-
Volume 69 (2021) Issue 1 Pages 118-123Absolute Purity Determination of a Hygroscopic Substance, Indocyanine Green, Using Quantitative NMR (qNMR) Read moreEditor's pick
Quantitative NMR (qNMR) has emerged as a new absolute quantitation method for small molecules. Authors examined the absolute purity determination of a hygroscopic substance indocyanine green (ICG) using qNMR. The three different humidity conditions yielded comparable purity means of 86.12 ± 2.70%, 84.19 ± 0.47%, and 82.26 ± 0.19% under non-controlled humidity, controlled humidity using a saturated NaBr solution, and using a constant temperature and humidity box, respectively. As the results using the constant temperature and humidity box showed the lowest variability, it is recommended to use it if the reference standard of ICG with its purity value is needed for Japanese Pharmacopoeia assays.
-
Volume 69 (2021) Issue 1 Pages 124-140β-Selective Glycosylation Using Axial-Rich and 2-O-Rhamnosylated Glucosyl Donors Controlled by the Protecting Pattern of the Second Sugar Read moreEditor's pick
Stereoselectivity in chemical glycosylation frequently varies in reaction substrates. This paper describes the influence of the protecting groups on rhamnose connected to the 2-O position of a glucosyl donor with axial-rich conformation on stereoselectivity in its glycosylation with cholestanol. The authors revealed that two bulky silyl groups existing at the 3-O and 4-O positions of rhamnose synergistically enhanced β-selectivity. In contrast, the silyl group introduced to the 2-O position decreased the selectivity. These results suggest that appropriately designing a protecting-group pattern for another sugar far from the reaction center of a glycosyl donor can control the stereoselectivity of glycosylation.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 12 Pages 1184-1192Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-(4-Methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-arylpyrimidin-2-amines as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors Read moreEditor's pick
Tubulin is an important target for developing anticancer drugs. To discover novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors, the authors designed and synthesized a new series of pyrimidine-based compounds based on the principle of molecular hybrid-based approach. Several compounds exhibited potent anti-tubulin activity and showed antiproliferative activities against MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cell lines. The results indicated that these compounds may have the potential for further development as anticancer agents.
-
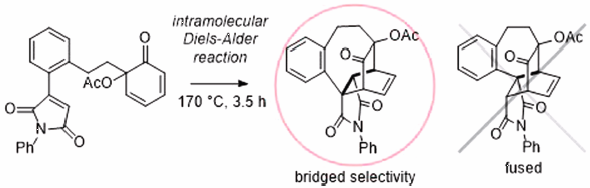
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 12 Pages 1201-1209Bridged-Selective Intramolecular Diels–Alder Reactions in the Synthesis of Bicyclo[2.2.2]octanes Read moreEditor's pick
Intramolecular Diels-Alder (IMDA) reactions are powerful synthetic methods for construction of complex carbon skeletons from relatively simple starting materials. Regioselectivity for producing fused or bridged products by the IMDA reactions is very important for planning a rational synthetic route for target molecules. It has been well known that the IMDA reactions usually provide fused products, while factors for selective formation of bridged products has not been understood well. The authors experimentally found some factors for giving bridged products selectively in IMAD reactions, and they explained the reasons for the observed bridged selectivity by DFT calculations.
-
Editor's pick
Stimulus-responsive molecules that modify nucleic acids in a site- and base-selective manner play an important role for genomic research. N-Acetyl-7-nitroindoline is a characteristic in that its acetyl group is photo-activated to acetylate amines to form amides. In this study, the N-acetyl-7-nitroindoline part was connected to the 2´-deoxyribose part, which was incorporated into the oligodeoxynucleotide probes, and their photo-reactivities toward the complementary RNA were investigated. One probe was photo-activated to deacetylate to the nitroso derivative. Photo-activation of another probe induced acetylation of the RNA. An interesting finding was the cross-link formation of another probe with the RNA strand.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 12 Pages 1220-1225Development of Nitrolactonization Mediated by Iron(III) Nitrate Nonahydrate Read moreEditor's pick
Nitrogen dioxide has been used as an oxidant and nitrating reagent in organic synthesis. However, its use is limited because it is harmful and hard to handle. Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate has attracted attention as a source of nitrogen dioxide because it is a readily available reagent of low toxicity and cost. This paper describes development of nitrolactonization mediated by iron nitrate as a source of nitrogen dioxide. Nitrolactones obtained by this reaction could lead to useful compounds, such as 1,2-aminoalcohol and amino acid derivatives bearing a tetrasubstituted carbon center.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 12 Pages 1226-1232Sequence-Independent Traceless Method for Preparation of Peptide/Protein Thioesters Using CPaseY-Mediated Hydrazinolysis Read moreEditor's pick
Peptide/protein thioesters function as an indispensable synthetic intermediate in Native Chemical Ligation (NCL) that has enjoyed great success in the chemical synthesis of proteins. Facile conversion of recombinant proteins to thioesters allows for the straightforward access to semi-synthetic proteins with chemically synthesized peptides used as an NCL partner. In this paper, the authors developed an efficient thioester-producing protocol. The protocol features the traceless conversion of the CysPro triple repeat–Leu-OH-tagged sequence to the corresponding thioesters by treatment with carboxypeptidase Y in the presence of hydrazine followed by an auto-processing of the CysPro units.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 11 Pages 1013-1024Effect of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Component Ratio on Analytical Performance Read moreEditor's pick
Molecular imprinting has been broadly perceived as the most advanced technology for preparing various materials that have a specific recognition site with selective adsorption. MIPs (Molecular Imprinted Polymer) are three-dimensional polymers with specific recognition sites for a certain molecule. A MIP is formed by crosslinking template with monomers to create copolymers. For every MIP, each template:monomer:crosslinker ratio shows a distinct performance for a specific analyte. Ratio effect on analytical performances are briefly outlined in this review. From all reports in this review, the synthesis of MIP using a template:monomer:crosslinker ratio of 1:4:20 is more likely to provide optimal imprinting efficiency.
-
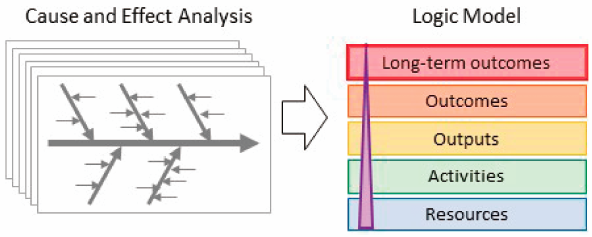
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 11 Pages 1034-1048Development of a Logic Model for Promoting Incorporation of the Concepts of Impurity-Related ICH Guidelines into Pharmacopoeias Based on Cause and Effect Analysis Read moreEditor's pick
With the globalization of the drug supply chain, the quality assurance of drugs is required worldwide. Pharmacopoeias provide public standards for the drug quality assurance, and smooth incorporation of the concepts of the international guidelines into pharmacopoeias is desired. In particular, impurities in drugs are to be controlled to ensure patient safety. The authors focused on the harmonized guidelines for residual solvents, elemental impurities, and mutagenic impurities, and proposed an approach for promoting incorporation of the concepts of the guidelines into pharmacopoeias by combining the cause and effect analysis and the logic model.
-
Editor's pick
In clinical practice, a thickening solution is frequently used to allow easy swallowing of tablets as well as foods by patients suffering from dysphagia. This study investigated the effect of thickening solution on tablet disintegration. Model tablets containing different disintegrants were prepared and their disintegration times were measured. The tablet disintegration times were significantly prolonged by immersion in thickening solution containing xanthan gum and the degree of prolongation differed depending on the type of disintegrant contained in the tablets. These findings provide valuable information for design of tablet formulation and clinical medication management for older patients with dysphagia.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 11 Pages 1074-1081Fragment-Based Discovery of Irreversible Covalent Inhibitors of Cysteine Proteases Using Chlorofluoroacetamide Library Read moreEditor's pick
Chlorofluoroacetamide (CFA) shows chemically tuned mild reactivity that is suitable as an electrophilic warhead for highly target selective covalent inhibitors. Assembly of a small set of CFA-appended fragment library and its screening against cysteine protease papain demonstrated the potential utility of CFA in novel covalent drug discovery using a fragment-based approach.
-
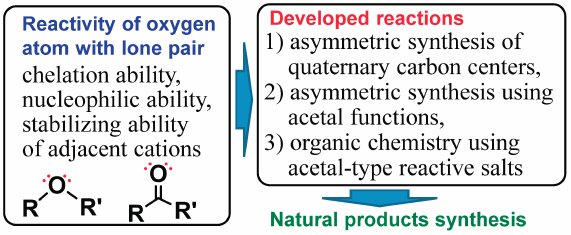
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 10 Pages 907-945Development of New Innovative Synthetic Organic Chemistry Using Lone Pairs of Oxygen Atoms Read moreEditor's pick
This review describes development of innovative reactions utilizing the characteristic reactivity of oxygen atoms, 1) asymmetric synthesis of chiral quaternary carbon centers, 2) asymmetric synthesis using acetal functions, and 3) organic chemistry using acetal-type reactive salt chemical species, and their application to the asymmetric synthesis of natural products such as Fredericamycin A, anthracycline antibiotics, scyphostatin, Sch 642305, stenin, claboronin, rubrenolide, rubrynolide, centrolobine, and decytospolides A and B, etc. In particular, reactions using acetal-type reactive salt chemical species can alter the retrosynthesis planned based on conventional reactions because they allow the coexistence of functional groups that normally cannot coexist.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 10 Pages 954-961Binding Assays Using a Benzofurazan-Labeled Fluorescent Probe for Estrogen Receptor–Ligand Interactions Read moreEditor's pick
Binding assays are widely used to study the estrogenic activity of endocrine-disrupting chemicals targeting the estrogen receptor (ER). In this study, the authors synthesized benzofurazan-labeled estradiol (BD-E2) derivatives as a fluorescent ligand for ER binding assays. BD-E2 compounds exhibit spectroscopic properties with high fluorescence intensities and large Stokes shifts in a hydrophobic environment. Analysis of the fluorescent ligands and human recombinant ER interactions revealed that the fluorescence intensity increased in hydrophobic environments, such as the receptor-binding site. By evaluation of the bound ligands based on changes in the fluorescence intensity, the authors established a simple, rapid, reliable ER binding assay.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 10 Pages 989-995Evaluation of Dantrolene Granules Extemporaneously Reformulated from Capsules in a Pharmacy Read moreEditor's pick
An extemporaneous preparation, sodium dantrolene granules, has been manufactured using planetary centrifugal granulation method in the pharmacy. The amount of water was determined based on plastic limit value of the formulation, which is a critical parameter of the granulation method. The granulation process completes within 45 s, followed by coating process (20 s). The resultant granules show sharp particle size distribution and excellent flowability. The bulky powder was reformulated to the granules with non-adhesive and free-flowing properties. Thus, the granulation improves the usability of the medicine in the dispensing and dosing processes.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 10 Pages 1001-1007Nitrate Ion Adsorption Characteristics of Activated Carbon Fibers with and without Quaternary Nitrogen Effective for Anion Adsorption Read moreEditor's pick
The quaternary nitrogen (N-Q) has been found to be an effective adsorption site for nitrate ions. However, in addition to N-Q, there are many functional groups such as C-π sites on activated carbon fibers (ACFs), and these functional groups have various effects on the adsorption capacity. Understanding the properties of functional groups other than N-Q can be expected to further improve ACFs adsorption performance. In this paper, the authors prepared the ACFs with and without N-Q and examined their adsorption properties.
-
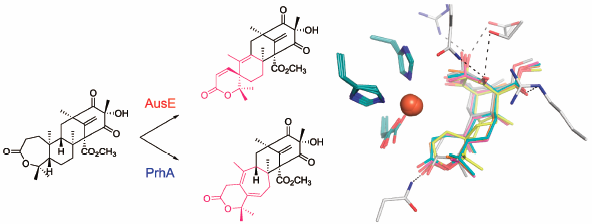
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 9 Pages 823-831Nonheme Iron- and 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases in Fungal Meroterpenoid Biosynthesis Read moreEditor's pick
The fungal meroterpenoid biosynthetic pathways exhibit an abundance of unusual chemistries and interesting enzyme reactions, including those of the multi-functional non-heme Fe(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases that perform selective C–H activation/functionalization with unusual substrate promiscuity and catalytic versatility. Structure–function studies of these remarkable enzymes provide an excellent platform for the development of useful biocatalysts for synthetic biology to create novel molecules for drug discovery.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 9 Pages 832-836Effect of Rubbing on the Distribution of Topically Applied Drugs into the Hair Follicles Read moreEditor's pick
Rubbing actions are often conducted to apply topical formulations onto the skin. However, few studies have reported the reasons for the acceleration of drug permeation through skin after topical application with or without rubbing. In addition, no studies observed the effect of rubbing direction on the skin penetration-enhancement effects. In this paper, the authors investigated the effects of rubbing direction on the skin permeation and disposition of a model hydrophilic drug, caffeine. This paper provides useful information on the effect of rubbing action and rubbing direction on the skin permeation of topically applied drugs.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 9 Pages 864-867Iriomoteolides-14a and 14b, New Cytotoxic 15-Membered Macrolides from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species Read moreEditor's pick
Marine dinoflagellates are well known as rich sources of biologically active compounds possessing unique chemical structures. This paper deals isolation and structure elucidation of two new cytotoxic 15-membered macrolides, iriomoteolodes-14a and 14b, from the marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium species collected off Iriomote Island, Okinawa. The structures including the absolute stereochemistry of eight stereocenters were determined on basis of spectroscopic data and chemical conversion method. These compounds are analogous to known macrolides, amphidinolides O and P, and the biosynthetic relationships for four compounds are also described.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 9 Pages 868-878Collaborative Study to Validate Purity Determination by 1H Quantitative NMR Spectroscopy by Using Internal Calibration Methodology Read moreEditor's pick
Quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance is a powerful tool in quantitative determination of the main component and impurities in a drug substance or a drug product because of its high accuracy, precision and efficiency. This method has the potential to establish metrological traceability easily and expected to be widely utilized for some compendial guidelines and official standards. In this study, the authors conducted an inter-laboratory comparison for qNMR methodology and confirmed that statistically qNMR has the competence to obtain the same quantification performance and accuracy as the conventional reliable methods.
-
Volume 68 (2020) Issue 9 Pages 885-890Labeling of Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress Hotspots by Hemin-Catalyzed Tyrosine Click Read moreEditor's pick
Tyrosyl radical generation plays a major role in hemin/peroxide-induced oxidative stress. The authors developed a method for trapping tyrosyl radicals using a derivative of N-methyl luminol, a tyrosine labeling reagent. The derivative selectively forms a covalent bond with tyrosine residue (tyrosine click reaction) under single-electron oxidation conditions. This reaction labels oxidative stress hotspots not only at the protein level but also at the level of tyrosine residues undergoing oxidation. The cover picture depicts an image of tyrosine click reaction to aid in the visualization of hemin/peroxide-induced oxidative stress generated in blood vessels.