
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
齋藤 周也, 武末 翔吾, 小茂鳥 潤, 深沢 剣吾, 三阪 佳孝2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 295-300
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
ジャーナル フリーIn order to form a Ti-Al intermetallic compound layer on a carbon steel surface, an atmospheric-controlled induction heating fine particle peening (AIH-FPP) treatment was performed at 1000°C in argon atmosphere. The shot particles were prepared by a mechanical milling method. Titanium and aluminum particles at molar ratios of one to three were mechanically milled by a planetary ball mill for 6 h. The treated surface was analyzed using a scanning electron microscope, an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer and X-ray diffraction. The reciprocating dry wear tests were performed under the following conditions; an opposing material of alumina balls of 3 mm in diameter, a load of 2.0 N, a sliding speed of 600 mm/min and a sliding distance of 224 m. The results showed that a Ti-Al intermetallic compound layer consisting mainly of TiAl3 formed on the surface of carbon steel by AIH-FPP treatment. This was because the shot particles were transferred to the substrate and the aluminum and titanium in the particles reacted neither excessively nor insufficiently. The AIH-FPP treated surface showed a higher wear resistance than that of the un-treated surface. This was because the wear mode of carbon steel changed from abrasive wear to adhesive wear owing to the formation of the Ti-Al intermetallic compound layer on the surface.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1340K) -
山本 敏弘, 古川 敬, 西野 秀郎2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 301-307
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/03/10ジャーナル フリーGuided wave testing offers an efficient screening method for thinning of pipe walls because of its long inspection range and its ability to inspect pipes with limited access. However, the existence of an elbow in pipes makes it difficult to interpret echo signals in guided wave testing. In the present study, to investigate the sensitivity of defect detection at a pipe elbow by guided wave testing, guided wave testing was performed on several 50A Sch 40 aluminum alloy piping specimens of the same configuration that includes an elbow. An artificial defect was produced at one of 12 different locations on the outer surface of the elbow of each piping specimen. The defect signals were observed as the defect depth was gradually increased at each defect location to obtain the defect sensitivity. The transmitted guided wave frequency was in turn set to 30 kHz, 40 kHz, and 50 kHz. At 30 kHz, high sensitivity values were obtained at the intrados of the elbows, whereas at 40 kHz and 50 kHz, high sensitivity values were obtained at their extrados. This paper also shows the results of computer simulations that used the same configuration as that used in the experiments to analyze the propagation behavior of guided waves passing through the elbow. In addition to the experimental results, the simulation results indicate that the defect-sensitive locations are controlled by the guided wave frequency. Thus, proper selection of the excitation frequency for guided wave testing enables defect detection in an intended area of an elbow with high sensitivity.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1205K) -
関田 愛子, 松垣 あいら, 中野 貴由2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 308-314
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/03/27ジャーナル フリーBone matrix exhibits highly anisotropic features derived from collagen/apatite orientation, that determine the mechanical function of bone tissue. Breast cancer is highly metastatic to bone tissue and causes osteolytic lesions through osteoclast activation. Nevertheless, the effects of osteoclast activation induced by cancer bone metastasis on bone microstructure, a notable aspect of the bone quality, remains uncertain. In the present study, the effects of osteolytic bone metastasis on the anisotropic microstructure of the bone matrix, particularly the integrity of collagen fibril orientation was investigated. Interestingly, hyperactivation of osteoclasts was induced by osteolytic breast cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro. The cancer cells-derived conditioned medium induced an increased number of nuclei and more specific podosome structures in osteoclasts. These results indicate the resorptive capacity of a single osteoclast was abnormally upregulated in the cancer-mediated environment, causing a geometrical aberration in resorption cavities. Histological studies on mouse femurs with metastasis of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells revealed that the osteoclasts in the metastatic bone were abnormally large and they generated resorption cavities that are irregular both in size and in shape. Notably, collagen matrix in newly formed bone in the metastatic bone exhibited a significantly disorganized architecture.
 Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageSchematic illustration of the analysis of the alterations in osteoclast biology and bone microstructure involved in cancer抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3101K)
Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageSchematic illustration of the analysis of the alterations in osteoclast biology and bone microstructure involved in cancer抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3101K) -
関田 愛子, 松垣 あいら, 小笹 良輔, 中野 貴由2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 315-319
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/03/31ジャーナル フリーBone tissue has a highly anisotropic microstructure derived from collagen matrix alignment and the crystallographic orientation of apatite. Bone is also a highly vascularized tissue; intraosseous vascularization and bone formation are intimately coupled. Meanwhile, the structural relations between intraosseous vascular networks and bone microstructure are as yet unknown, partially due to technical difficulties in visualizing precise intraosseous vasculatures. The aim of this study is to develop a visualization method suitable for the structural analysis of intraosseous vascular networks and to reveal the relations between bone microstructure and the arrangement patterns of intraosseous vasculatures both in intact and metastasized bones. Three-dimensional vascular networks were successfully visualized, and region-dependent arrangement patterns of blood vessels were clarified using fluorescent dye-conjugated lectin. Interestingly, the anisotropic structural correlation between bone matrix and the vascular system in a region-specific manner was clarified. In addition, the impaired anisotropic vascular networks in metastasized bone was clarified. The obtained results indicate the molecular interactions between the vascular system and bone tissue as a novel contributor for realization of anisotropic bone matrix construct.
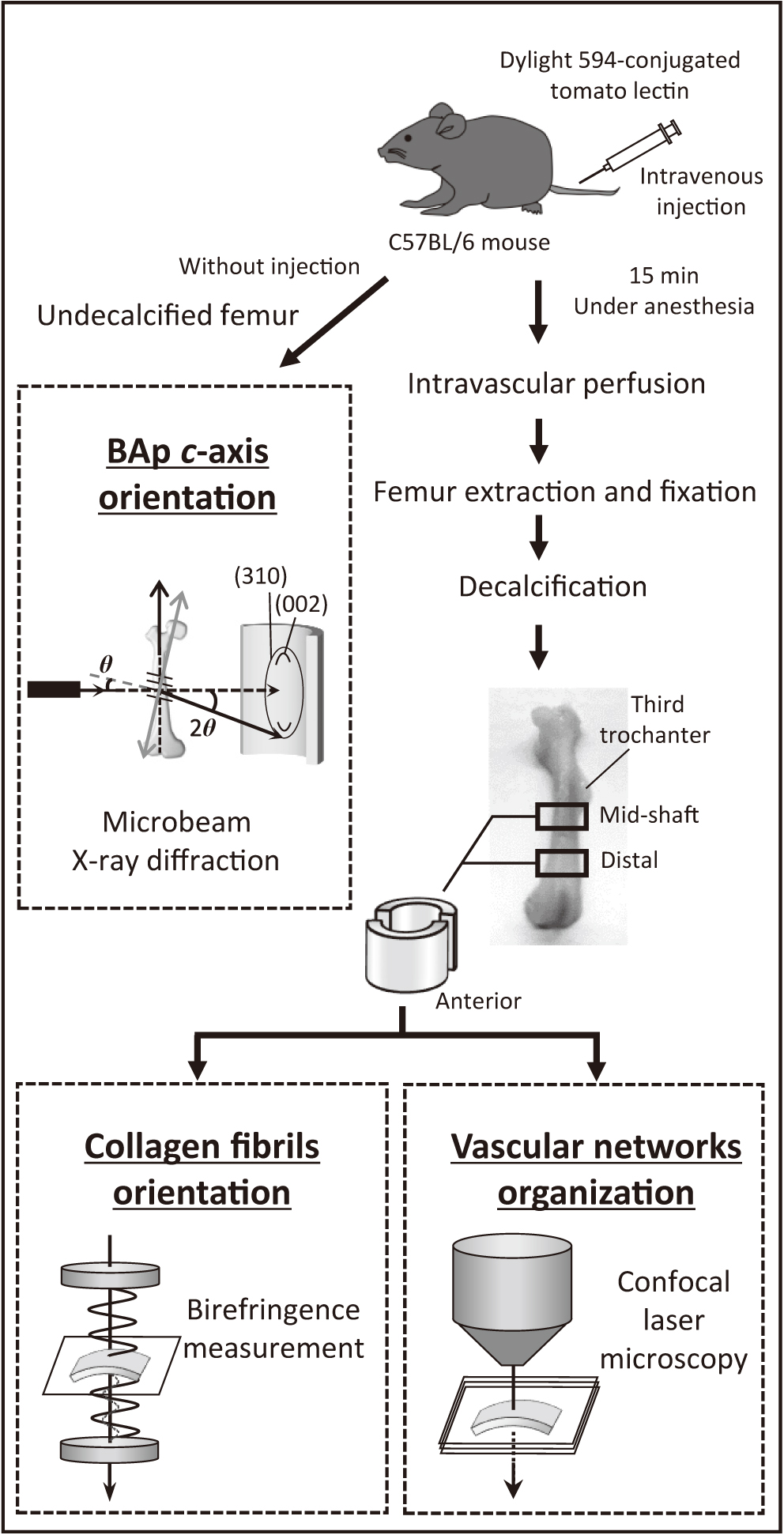 Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageA schematic illustration of procedures for analyzing biological apatite (BAp) c-axis orientation, collagen fibrils orientation, and vascular networks organization in mouse non-Haversian femurs.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1015K)
Fig. 1 Fullsize ImageA schematic illustration of procedures for analyzing biological apatite (BAp) c-axis orientation, collagen fibrils orientation, and vascular networks organization in mouse non-Haversian femurs.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1015K) -
小林 宙, 庄司 浩史, 浅野 聡, 今村 正樹2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 320-326
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
ジャーナル フリーSumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd. (SMM) has gradually increased the mixed sulfide (MS: mixture of nickel and cobalt sulfides) production from nickel laterite ore as raw material for the SMM's unique Matte Chlorine Leach and Electro-winning (MCLE) process over the past decade. This process has significant cost advantages because it is capable of selectively and effectively leaching nickel from MS; however, chlorine leaching requires expensive corrosion-resistant facilities. A new process that could be operated using lower-cost facilities has therefore been desired. To meet its development needs, this study evaluated a process for nickel-selective leaching from MS, which is similar to the existing process for refining of ZnS. The process uses sulfuric acid, which does not require high-cost facilities. The mechanism of nickel leaching from MS using sulfuric acid was identified. It was shown that nickel-selective leaching using sulfuric acid is difficult because of the formation of elemental sulfur and NiS2 precipitates on the MS surface that interfere with the leaching reaction.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1128K) -
鈴木 飛鳥, 湯川 宏, 南部 智憲, 松本 佳久, 村田 純教2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 327-334
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/05/12ジャーナル フリーThe hydrogen permeability of Pd–Ag alloy membranes has been investigated over a wide temperature range between 100°C and 500°C. The hydrogen permeation coefficient, Φ, for Pd–23 mol%Ag decreases with decreasing temperature above 300°C, in good agreement with the previous literature. However, Φ starts to increases below 250°C, and a peak is observed at around 180°C. Considering the silver concentration and operating temperature, the α–α′ phase transition never occurs in this condition. In other words, the α–α′ phase transition is not the reason for the anomalous peak behavior of Pd–23 mol%Ag alloy at low temperature. In addition, it is confirmed that the diffusion–limiting hydrogen permeation reaction takes place from room temperature up to 500°C. To understand the reason for the peak appearance, the hydrogen permeability has been analyzed in view of the new description of hydrogen permeation based on hydrogen chemical potential. As a result, it is found that the temperature dependence of the PCT factor, fPCT, is dominant for the peak appearance, meaning that the corresponding pressure–composition–isotherms (PCT curves) are essential for the understanding of hydrogen permeability of the alloy. Dependences of the pressure condition and silver concentration on the peak behavior have also been investigated. The peak temperature increases with increasing the hydrogen pressure at feed side. In addition, the peak appears at lower temperature and becomes remarkable with decreasing silver concentration of Pd–Ag alloy membrane. In other words, the composition of Pd–Ag alloy membranes must be designed based on the operating temperature or pressure condition. Thus, this study suggests new possibilities of alloy design for Pd–Ag alloy membranes.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1213K)
-
2017 年 81 巻 6 号 p. 335
発行日: 2017/06/01
公開日: 2017/05/25
ジャーナル フリーJ-STAGEにおいて,平成29年3月8日に外部からの攻撃を検知されたことから,緊急セキュリティ対応のため,同日11時より3月15日15時までサービスを停止いたしました.
標記2論文は,3月15日15時にサービスを再開した時点で初めて公開されたため,正しい公開日は下記の通りとなります.
Published March 15, 2017
お詫びして訂正いたします.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (312K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|