides, these reagents enabled us to detect infinitesimal amounts of amino acids derived from mild degradative analysis of the samples. Herein, we firstly report the improved LC-MS protocols for the highly sensitive analyses of amino acids. Second, two new labeling reagents were synthesized and their detection sensitivities evaluated. These studies increase our understanding of the structural basis of these highly sensitive labeling reagents, and should provide opportunities for future on-demand structural modifications of the reagents to enhance their hydrophobicity, stability, and affinity for applications to specialized HPLC columns.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2278K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2278K) Full view HTML -
Yosuke Ozawa, Yutaro Watanabe, Daisuke Ando, Tatsuo Koide, Toshiro Fuk ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 271-277
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
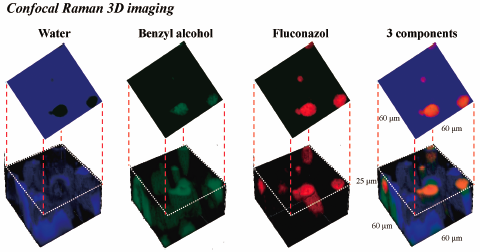
Supplementary materialVibrational spectroscopic imaging has become useful analytical tools for quality control of drug products. In this study, we applied microscopic attenuated total reflection (ATR)-IR and confocal Raman microscopy to elucidate microscopic structure of creams and for the formulation design in the development of semi-solid drug products. The model creams were prepared with prednisolone (PRD) and fluconazole (FLC) as active pharmaceutical ingredients and oily solvents such as mineral oil (MO), isopropyl myristate (IPM), benzyl alcohol (BA) and diethyl sebacate (DES). As a result of microscopic ATR-IR imaging, several domains indicating oily internal phase were observed, which had absorption around 1732 and 1734 cm−1 derived from MO, IPM and DES. In addition, domains of BA around 1009 cm−1 were observed at the complemental or similar position in the formulation with MO or DES, respectively. These results suggested that the creams were oil-in-water type and the distribution of domains would reflect the compatibility of the solvents. The contents of PRD and BA were determined quantitatively in each layer after the intentional separation of the creams and the results agreed well with the imaging analysis. Whereas, confocal Raman imaging allowed to visualize the distribution of the components in depth direction as well as two-dimensional plane. In particular, the Raman imaging would ensure the coexistence of FLC and BA as oily phase in the cream. From these results, the feasibility of spectroscopic imaging techniques was successfully demonstrated for the formulation design of semi-solid dosage forms.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8350K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8350K) Full view HTML
-
Ryosuke Kori, Keigo Murakami, Yoshitake Nishiyama, Tatsuya Toma, Satos ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 278-280
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe disclose our studies on a copper-mediated reaction of alkynes with trimethylsilyl azide to afford nitriles, and proposed a reaction mechanism, which involves an iodoalkyne and an iodotriazole as intermediates.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (469K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (469K) Full view HTML -
 Yuki Nakamura, Takayuki Ochiai, Kazuishi Makino, Naoyuki Shimada2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 281-285
Yuki Nakamura, Takayuki Ochiai, Kazuishi Makino, Naoyuki Shimada2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 281-285
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe first concise total syntheses of O-3′-senecioyl α-bisabolol β-D-fucopyranoside (4a) and O-3′-isovaleroyl α-bisabolol β-D-fucopyranoside (4b) were achieved through final-stage site-selective acylation via the activation of cis-vicinal diols by imidazole-containing boronic acid catalysts as a key step. This synthetic method was also effective for the syntheses of unnatural analogues with modified acyl side chains or carbohydrate moiety.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe site-selective transformation provides a powerful strategy for synthesizing complex and diverse multi-functionalized molecules. In this article, the first total syntheses of O-3’-acyl α-bisabolol β-D-fucopyranoside natural products and their analogues by using boronic acid-catalyzed site-selective acylation in the final stage is described. This approach allows us to construct compound libraries for the purpose of structure–activity relationship studies. The cover art illuminates key feature of this work by characteristic chemical transformation.
Download PDF (782K) Full view HTML -
 Yuki Igarashi, Miki Takahashi, Tomoaki Tsutsumi, Koichi Inoue, Hiroshi ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 286-290
Yuki Igarashi, Miki Takahashi, Tomoaki Tsutsumi, Koichi Inoue, Hiroshi ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 286-290
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialMonitoring analysis of 14 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), 9-chlorohexadecafluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate (F-53B) and dodecafluoro-3H-4,8-dioxanonanoate (ADONA) in bottled drinking water, tea and juice samples was performed using LC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and solid-phase extraction (SPE). In the electrospray negative ion mode, the limit of detection and limit of quantification (LOQ) values were 0.1 to 0.8 ng/mL and 0.2 to 1.6 ng/mL, respectively. The calibration curves were linear from LOQ to 50 ng/mL (r2 > 0.999). The SPE procedure (Presep PFC-II) was utilized for sample preparation and recovery rates for three standards (35, 70 and 140 ng/L) were 80.4–118.8% with relative standard deviation (RSD) ≤ 0.6%. Using the developed method, various samples (n = 54) from Japanese markets were investigated for PFAS and F-53B contamination, and values below the LOQ were observed. It is concluded that for monitoring products in the Japanese market, our method represents a significant improvement over complex techniques for the quantification of PFAS and related compounds from various foods.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes the monitoring analysis of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), 9-chlorohexadecafluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate (F-53B) and dodecafluoro-3H-4,8-dioxanonanoate (ADONA) in drinking bottle water, tea and juice samples. Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry and solid phase extraction showed that recovery values were 80.4–118.8% with RSD ≤ 0.6%, and application is that investigation of non-contamination of PFAS, F-53B and ADONA in these drinking samples from Japanese markets. Using the developed method, it suggests that these screening assay of PFAS in various food samples is more widely distributed for human exposure assessment.
Download PDF (740K) Full view HTML -
 Masateru Ono, Saki Taketomi, Yuichi Kakiki, Shin Yasuda, Masafumi Okaw ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 291-297
Masateru Ono, Saki Taketomi, Yuichi Kakiki, Shin Yasuda, Masafumi Okaw ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 291-297
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlkaline hydrolysis of crude resin glycoside fraction of the seeds of Ipomoea muricata (L.) Jacq. (Convolvulaceae) yielded a new glycosidic acid, muricatic acid D; three known glycosidic acids, namely, muricatic acids A, B, and C; and three known organic acids, namely, isobutyric, 2S-methylbutyric, and 2S-methyl-3S-hydroxybutyric acid. Two new genuine resin glycosides with macrolactone structures (jalapins), muricatins X and XI, were also isolated from the fraction. Their structures were determined using spectroscopic data and chemical evidence.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickResin glycosides are well known as the purgative ingredients, which are commonly found in plants belonging to the Convolvulaceae family. The seeds of Ipomoea muricata are used as a laxative and carminative folk medicine. The authors isolated two new genuine resin glycosides with macrolactone structures from the seeds of I. muricata. Their structures were determined based on spectroscopic data including 1D- and 2D-NMR spectra and MS and examination of the component organic and glycosidic acids generated by alkaline hydrolysis of the crude resin glycoside fraction.
Download PDF (527K) Full view HTML -
Haruka Imai, Ryo Koyama, Yoshikazu Horino, Hitoshi Abe2021 Volume 69 Issue 3 Pages 298-301
Published: March 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIsodehydrodigallic acid, which is an important component of several ellagitannin compounds, was easily synthesized using a classical Ullmann condensation reaction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (437K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (437K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|