
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hongjie Guo, Shuyu Liu2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 326-333
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録This review highlights the cocrystals of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) derived from traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) in categories, ∆pKa rule, preparation, characterization, and physicochemical properties, reported in 113 literature reports. It is founded that the formation of all of the cocrystals is in accordance with ∆pKa rule. Three preparation methods such as evaporation cocrystallization, grinding method, and suspension method, are used most, accounting for 44, 27, and 16%, respectively. Almost all cocrystals are characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD). Thermal analysis techniques are used for 81% of cocrystals, and more than half of cocrystals are characterized by IR. Forty-four percent of cocrystals are determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction (SXRD) since it is difficult to get the single crystals of cocrystals. Most cocrystals of APIs in TCMs exhibit 1–10 folds enhancement in solubility, dissolution, dissolution rate, and bioavailability, and a few of them are increased by dozens or even hundreds of times in these properties. This review provides a meaningful reference for more and more APIs in TCMs prepared for pharmaceutical cocrystals in future.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1941K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1941K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Jing Sun, Mengdi Pang, Xiaozhu Tang, Qianqian Xu, Daiyin Peng, Weidong ...2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 334-341
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/03/01ジャーナル フリー HTMLGambogenic acid (GNA), which has a broad spectrum of anti-tumor activity, is considered as a potential anticancer ingredient. In this study, we examined the anti-tumor effect and the effect of GNA on CYP and pregnane X receptor (PXR). In anti-tumor experiments, an A549 cells tumor-bearing nude mice model was established. Tumor weights and volumes were measured. Inhibition ratio (IR) was calculated. In a pharmacokinetic study, after intragastrical administration of GNA in rats, a cocktail method was adopted to evaluate the activities of CYP2C6, 2C11 and 3A1; RT-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and Western blot (WB) assays were applied to evaluate the mRNA and protein expression levels, respectively. Compared with injection, oral administration also can inhibit tumor growth. Moreover, GNA increased the activities of CYP2C11 and CYP3A1 in the high-dose group as well as the mRNA and protein expression levels. The mRNA and protein expression levels of PXR were also slightly induced. Our study suggested that, oral administration of GNA was effective in inhibiting tumor growth in mice and could induced the activities of CYP2C and CYP3A in rats.
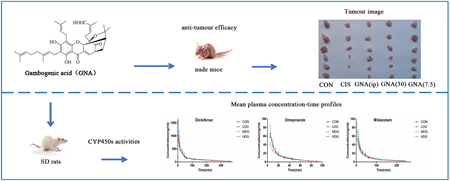 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2888K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2888K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Bayu Ardiansah, Nur Rohman, Mochammad Arfin Fardiansyah Nasution, Hiro ...2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 342-348
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic condition that is a major health concern around the world. The current study investigates the synthesis of a series of chalcone and 1H-1,2,3-triazole hybrid compounds and their in vitro inhibitory potential against α-glucosidase. The antidiabetic analysis revealed that compounds 4a and 4b are highly active agents with IC50 of 3.90 and 4.77 µM, respectively. These results are close to quercetin (IC50 = 4.24 µM) as the reference standard. Molecular docking study strongly supports the active interaction of the 4a and 4b to the enzyme through cation–π interaction and hydrogen bonding between the ligands and the active site of Saccharomyces cerevisiae α-glucosidase enzyme. This study broadened the potential of designing chalcone-triazole hybrid compounds as antidiabetic drug candidates in the pharmaceutical sector.
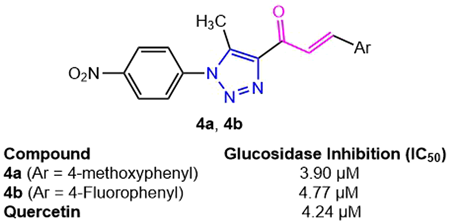 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2185K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2185K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Jin-Bu Xu, Jin Bi, Peng Wen, Shi-Xing Miao, Xiao-Huan Li, Feng Gao2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 349-353
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/03/02ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The direct modification of structurally complex natural product dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) through iron-catalyzed direct hydroamination of DHEA with various nitro(hetero)arenes was carried out to afford 5α-arylamino-DHEAs (1–25) in good yields (53–72%). Though as a radical reaction, it features high stereoselectivity, and only the 5α-substituted derivatives were produced. The in vitro antiproliferative activity of these synthesized compounds against the human breast cancer MCF-7 cell was evaluated, showing that most of DHEA analogues possessed the moderate cytotoxic activity. The preliminary structure–activity relationship analysis revealed that the electron-withdrawing groups installed at the para-position of arylamine ring had a great contribution to the improvement of the DHEA’s cytotoxic potency. Among them, (4-trifluoromethylaniline)-DHEA (4) displayed the most potent cytotoxicity, with an IC50 value of 19.3 µM, which was 2.3-fold more active than DHEA.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (702K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (702K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Kosuke Yoshikawa, Natsuki Kato, Takeshi Nanjo, Yoshiji Takemoto2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 354-359
Kosuke Yoshikawa, Natsuki Kato, Takeshi Nanjo, Yoshiji Takemoto2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 354-359
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録With the aim of achieving the convergent elongation of peptide chains, an amide bond formation reaction that enables a peptide fragment coupling has long been pursued. The decarboxylative amidation recently reported by our group is a potential solution to this problem. In this article, a mechanistic analysis of the t-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) mediated-decarboxylative amidation of α-ketoacids that results in a significant advance in convergent peptide synthesis is described. Despite the observation of epimerization with low bulk substrates in preliminary studies, a systematic examination and understanding of the reaction mechanism enabled the development of a modified epimerization-free reaction whereby peptide fragment couplings using peptide α-ketoacids were successfully achieved.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe development of peptide bond formation reaction enabling a convergent peptide fragment coupling is a major challenge of recent years for synthetic chemists due to the rapidly growing interest in the discovery of drugs base on the middle molecule peptides. The decarboxylative amidation recently reported by authors’ group is a potential solution to this problem. In this article, a mechanistic analysis and the further development of the t-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) mediated-decarboxylative amidation of α-ketoacids are described. A systematic examination and understanding of the reaction mechanism enabled a modified epimerization-free reaction whereby peptide fragment couplings using peptide α-ketoacids were successfully achieved.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1632K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kazunori Miwa, Yan Guo, Masayuki Hata, Norio Yamamoto, Tyuji Hoshino2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 360-367
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Computational screening is one of the fundamental techniques in drug discovery. Each compound in a chemical database is bound to the target protein in virtual, and candidate compounds are selected from the binding scores. In this work, we carried out combinational computation of docking simulation to generate binding poses and molecular mechanics calculation to estimate binding scores. The coronavirus infectious disease has spread worldwide, and effective chemotherapy is strongly required. The viral 3-chymotrypsin-like (3CL) protease is a good target of low molecular-weight inhibitors. Hence, computational screening was performed to search for inhibitory compounds acting on the 3CL protease. As a preliminary assessment of the performance of this approach, we used 51 compounds for which inhibitory activity had already been confirmed. Docking simulations and molecular mechanics calculations were performed to evaluate binding scores. The preliminary evaluation suggested that our approach successfully selected the inhibitory compounds identified by the experiments. The same approach was applied to 8820 compounds in a database consisting of approved and investigational chemicals. Hence, docking simulations, molecular mechanics calculations, and re-evaluation of binding scores including solvation effects were performed, and the top 200 poses were selected as candidates for experimental assays. Consequently, 25 compounds were chosen for in vitro measurement of the enzymatic inhibitory activity. From the enzymatic assay, 5 compounds were identified to have inhibitory activities against the 3CL protease. The present work demonstrated the feasibility of a combination of docking simulation and molecular mechanics calculation for practical use in computational virtual screening.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1312K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1312K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Junko Tsukioka, Seikou Nakamura2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 368-373
Junko Tsukioka, Seikou Nakamura2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 368-373
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDried and fermented (processed) leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla Seringe var. thunbergii Makino (Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium) are currently used as a crude drug with a sweet taste for diabetic patients and as an oral refrigerant. The sweet taste of this crude drug is primarily attributed to phyllodulcin. However, there are currently no standards for the cultivation of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii and the isolation and production of the primary constituents of this crude drug. In the present study, we prepared five types of soils with different pH values (pH 7.5–5.0) and investigated the effects of these soils on the growth of this plant. The contents of phyllodulcin and its glycoside, phyllodulcin 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, in the leaves of plants grown in these soils were quantified. Furthermore, the correlation between the sweetness of Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium and phyllodulcin was investigated. The results showed that soils with pH ranging from 7.0 to 5.5 was not only suitable for plant growth but also increased the content of phyllodulcin and phyllodulcin 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside in the leaves. Altogether, these findings could be useful for the development of high-quality Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium.
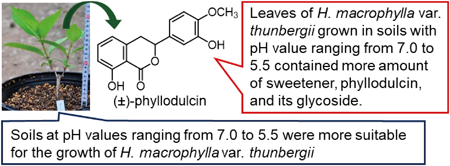 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla Seringe var. thunbergii Makino is listed as a Sweet Hydrangea Leaf (Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium) in the 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. The authors reported soils with pH ranging from 7.0 to 5.5 was not only suitable for this plant growth but also increased the content of phyllodulcin as sweetener in the leaves. In addition, a correlation between the sweetness of the crude drug and phyllodulcin was shown. These findings could be useful for the development of the crude drug with high-quality.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2099K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Tomoyasu Hirose, Kaori Ozaki, Yukiko Saito, Reiko Takai-Todaka, Hidehi ...2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 374-379
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Screening for bioactivity related to anti-infective, anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and anti-viral activity, led us to identify active compounds from a methanol extract of Litsea japonica (Thub.) Juss. and the hot water extract of bark of Cinnamomum sieboldii Meisn (also known as Karaki or Okinawa cinnamon). The two main components in these extracts were identified as the catechin trimers (+)-cinnamtannin B1 and pavetannin B5. Moreover, these extracts exhibited anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) activity. The structures of these catechin trimers were previously determined by chemical and spectroscopic methods. Pavetanin B5 has never been reported to be isolated as a pure form and has been obtained as a mixture with another component. Although other groups have reported the putative structure of pavetannin B5, preparation of the methylated derivative of pavetannin B5 in this study allowed us to obtain the pure form for the first time as the undecamethyl derivative and confirm its exact structure. Commercially available (+)-cinnamtannin B1 and aesculitannin B (C2′-epimer of cinnamtannin B1) both of which contained pavetannin B5 as a minor component, and C. sieboldii bark extract (approx. 5/2 mixture of (+)-cinnamtannin B1/pavetannin B5) were assessed for anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Both C. sieboldii bark extract and commercially available aesculitannin B showed viral growth inhibitory activity.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1079K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1079K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Abdul Rahim, Saidanxia Amuti, Ahmad Najib, Katsunori Miyake, Yohei Sai ...2023 年 71 巻 5 号 p. 380-384
発行日: 2023/05/01
公開日: 2023/05/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録A phytochemical study on Spermacoce ocymoides has led to the isolation of a novel bis-indole alkaloid, spermaocymine A (2), together with the known alkaloid 4-methyl-borreverine (1), as well as an anthraquinone, 8-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methoxyanthracene-9,10-dione (3). The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by analyzing spectroscopic and spectrometric data, including one-dimensional (1D)- and 2D-NMR and high resolution (HR)-MS. Newly isolated alkaloid 2 was a C-3,14-stereoisomer of 1, the first natural stereoisomer of related bis-indoles containing an indeno[1,2-b]indole skeleton with an epiminoethano bridge. When 1–3 were assayed against five tumor cell lines including multi-drug resistant cells, compound 1 exhibited potent antiproliferative activity with IC50 values of 6.2–11.5 µM.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (507K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (507K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|