
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Mengchao YE, Jinxia MA, Chao XIANG, Fengjiao HE2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057001
発行日: 2023/05/17
公開日: 2023/05/17
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLMetal Cu has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, but poor mechanical properties. Incorporating ceramic particles into the Cu matrix to prepare Cu-based composites is one of the most effective methods to improve the mechanical properties. This paper reports a simple and efficient one-step method for the electrochemical preparation of nano-Al2O3 reinforced Cu-based composite; the electrodeposition process and properties of the prepared materials were also studied. Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy measurements showed that the Al2O3 nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed in the Cu matrix of the electrodeposited Cu–Al2O3 composites. Incorporating Al2O3 nanoparticles affected the grain size and microstructure of the composites, improving the mechanical properties of the Cu matrix. Increasing the Al2O3 concentration in the electrolyte resulted in the grain size of the composites decreasing to a range of 40.8–98.5 nm. Meanwhile, the preferred orientation of the present composites changed from (111) to (220) crystal plane. The Cu–Al2O3 composite had a tensile strength of 509 MPa, a hardness of 220 Hv, and an elongation to failure of 23.88 %, indicating that the material had a high tensile strength while maintaining excellent ductility. Compared with the original monolithic Cu, the performance of the Cu–Al2O3 composite was nearly doubled.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5821K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Taro KINUMOTO, Toru TOMITA, Mai SATO, Miki MATSUOKA, Ryuta ICHIKI2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057002
発行日: 2023/05/19
公開日: 2023/05/19
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/04/08ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLAn atmospheric-pressure nitrogen plasma jet (APN2PJ) treatment for conductive boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrode is reported for the first time. APN2PJ is a unique technique that can generate NH and nitrogen-related radicals at high density even under atmospheric pressure. These radicals attacked BDD, changing its surface morphology and introducing nitrogen doping as far as inner part of BDD. In addition, “sediments” appeared on the surface after APN2PJ treatment. The specific capacitance of BDD was increased after APN2PJ treatment. Furthermore, a further increase in the specific capacity was observed after sonication of the treated samples, which might be related to the disappearance of these “sediments”.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4977K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Jianke LI, Wenjie LIANG, Xincheng MIAO, Beibei HAN, Guiying XU, Kun WA ...2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057003
発行日: 2023/05/19
公開日: 2023/05/19
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/04/14ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
J-STAGE DataHerein, the novel sodium ion hybrid capacitors (SIHCs) are successfully and facilely fabricated by utilizing the same carbon resource of magnesium citrate. Namely, the carbons which are fabricated by immediate carbonizations of magnesium citrate are used as positive electrodes, and N, S-doped carbons prepared by co-carbonizations of magnesium citrate with ammonium persulfate are determined as negative electrodes. The detailed electrochemical evaluations demonstrate that fabricated SIHCs possess tremendous Na+ storage performance. For instance, the fabricated SIHC(1//1) shows an energy density of 100.8 Wh Kg−1 at a power density of 136.8 W Kg−1, when current density was 0.1 A g−1. Furthermore, when the current density was set at 5.0 A g−1, this SIHC(1//1) also exhibits a power density of 12957.6 W Kg−1 at an energy density of 46.9 Wh Kg−1. These results reveal that SIHC(1//1) has the powerful competitiveness in high energy and power-required electricity storage applications.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (6149K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hikaru SANO, Yusuke MORINO, Yasuyuki MATSUMURA, Koji KAWAMOTO, Hiroyuk ...2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057004
発行日: 2023/05/26
公開日: 2023/05/26
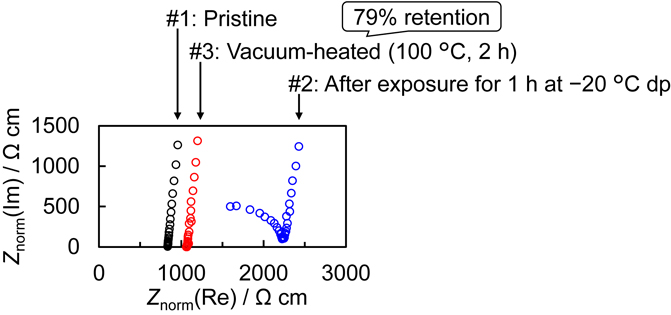
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLSulfide-based solid electrolytes are desirable for use in all-solid-state batteries owing to their high ionic conductivity and plasticity. However, they generally degrade upon exposure to water and can generate toxic hydrogen sulfide even in dry-room atmospheres. To prevent their degradation, surface stabilization is required and further research into the degradation mechanism is necessary. In the present study, the stability of Li3PS4–LiI glass ceramic (LPSI) has been examined under low-humidity conditions. In contrast to an argyrodite-type solid electrolyte, exposure of LPSI to dry air with a dew point of −20 °C resulted in low H2S-gas generation and reduced ionic conductivity of LPSI. Since the conductivity mostly recovered after vacuum heating at 100 °C, the H2S generation is not considered to be the major reason for the reduction in conductivity. On the contrary, it is suggested that water molecules are present on the LPSI powder particles after dry-air exposure, resulting in the formation of a degraded LPSI layer and low ionic conductivity, and that most of the water molecules are removed during vacuum heating, resulting in the recovery of conductivity. Furthermore, optimal vacuum-heating conditions were obtained from X-ray diffraction and temperature-programmed desorption-mass spectrometry measurements, indicating an optimal temperature and heating time of 100 °C and 2 h, respectively. Impedance measurements were used to probe the degradation of the surface layer. The condition of the surface layer was affected by the pellet-forming pressure, and it was easier to detect the degradation of the surface layer when the pellets were formed at low pressures. This paper contributes to the formulation of guidelines for the development of water-resistant solid electrolytes.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3251K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3251K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Fengcui LI, Chengyuan LIU, Rujia LIU, Jiangyu YU, Zhiwei LIU2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057005
発行日: 2023/05/27
公開日: 2023/05/27
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/05/03ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
J-STAGE DataThe effect of electrolyte additive 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) on the electrochemical stability of aluminum-graphite battery using acetamide-AlCl3 electrolyte is investigated comparatively. Original dendritic and dead aluminum are observed in Al-Al cells at a high operation rate. Original dendritic and dead aluminum are observed in the anode and separator of Al-Al cells at a high operation rate. DCE is a preferred electrolyte additive to reduce the polarization of the acetamide-AlCl3 electrolyte. Furthermore, DCE can effectively suppress the dendrites on the Al anode in Al|acetamide-AlCl3|Al cells. Besides, it has a positive effect on improving the discharge specific capacity and cycle stability of aluminum-graphite batteries with a high coulombic efficiency over 300 cycles. This result indicates that organic additive is suitable to improve the electrochemical performance of aluminum-graphite batteries.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3919K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Wen LI, Hao ZHOU, XueKe LUO, BinBin LYU, SiJia HAO2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057006
発行日: 2023/05/31
公開日: 2023/05/31
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/05/03ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLA novel approach for real-time detection of lithium-ion battery thermal runaway has been proposed to enable the monitoring of thermal runaway states during storage, transportation, and use, and to prevent safety hazards such as fire and explosion. This approach uses the fusion of high-precision, high-sensitivity photoelectric and electrochemical detection techniques based on the dual-wavelength principle. To analyze the thermal runaway mechanism of lithium-ion batteries, four important gas parameters — CO, EX, H2, and CO2 — were obtained to indicate the thermal runaway state, and the characterization of these parameters under different thermal runaway states of lithium-ion batteries was studied. A real-time detection system is designed and validated through experiments involving overcharging, over-discharging, and puncturing of lithium-ion batteries. This method is suitable for the real-time detection of thermal runaway in lithium-ion battery products and can also provide a basis for evaluating the life and reliability of lithium-ion batteries.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4168K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hongyi LI, Siqi TONG, Hongfa WANG, Yi WANG2023 年 91 巻 5 号 p. 057007
発行日: 2023/05/31
公開日: 2023/05/31
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
J-STAGE DataMicrobial desalination cells (MDCs) provide a sustainable approach to desalinate saltwater powered by bacterial metabolism during organic oxidation. A systematic study was conducted to clarify the ion-dominated interactions for preventing unpredictable risks for long-term MDC operations in the treatment of complex ion-containing wastewaters. The investigation showed that the migration and unequal scaling of cations at different ion exchange membrane (IEM) surfaces greatly influenced their transmembrane processes, which were directly affected by the hydrolysis and precipitation behavior controlled by the solubility product and ambient solution, resulting in the following removal efficiency of MDCs: Na+ > Ca2+ > Cu2+ > Al3+ > Fe3+. A further study showed that the precipitation antagonism and pH buffer effect of multiple cations could positively promote the desalination of sparingly soluble cations. Eventually, the desalination efficiency of MDC in the treatment of actual industrial tailwater was maintained at 63.2–74.1 %. These findings not only elucidated the kinetics of ion migration in detail but also offered new application possibilities for MDCs.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (7360K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (7360K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|