-
Editor's pick
One of the oldest dye plants, Mercurialis leiocarpa (Euphorbiaceae), had been used as a blue dye until indigo dye appeared in Japan. The constituents are expected the application as medicines. In this paper, the authors isolated a new nitrogen-containing asymmetric dimer, leiocarpanine A, from the aerial parts of this plant and described the chemical elucidation, the estimation of the generation process, and the concise synthesis by mimicking the generation process through radical intermediates. This synthetic method provides a rapid and concise pathway to construct a library of nitrogen-containing dimers that might be useful for drug discovery.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 6 Pages 526-533Development of Specific Fluorogenic Substrates for Human β-N-Acetyl-D-hexosaminidase A for Cell-Based Assays Read moreEditor's pick
Inhibitors of human β-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidase A, hHEXA, have the potential to a pharmacological chaperone for Sandhoff disease and Tay-Sachs disease as lysosomal storage diseases. The hHEXA inhibitors have been shown to successfully enhance hHEXA levels, leading to the chronic form of these diseases. To develop hHEXA inhibitors, authors analyzed the hHEXA active site structure and designed the specific hHEXA fluorogenic substrates based on the authors’ substrate design platform. The designed substrates were synthesized and these were exhibited excellent specificity and sensitivity for hHEXA in three human cell lines. These are all new substrates that can be utilized to screen hHEXA inhibitors in human cells.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 6 Pages 534-537Development of Hydrophilic Polyacrylamide Gel-Based Condensing Reagents Comprised of Chlorotriazine Read moreEditor's pick
There is a great need for reagents that are environmentally benign, easy to handle, inexpensive, and safe in organic synthesis. In this context, the authors have developed hydrophilic polyacrylamide-gel based triazine-type condensing reagents, PAG-Trz-Cls, which were synthesized from inexpensive materials via radical polymerization. PAG-Trz-Cls are non-hygroscopic solid, high-loading, well-swollen in water and alcohol. Owing to these features, condensation between highly polar carboxylic acids and amines in an aqueous solvent successfully proceeded, and purification of the resulting amides can be readily carried out by filtration.
-
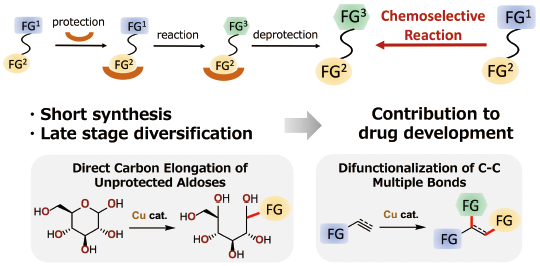
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 405-420Development of Copper-Catalyzed Chemoselective Reactions Read moreEditor's pick
“Soft” nature of copper catalysis enabled two types of chemoselective reactions. First, C-C bond forming reactions at an anomeric carbon of unprotected aldoses were developed by taking advantage of orthogonal reactivity between “soft” organocopper species and “hard” polar functional groups, free hydroxy groups. Second, preferential reaction between “soft” copper species and “soft” C-C multiple bonds enabled difunctionalization of the multiple bonds by controlling the reaction order of three reactive species. Well-controlled stereo- and/or regioselectivity of the reactions is another important feature of the copper catalysts.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 436-442Constituents of the Fruiting Body of Poisonous Mushroom Omphalotus japonicus Read moreEditor's pick
Omphalotus japonicus (Tsukiyotake in japanese) is well-known as a poisonous mushroom in Japan. In this study, the authors isolated six new sesquiterpenes, four known sesquiterpenes and two known steroids from the fruiting body of O. japonicus with column chromatography, solid-phase extraction (SPE), and HPLC. The chemical structures were determined with NMR, MS and IR spectra. Relative configuration was determined with NOE correlations and absolute configuration was determined with ECD calculation. Three new compounds showed growth-restoring activity against mutant yeast via calcium-signal transduction.
-
Editor's pick
This paper describes that the synthesis and evaluation of novel indirect adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators. The series of compounds selectively inhibited cell growth in several human breast cancer cell lines by activating AMPK. The back-up medicinal chemistry synthetic research on ASP4132, a previously reported clinical compound that acts as an indirect AMPK activator, led to the successful identification of 27b as a second-generation clinical candidate with promising profiles such as high aqueous solubility and less human Ether-a-go-go Related Gene (hERG) channel inhibitory activity.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 466-472Discovery of 1,3-Disubstituted 2,5-Diketopiperazine Derivatives as Potent Class I HDACs Inhibitors Read moreEditor's pick
The 2, 5-diketopiperazine (DKP) scaffold exists in many natural product families, ranging from fungi and bacteria to the plant kingdom and mammals. Because of the privileged structure and the ability to bind vast receptors, it has become extremely attractive synthetic target for the assembly of natural product-like libraries for drug discovery. In this article, a series of novel derivatives containing DKP skeleton were developed as targeted inhibitors. Several compounds exhibited distinct HDAC1 inhibitory activities and showed antiproliferative activities against K562 and HL-60 tumor cell line.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 473-478Instrument-Dependent Factors Affecting the Precision in the Atomic Force Microscopy Stiffness Measurement of Nanoscale Liposomes Read moreEditor's pick
Instrument-dependent factors affecting the precision in the atomic force microscopy stiffness measurement of nanoscale liposomes was examined. The tip shape evaluation method previously developed can be widely used via IC-mode force curve measurements as well as via QI mode. It was also revealed that spatial drift of the cantilever position was instrument-dependent factors which could affect the precision of liposome stiffness measurements in the case of IC-mode force curve measurement. These findings will promote the usage of the AFM stiffness measurement method for the characterization of lipid nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems.
-
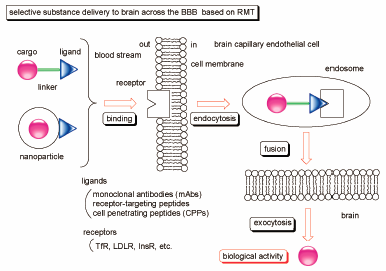
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 4 Pages 316-325Smart Strategies for Therapeutic Agent Delivery into Brain across the Blood–Brain Barrier Using Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis Read moreEditor's pick
In drug development, drug delivery into brain across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a serious problem. Particularly, the BBB is impermeable to large and medium-sized molecules. Accordingly, drugs for diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) are unable to elicit their activity in brain. However, receptor-mediated transcytosis can solve such impermeability. Actually, using receptors such as transferrin receptor (TfR), low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), and insulin receptor (InsR), that express on the surface of brain capillary endothelial cells, delivered well-designed drugs into brain through endocytosis and exocytosis. This methodology will be a promising approach to cure patients suffering from CNS diseases.
-
Editor's pick
An efficient synthetic method for 2,5-disubstituted tetrazoles from 5-substituted tetrazoles is developed. In this paper, the authors established a cobalt-catalyzed site-selective alkylation of tetrazoles via atom-economic hydroamination reaction between tetrazoles and non-activated olefins. The authors also applied the developed reaction to an asymmetric intermolecular hydroamination of non-activated olefins, which is one of the longstanding problems in synthetic organic chemistry.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 4 Pages 345-362Design and Synthesis of 2-(1-Alkylaminoalkyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines as New Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein Inhibitors Read moreEditor's pick
This report describes the design, synthesis, and evaluation of a new series of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives for treatment against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine series of compounds containing a piperidine ring at the 2-position of the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold are known as candidate RSV fusion (F) protein inhibitor drugs. The piperidine ring has been revealed to facilitate the formation of an appropriate dihedral angle between the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold and the plane of the amide bond for exertion of anti-RSV activity. A molecular-dynamic study on pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives focusing on the dihedral angles proposed and demonstrated potent anti-RSV inhibitors with an acyclic chain instead of a piperidine ring. A subsequent optimization study on pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives containing 1-methylaminopropyl group led to a highly potent anti-RSV agent with an EC50 value of less than 1 nM.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 4 Pages 380-383Total Syntheses and Cytotoxic Evaluations of Cryptolactones A1, A2, B1, B2, and Their Derivatives Read moreEditor's pick
Aphids have unique polyketide pigments, which possess interesting biological activities such as cytotoxicity. In this article, the authors have focused on cryptolactone A1, A2, B1, and B2, colorless polyketide lactones, isolated from a colorless aphid, Cryptomyzus sp., and accomplished the asymmetric total syntheses of these compounds, their analogs bearing shorter carbon chains, and their antipodes. The investigation of structure-activity relationships among these compounds was carried out and revealed that both enantiomers exhibited similar cytotoxic properties towards HL-60 cell lines. However, compounds with shorter carbon chains were less cytotoxic than the others.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 4 Pages 384-391Nucleophilic Addition Reaction with Dearomatization of Naphthalene Ring Read moreEditor's pick
Organic reactions using dearomatization have attracted much attention as a new approach to constructing complicated cyclic molecules. This paper describes the regioselectivity of nucleophilic addition of organolithium species (in particular, n-BuLi and sec-BuLi) to various aromatic lactones. The results of many experiments indicated that the regioselectivity varied greatly depending on various factors, such as the bulkiness of both substrates and organolithium species, and types of solvent and cosolvent. It is particularly interesting that the reactions mechanism of the addition of organolithium species differed between n-BuLi (via ionic process) and sec-BuLi (via one electron transfer process).
-
Editor's pick
Cutting-edge contributions from invited poster presentations providing significant research works in the fifth International Symposium for Medicinal Sciences (ISMS) in the 139th Chiba annual meeting in 2019 are assembled for the Current Topics section in this issue of the Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.
-
Editor's pick
The principal catalytic reaction of ferric lipoxygenases is dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids under normoxia. On the contrary, at a lower oxygen content, lipoxygenases concomitantly convert polyunsaturated fatty acids and their hydroperoxides into fatty acid allyl-radicals and fatty acid alkoxyl radicals, respectively, through one-electron redox reaction. The former radicals simultaneously react with oxygen molecule, producing fatty acid peroxyl radicals. In general, free radicals tend to abstract one electron from molecules. However, fatty acid alkoxyl radicals donate one electron to the aggressive free radicals including fatty acid peroxyl radicals, resulting in the oxo-fatty acids generation, which act as PPAR agonists.
-
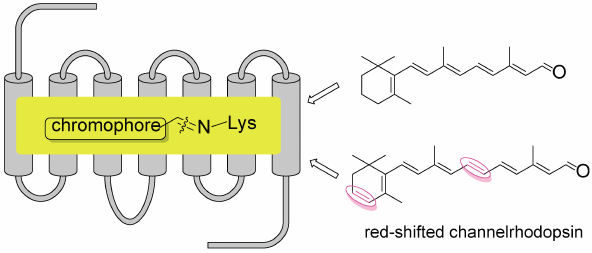
Editor's pick
Optogenetics is a new technology to control neural activity by light using ChRs. ChRs now used in optpgenitics are mostly sensitive to blue-green light (430-550 nm), and have several limitations. To overcome these problem, the development of red-shifted ChRs are eagerly required. In this paper, six kinds of new chromophores with one double bond inserted into the polyene side chain of retinal (A1) or 3,4-didehydroretinal (A2) were prepared. Among them, A2-10ex (an extra double bond was inserted at C10-C11 position of A2) bound with ChrimsonR to afford new ChR with the greatest red-shifted absorption peak at 654 nm.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 3 Pages 273-287Novel Steroidal Glycosides from the Whole Plants of Helleborus foetidus Read moreEditor's pick
Phytochemical analysis of the whole Helleborus foetidus plants identified 28 steroidal glycosides, including 20 novel spirostanol glycosides and a novel furostanol glycoside. The structures of the newly identified compounds were elucidated by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy and hydrolytic cleavage. Three isolated compounds were determined to be spirostanol trisdesmosides, which are unique in structure bearing sugar moieties at the C-1, -21, and -24 hydroxy groups of the aglycone unit. The isolated compounds were evaluated for cytotoxic activity against HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells and A549 human lung carcinoma cells, and several compounds exhibited moderate cytotoxic activity.
-
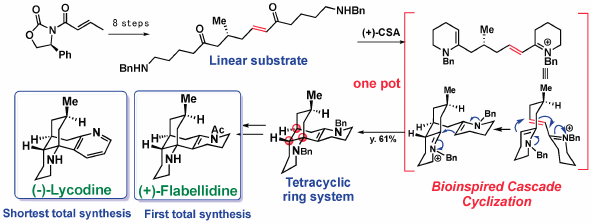
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 2 Pages 103-116Total Syntheses of Lycopodium and Monoterpenoid Indole Alkaloids Based on Biosynthesis-Inspired Strategies Read moreEditor's pick
The lessons from nature on biosynthesis of natural products might be beneficial for synthetic organic chemists to design unique synthetic approaches as well as to facilitate development of new synthetic methodologies. This review emphasized the merits of biosynthetic consideration in the chemical synthesis of complex natural products by describing the total syntheses of Lycopodium alkaloids and monoterpenoid indole alkaloids conducted in author’s laboratory.
-
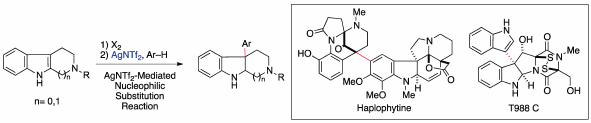
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 2 Pages 117-128Synthetic Studies toward Dimeric Indole Alkaloids Based on Convergent Synthetic Strategy Read moreEditor's pick
Various dimeric compounds comprising two structurally different indole units are ubiquitous in nature. These compounds are a pharmaceutically important class of natural products because several compounds in this class exhibit display greater potency and unique biological activities compared with the corresponding monomeric compounds. In particular, these dimeric compounds, which possess molecular weights that deviate from Lipinski’s rule, are anticipated to be useful as new drug candidates in the middle molecule drug discovery. This review presents an overview of efficient convergent syntheses of dimeric indole alkaloids, haplophytine, and T988s with the development of synthetic methodologies for linking the two indole units.
-
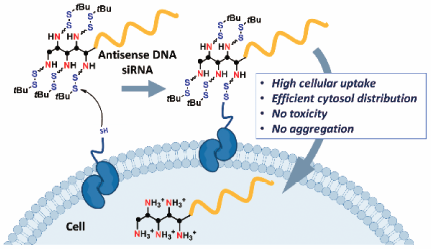
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 2 Pages 129-132Intracellular Delivery of Antisense DNA and siRNA with Amino Groups Masked with Disulfide Units Read moreEditor's pick
A new efficient delivery method of oligonucleotide (ON) therapeutics is developed. Here, antisense ON and small interfering RNA (siRNA) with disulfide-masked amino units were designed and synthesized for efficient intracellular delivery. The developed method actually enabled direct delivery of these ON into the cytosol, where these ON showed the targeted silencing effects, with minimal cytotoxicity. The molecular design and evaluation reported in this article would be very informative for further developing efficient cytosol-delivery methods of therapeutic ONs for medicinal application.