
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Midori A. Arai2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 503-515
Midori A. Arai2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 503-515
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
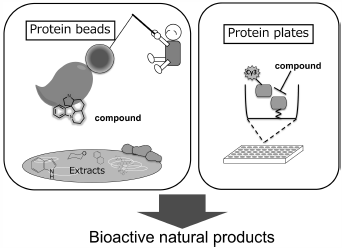
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNatural products are very attractive for development of medicine. Their structure and bioactivities are often beyond human knowledge and imagination. We have developed isolation methods for target protein-oriented natural products so as quickly to discover bioactive compounds from natural resources. This review summarizes our recent results including protein beads methods for neural stem cells differentiation activators and new cancer drug candidates. Syntheses of isolated compounds are described. We also developed protein plate method for identification of protein–protein interaction inhibitors. Because protein binding ability is tightly related to bioactivity, protein-based natural products isolation is a powerful means to find new candidate medicines.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickStructure and bioactivities of natural products are often beyond human knowledge and imagination. In this article, the author developed original screening methods based on protein binding activity. Protein beads method and protein plate method were described. Protein beads method led to the discovery of neural stem cell differentiation activators which inhibited Hes1 dimer formation as a new mechanism. The author also developed protein plate method for protein-protein interaction inhibitors to find new cancer drug candidates. Because protein binding ability is tightly related to bioactivity, protein-based natural products isolation is a powerful means to find new candidate medicines.
Download PDF (8558K) Full view HTML -
 Ryo Yazaki2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 516-525
Ryo Yazaki2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 516-525
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
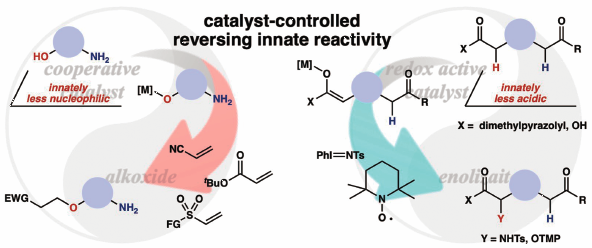
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCatalytic chemoselective reactions of innately less reactive functionalities over more reactive functionalities are described. A cooperative catalyst comprising a soft Lewis acid/hard Brønsted base enabled chemoselective activation of a hydroxyl group over an amino group, allowing for nucleophilic addition to electron-deficient olefins. The reaction could be applicable for a variety of amino alcohols, including pharmaceuticals, without requiring a tedious protection–deprotection process. Chemoselective enolization and subsequent α-functionalization of carboxylic acid derivatives were also achieved by a redox active catalyst through the radical process, providing unnatural α-amino/hydroxy acid derivatives bearing a complex carbon framework and a diverse set of functionalities. The present chemoselective catalysis described herein offers new opportunities to expand the chemical space for innovative drug discovery research.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickA cooperative catalyst comprising a soft Lewis acid/hard Brønsted base enabled chemoselective activation of a hydroxyl group over an amino group. The present chemoselective catalysis could be applicable for a variety of amino alcohols, including pharmaceuticals, without requiring a tedious protection-deprotection process. Chemoselective enolization and subsequent α-functionalization of carboxylic acid derivatives were also achieved by a redox active catalyst through the radical process, providing unnatural α-amino/hydroxy acid derivatives bearing a complex carbon framework and a diverse set of functionalities. The present chemoselective catalysis described herein offers new opportunities to expand the chemical space for innovative drug discovery research.
Download PDF (1893K) Full view HTML
-
 Misaki Nakano, Rikako Nakamura, Yuto Sumida, Kazunori Nagao, Taniyuki ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 526-528
Misaki Nakano, Rikako Nakamura, Yuto Sumida, Kazunori Nagao, Taniyuki ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 526-528
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
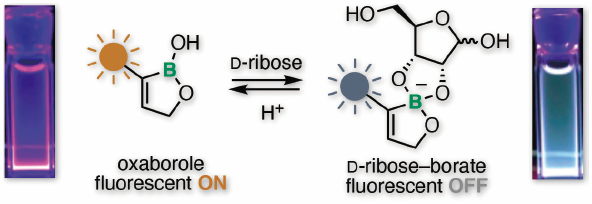
Supplementary materialThe optical property of fluorescent unit-conjugated aliphatic oxaboroles has been investigated. The oxaboroles provide good fluorescence quantum yields and selective recognition toward D-ribose and D-ribose containing molecules. The molecular recognition induced significant fluorescence quenching. The property of the boroles showed the possibility of the boron-based nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) sensor probe.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe optical property of fluorescent unit-conjugated aliphatic oxaboroles has been investigated in this featured article. The authors described the synthesis of fluorescent-oxaboroles by originally developed methods and the optical behavior of the boroles with various sugars. The oxaboroles provide good fluorescence quantum yields and selective recognition toward D-ribose and D-ribose-containing molecules. The molecular recognition induced significant fluorescence quenching. The authors also revealed the positive correlation between the LUMO energy of the oxaborole and the relative fluorescence intensity. The property of the boroles showed the possibility of the boron-based NAD sensor probe.
Download PDF (628K) Full view HTML
-
Hui Feng, Bing Xie, Zhuoqi Zhang, Jun Yan, Mingyue Cheng, Yafeng Zhou2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 529-536
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEmerging evidence highlights the importance of microRNAs (miRNAs) as functional regulators in cardiovascular disease. This study aimed to investigate the functional significance of miR-135a in the regulation of cardiac injury after isoprenaline (ISO) stimulation and the underlying mechanisms of its effects. Murine models with cardiac-specific overexpression of miR-135a were constructed with an adeno-associated virus expression system. The cardiac injury model was induced by ISO injection (60 mg/kg per day for 14 d). In vitro, we used H9c2 cells to establish a cell injury model by ISO stimulation (10 µM). The results indicated that miR-135a was increased during days 0–6 of ISO injection and was then downregulated during days 8–14 of ISO injection. The expression of miR-135a was consistent with the in vivo findings. Moreover, mice with cardiac overexpression of miR-135a exhibited reduced cardiac fibrosis, lactate dehydrogenase levels, Troponin I, inflammatory response and apoptosis. Overexpression of miR-135a also ameliorated cardiac dysfunction induced by ISO. MiR-135 overexpression in H9c2 cells increased cell viability and decreased cell apoptosis and inflammation in response to ISO. Conversely, miR-135 silencing in H9c2 cells decreased cell viability and increased cell apoptosis and inflammation in response to ISO. Mechanistically, we found that miR-135a negatively regulated toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), which was confirmed by luciferase assay. Furthermore, the TLR4 inhibitor eritoran abolished the adverse effect of miR-135 silencing. Overall, miR-135a promotes ISO-induced cardiac injury by inhibiting the TLR4 pathway. MiR-135a may be a therapeutic agent for cardiac injury.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2076K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2076K) Full view HTML -
 Honami Kojima, Toshio Kurihara, Miyako Yoshida, Tamami Haraguchi, Haru ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 537-547
Honami Kojima, Toshio Kurihara, Miyako Yoshida, Tamami Haraguchi, Haru ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 537-547
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe aim of this study was to evaluate bitterness by using “CCDP; Change in concentration-dependent potential” considering dose-dependency of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) as new and useful bitterness evaluation index compared with bitter sensor output value which is conventional bitterness evaluation index for 48 pediatric medicines from the recent edition of the WHO model list of essential medicines for children (7th edn, 2019). Solutions (0.01, 0.03, 0.1 mM) of the compounds were evaluated by an artificial taste sensor using membranes sensitive to bitterness. The dose–response slope of the sensor outputs was defined as CCDP. On the basis of principal component analysis of CCDPs, chlorpromazine hydrochloride, amitriptyline hydrochloride, propranolol hydrochloride, primaquine phosphate and haloperidol were predicted to express the strongest levels of basic bitterness, surpassing that of quinine hydrochloride. Correlation analysis (Fisher’s exact tests and multiple regression analysis) was performed to determine the relation between CCDPs and various physicochemical properties participated in hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity. It is revealed that contribution physicochemical factors are different by individual basic bitterness sensor (AC0, AN0 or BT0), and this result becomes the criterion of the sensor choice to evaluate basic bitterness intensity using basic bitterness sensors. Hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions could be simulated by ligand docking modeling for haloperidol, miconazole and quinine hydrochloride. The pharmaceutical products need a bitterness evaluation in consideration of concentration-dependency to vary in a dose depending on a patient individual. Thus, it was concluded that CCDP correlated to hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity is useful as a bitterness evaluation index of APIs in pediatric medicines.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickQuantitative evaluation for bitterness of pediatric medicine is essential for adherence. The authors proposed criteria, change in concentration-dependent potential (CCDP), dose-response slope of the sensor outputs of active pharmaceutical ingredients measured by an artificial taste sensor, which is new and useful bitterness evaluation index for 48 pediatric medicines from the recent edition of the WHO model list of essential medicines for children (7th ed., 2019). CCDP by individual basic bitterness sensor well correlated to various physicochemical factors related hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity. Therefore, CCDP proved to be useful as a bitterness evaluation index of APIs in pediatric medicines.
Download PDF (2360K) Full view HTML -
Keita Yaginuma, Shuichi Tanabe, Hirokazu Sugiyama, Manabu Kano2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 548-556
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSoft sensors play a crucial role as process analytical technology (PAT) tools. They are classified into physical models, statistical models, and their hybrid models. In general, statistical models are better estimators than physical models. In this study, two types of standard statistical models using process parameters (PPs) and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) were investigated in terms of prediction accuracy and development cost. Locally weighted partial least squares regression (LW-PLSR), a type of nonlinear regression method, was utilized. Development cost was defined as the cost of goods required to construct an accurate model of commercial-scale equipment. Eleven granulation lots consisting of three laboratory-scale, two pilot-scale, and six commercial-scale lots were prepared. Three commercial-scale granulation lots were selected as a validation dataset, and the remaining eight granulation lots were utilized as calibration datasets. The results demonstrated that the PP-based and NIRS-based LW-PLSR models achieved high prediction accuracy without using the commercial-scale data in the calibration dataset. This practical case study clarified that the construction of accurate LW-PLSR models requires the calibration samples with the following two features: 1) located near the validation samples on the subspace spanned by principal components (PCs), and 2) having a wide range of variations in PC scores. In addition, it was confirmed that the reduction in cost and mass fraction of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) made the PP-based models more cost-effective than the NIRS-based models. The present work supports to build accurate models efficiently and save the development cost of PAT.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2779K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2779K) Full view HTML -
Yukiko Karuo, Riona Shiraki, Ayaka Yoshida, Ryo Tsunokawa, Mayuko Naka ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 557-563
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSperm activation is an essential process by which the male gametes become capable of fertilization. Because the process in Caenorhabditis elegans is readily reproducible in vitro, this organism serves as an excellent model to investigate it. C. elegans sperm activation in vivo occurs during spermiogenesis. Membranous organelles (MOs) contained within spermatids fuse with the plasma membrane, resulting in extracellular release of their contents and relocation of some proteins indispensable for fertilization from the MO membrane onto the sperm surface. Intriguingly, these cytological alternations are exhibited similarly in mouse spermatozoa during the acrosome reaction, which also represents a form of sperm activation, prompting us to hypothesize that C. elegans and mice share a common mechanism for sperm activation. To explore this, we first screened a chemical library to identify compounds that activate C. elegans spermatozoa. Because a quinolinol analog named DDI-6 seemed to be a candidate sperm activator, we synthesized it to use for further analyses. This involved direct dechlorination and hydrogenolysis of commercially available 5-chloro-8-quinolinol, both of which are key steps to yield 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-8-quinolinol, and we subsequently introduced the sulfonamide group to the compound. When C. elegans spermatids were stimulated with solvent alone or the newly synthesized DDI-6, approx. 3% and approx. 28% of spermatids became MO-fused spermatozoa, respectively. Moreover, DDI-6 triggered the acrosome reaction in approx. 20% of mouse spermatozoa, while approx. 12% became acrosome-reacted after mock stimulation. Thus, DDI-6 serves as a moderately effective activator for both C. elegans and mouse spermatozoa.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1245K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1245K) Full view HTML -
 Ryo Saito, Goh Sennari, Asuka Nakajima, Aoi Kimishima, Masato Iwatsuki ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 564-572
Ryo Saito, Goh Sennari, Asuka Nakajima, Aoi Kimishima, Masato Iwatsuki ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 564-572
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialNovel derivatives of puberulic acid were synthesized and their antimalarial properties were evaluated in vitro against the Plasmodium falciparum K1 parasite strain, cytotoxicity against a human diploid embryonic cell line MRC-5, and in vivo efficacy using a Plasmodium berghei-infected mouse model. From previous information that three hydroxy groups on the tropone framework were essential for antimalarial activity, we converted the carboxylic acid moiety into the corresponding esters, amides, and ketones. These derivatives showed antimalarial activity against chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium in vitro equivalent to puberulic acid. We identified that the pentane-3-yl ester, cyclohexyl ester, iso-butyl ketone, cyclohexyl methyl ketone all show an especially potent antiparasitic effect in vivo at an oral dose of 15 mg/kg without any apparent toxicity. These esters were more effective than the existing commonly used antimalarial drug, artesunate.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickNovel 25 derivatives of puberulic acid were synthesized by utilizing the authors’ total synthetic route. According to previous structure-activity relationships information, they focused on the carboxylic acid moiety in puberulic acid and converted it into the corresponding esters, amides and ketones. Antimalarial evaluations in vitro and in vivo of these derivatives were carried out and revealed detailed SAR information. It was clarified that several ester and ketone derivatives conserve strong antimalarial activity similar to that of puberulic acid without any obvious toxicity in oral dose of 15 mg/kg.
Download PDF (931K) Full view HTML -
Sayaka Masada, Junko Hosoe, Ryoko Arai, Yosuke Demizu, Takashi Hakamat ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 573-580
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Advance online publication: March 30, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialOwing to occasional health damages caused by health food products derived from Pueraria mirifica (PM), the Japanese government has designated PM as an “ingredient calling for special attention.” Miroestrol is a specific isoflavone isolated from PM and possesses very strong estrogenic activity enough to induce side effects in small amount. Therefore, routine analyses for miroestrol quantification is recommended to control the safety and quality of PM products. However, miroestrol content in PM is quite low, and commercial reagent for its detection is rarely available. In this study, we developed a quantitative analysis method for miroestrol in PM without using its analytical standard by using the relative molar sensitivity (RMS) of miroestrol to kwakhurin, another PM-specific isoflavone, as a reference standard. The RMS value was obtained by an offline combination of 1H-quantitative NMR spectroscopy and a LC/photo diode array (PDA) and miroestrol content was determined by single-reference LC/PDA using RMS. Furthermore, we investigated miroestrol content in commercially available PM crude drugs and products, and the RMS method was compared with the conventional calibration curve method in terms of performance. The rate of concordance of miroestrol contents determined by two method was 89–101%. The results revealed that our developed LC/PDA/MS method with RMS using kwakhurin as a reference standard was accurate for routine monitoring of miroestrol content in PM crude drugs and products to control their quality.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1223K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1223K) Full view HTML
-
Kazuhiko Hayashi, Yoshimi Ichimaru, Kirara Sugiura, Azusa Maeda, Yumi ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 581-584
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
Advance online publication: March 31, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialLithium cations were observed to accelerate the hydrolysis of esters with hydroxides (KOH, NaOH, LiOH) in a water/tetrahydrofuran (THF) two-phase system. Yields in the hydrolysis of substituted benzoates and aliphatic esters using the various hydroxides were compared, and the effects of the addition of lithium salt were examined. Moreover, it was presumed that a certain amount of LiOH was dissolved in THF by the coordination of THF with lithium cation and hydrolyzed esters even in the THF layer, as in the reaction by a phase-transfer catalyst.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (663K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (663K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Ishizu, Miku Tokunaga, Moeka Fukuda, Mana Matsumoto, Takeshi G ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 585-589
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
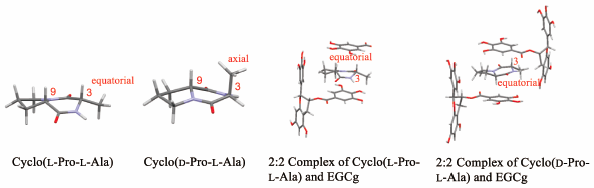
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe addition of an aqueous solution of diketopiperazine cyclo(Pro-Xxx) (Xxx: amino acid residue) to an aqueous solution of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCg) led to precipitation of the complex of EGCg and cyclo(Pro-Xxx). The molecular capture abilities of cyclo(Pro-Xxx) using EGCg were evaluated by the ratio of the amount of cyclo(Pro-Xxx) included in the precipitates of the complex with EGCg to that of the total cyclo(Pro-Xxx) used. Stronger hydrophobicity of the side chain of the amino acid residue of cyclo(Pro-Xxx) led to a higher molecular capture ability. Furthermore, the molecular capture ability decreased when the side chain of the amino acid residue had a hydrophilic hydroxyl group. When diketopiperazine cyclo(Pro-Xxx), excluding cyclo(D-Pro-L-Ala), was taken into the hydrophobic space formed by the three aromatic A, B, and B′ rings of EGCg, and formed a complex, their conformation was maintained in the hydrophobic space. Based on nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) measurement, the 3-position methyl group of cyclo(D-Pro-L-Ala) in D2O was axial, whereas that of cyclo(L-Pro-L-Ala) was equatorial. When cyclo(D-Pro-L-Ala) was taken into the hydrophobic space of EGCg and formed a 2 : 2 complex, its 3-position methyl group changed from the axial position to the equatorial position due to steric hindrance by EGCg.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (752K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (752K) Full view HTML -
Koichiro Ota, Kazuo Kamaike, Hiroaki Miyaoka2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 590-594
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialEiseniachloride B is a marine chlorinated oxylipin isolated from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis. This natural product contains cyclopentane, chlorohydrin, and 14-membered lactone systems that incorporate five stereogenic centers. In this paper, we report on the total synthesis of structurally unique oxylipin eiseniachloride B from optically active lactol via ecklonialactone B in a linear sequence comprising 11 steps with a 12.1% overall yield.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (427K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (427K) Full view HTML -
Ippei Watanabe, Keiji Yoshioka, Katsuya Takahashi, Hirotaka Hoshi, May ...2021 Volume 69 Issue 6 Pages 595-599
Published: June 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialRetention durability, especially in the eye, is one of the most important properties of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices (OVDs) during ocular surgery. However, the information on the physical properties of OVDs is insufficient to explain their retention durability. The purpose of this study is to clarify the mechanism of OVD retention to improve understanding of the behavior of OVDs during ocular surgery. To elucidate the mechanism of OVD retention, we have developed a new test method for measuring repulsive force. As a result, the maximum repulsive force of OVDs was positively and well correlated with the retention durability of investigated OVDs. Consequently, we demonstrated that the repulsive force could be used as an index of retention durability on the ocular surface and in the eye. We directly compared the intraocular retention durability of three OVDs (Shellgan, Viscoat, and Opegan-Hi) in ex vivo porcine eyes. Opegan-Hi was immediately removed from the anterior chamber, but Shellgan and Viscoat remained largely in the anterior chamber as determined by fluorescence imaging. These results showed that the intraocular retention behavior of OVDs was similar to their ocular surface behavior in our previous report, suggesting that retention durability is dependent on the OVD itself. The retention durability of Shellgan seemed to be higher than that of Viscoat, and the maximum repulsive force of Shellgan was 1.35-fold higher than that of Viscoat. Therefore, the repulsive force might be a useful index for assessing the difference in the retention durability between OVDs such as Shellgan and Viscoat.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3211K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3211K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|