
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
船川 義正原稿種別: オーバービュー
2017 年 81 巻 10 号 p. 447-457
発行日: 2017/10/01
公開日: 2017/09/25
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe interface-precipitation has been observed as row carbide arrange since 1960’s. Whereas the interface-precipitated carbides in steels were NbC, TiC, VC and Cr23C6 in the early stage, composite TiC containing Mo and W has been also become to observe recently. Several kinds of the mechanism of the interface-precipitation have been suggested and ledge mechanism and bowing mechanism which combined interface barging and carbide precipitation are widely accepted since the mechanisms successfully explained a large amount of the experimental results. Fine interface-precipitates in low carbon steel realize high strength steel sheets, plates, bars and rods which are non-quenched and tempered. Especially, in sheet products, in which fine carbides can be easily generated, ferritic steel of 1180 MPa in tensile strength is successfully obtained by dispersing fine carbides with the diameter of several nano-meters.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2079K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
力久 弘章, 森 貴志, 津志田 雅之, 北原 弘基, 安藤 新二原稿種別: 論文
2017 年 81 巻 10 号 p. 458-466
発行日: 2017/10/01
公開日: 2017/09/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/07/28ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this study, tensile tests of Mg-Y alloy single crystals and polycrystals were carried out to investigate influence of yttrium on activities of <c+a> slip systems and a relationship between ductility of magnesium and active <c+a> slip systems. Tensile directions of the single crystals and the polycrystals were parallel to (0001) and its rolling direction, respectively. Both tests were carried out at room temperature. Yield stress and ductility of Mg-(0.6-1.1)at%Y alloy single crystals were higher than that of pure Mg and the crystals were yielded due to first order pyramidal <c+a> slip (FPCS). Mg-0.9 at%Y alloy polycrystals showed higher ductility than pure Mg. The number of grains in which second order pyramidal slip can be activated was larger than that of non-basal slips in pure Mg, while the number for FPCS was increased with increasing strain in Mg-0.9 at%Y alloy. We supposed that high ductility of Mg-0.9 at%Y alloy would be caused activation of FPCS by yttrium addition.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2143K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
杉尾 健次郎, 崔 龍範, 佐々木 元原稿種別: 論文
2017 年 81 巻 10 号 p. 467-474
発行日: 2017/10/01
公開日: 2017/09/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/07/28ジャーナル フリー HTMLTo investigate the degree of the effect of the interfacial thermal resistance between the matrix and the reinforcement, the effective thermal conductivity of aluminum matrix composites (Al/SiC, Al/TiB2, Al/Al2O3 and Al/SiO2) was calculated with the new simulation code which can take account of heat transfer at the interface. The critical element size was defined by a simple equation, Lcr = h/λ, where λ is the harmonic mean of thermal conductivities of the reinforcement and the matrix, and h is the coefficient of heat transfer between the reinforcement and the matrix. This critical element size is important value to design composites. If the size of the reinforcement is smaller than the critical element size, it is predicted that the effective thermal conductivity will decrease by the interfacial thermal resistance. On the other hand, if the size of the reinforcement is large enough, the effective thermal conductivity will not decrease. The validity of the critical element size for aluminum matrix composites was confirmed in this study.
Mater. Trans. 57(2016) 582-589に掲載
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1763K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
相原 雄太, 鎌田 康寛, 村上 武, 小林 悟, 渡辺 英雄原稿種別: 論文
2017 年 81 巻 10 号 p. 475-479
発行日: 2017/10/01
公開日: 2017/09/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/08/04ジャーナル フリー HTMLWe investigated the microstructure, magnetic hysteresis properties, and micro-Vickers hardness of nuclear reactor pressure vessel(RPV)steel cladded with austenitic stainless steel. Characterization of the crystalline structure by electron backscatter diffraction revealed the existence of a delta ferrite phase in the austenitic cladding, and the formation of coarse and fine grain microstructures in the heat affected zone(HAZ)of the RPV steel. The block specimen was cut into small pieces and magnetic hysteresis loops were measured with a vibrating sample magnetometer. Although the saturation magnetization of the RPV steel was constant, the coercivity in the HAZ region decreased gradually as a function of distance from the weld fusion boundary. A linear correlation was confirmed between the coercivity and hardness. This study demonstrates the feasibility of a magnetic evaluation of hardness and microstructures in RPV steel.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1383K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
小笹 良輔, 松垣 あいら, 礒部 仁博, 佐久 太郎, 中野 貴由原稿種別: 論文
2017 年 81 巻 10 号 p. 480-484
発行日: 2017/10/01
公開日: 2017/09/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/08/04ジャーナル フリー HTMLBone tissue has a highly anisotropic microstructure composed of biological apatite (BAp) and collagen fibrils, which is closely related to bone mechanical function. The formation of anisotropic bone microstructure is governed by bone-forming osteoblasts; therefore, establishment of isolation method of osteoblasts and assessment of their arrangement for generating bone tissue with optimally oriented microstructure during bone reconstruction are important. In this study, we established the isolation and culture conditions of mature osteoblasts derived from juvenile mice (2-week-old). Osteoblasts from juvenile mice expressed significantly higher level of osteoblastic markers (alkaline phosphatase, osterix, and osteocalcin) than osteoblasts from neonatal mice, indicating that juvenile osteoblasts are promising materials for bone tissue engineering. Moreover, the mature osteoblasts aligned along the collagen molecule direction of substrate. This is the report that shows preferential orientation of mature osteoblasts isolated from juvenile mice.
Mater. Trans. 58(2017) 958-962に掲載
 Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageSchematic illustration of the procedure of primary osteoblast culture on oriented collagen substrate. Phase contrast image indicates osteoblasts migrating from bone chip. Scale bars=100 µm.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1102K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageSchematic illustration of the procedure of primary osteoblast culture on oriented collagen substrate. Phase contrast image indicates osteoblasts migrating from bone chip. Scale bars=100 µm.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1102K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
木下 義樹, 森下 政夫, 野﨑 安衣, 山本 宏明原稿種別: 論文
2017 年 81 巻 10 号 p. 485-493
発行日: 2017/10/01
公開日: 2017/09/25
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe thermodynamic properties for Nd2(MoO4)3 were investigated. Nd2(MoO4)3 is one of the end member of the yellow phases which are known as hygroscopic harmful phases in the nuclear fuel waste glasses. The standard molar entropy,
 , at 298.15 K of Nd2(MoO4)3 was determined by measuring its isobaric heat capacities,
, at 298.15 K of Nd2(MoO4)3 was determined by measuring its isobaric heat capacities,  , from 2 K via the fitting functions including the Debye-Einstein formula and electronic- as well as magnetic terms. The Neel temperature, TN, estimated by extrapolating the magnetic- term in the fitting function. Its standard Gibbs energy of formation,
, from 2 K via the fitting functions including the Debye-Einstein formula and electronic- as well as magnetic terms. The Neel temperature, TN, estimated by extrapolating the magnetic- term in the fitting function. Its standard Gibbs energy of formation,  , was determined by combining
, was determined by combining  datum with the standard enthalpy of formation,
datum with the standard enthalpy of formation, 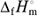 , which were estimated from ones for Ce2(MoO4)3 and Sm2(MoO4)3. The unknown standard Gibbs energies of solution,
, which were estimated from ones for Ce2(MoO4)3 and Sm2(MoO4)3. The unknown standard Gibbs energies of solution, 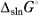 , at 298.15 K for Nd2(MoO4)3 were predicted from the reference data for MoO42-(aq) and Nd3+(aq). The obtained thermodynamic values are as follows:
, at 298.15 K for Nd2(MoO4)3 were predicted from the reference data for MoO42-(aq) and Nd3+(aq). The obtained thermodynamic values are as follows:
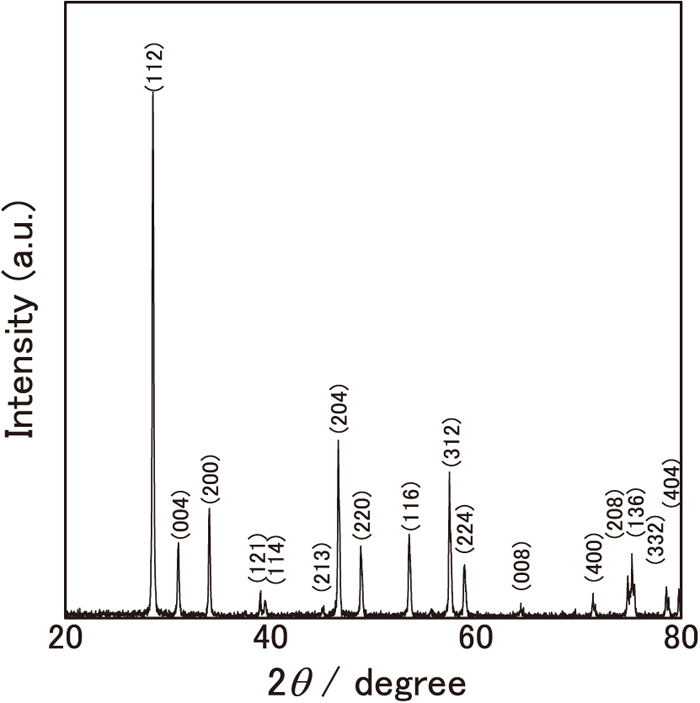 Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageXRD pattern of Nd2(MoO4)3 prepared in the present study.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (968K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageXRD pattern of Nd2(MoO4)3 prepared in the present study.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (968K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|