
- Issue 12 Pages 695-
- Issue 11 Pages 611-
- Issue 10 Pages 551-
- Issue 9 Pages 485-
- Issue 8 Pages 405-
- Issue 7 Pages 345-
- Issue 6 Pages 281-
- Issue 5 Pages 239-
- Issue 4 Pages 191-
- Issue 3 Pages 137-
- Issue 2 Pages 83-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue Special_Issue P・・・
- Issue Supplement2 Pag・・・
- Issue Supplement1 Pag・・・
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Takao Tsuneki, Yasuhiro Yuasa, Hidenori Maki, Taihei Takeuchi, Yuta Ma ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 313-320
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis case pertains to a 70-year-old man who was given a diagnosis of ulcerative lesions in the lesser curvature of the stomach on upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Group 5 was diagnosed based on biopsy findings and the patient was referred to our department for surgery. Laparoscopic distal gastrectomy revealed the following: pT1bN2M0, pStage IIA, HER2 (IHC2+, FISH positive). The patient was followed up postoperatively; however, 8 months later, he developed hepatic metastasis in the lateral segment of the liver. Three courses of S-1+cisplatin+trastuzumab therapy were administered and shrinking of the tumor was observed. Since no new lesions were noted, laparoscopic partial hepatectomy was performed. Postoperatively, the patient was administered S-1 orally for 1 year. Currently, approximately 4 years since the hepatectomy, the patient is recurrence free. Here, we report our findings of a case in which laparoscopic partial hepatectomy was performed after chemotherapy for solitary liver metastasis noted after the surgery for HER2-positive gastric cancer.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1721K) Full view HTML -
Kenta Ishii, Manabu Takano, Akifumi Nakagawa, Atsushi Ogawa, Kenzo Ono ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 321-328
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA 39-year-old woman was referred to our hospital due to anemia. An upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed a type 2 tumor at the posterior wall of the duodenal bulb, while adenocarcinoma was diagnosed histopathologically. Enhanced CT showed no evidence of distant metastasis. The patient underwent pancreatoduodenectomy with curative intent. Histological findings revealed adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation in most areas of the resected specimen. Immunohistochemical findings were positive for alpha-fetoprotein. Neuroendocrine differentiation was observed in approximately 5% of the tumor. Although the tumor was macroscopically localized mainly in the duodenal bulb, the patient was given a diagnosis of gastric cancer with duodenal invasion because moderately differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma was found in the gastric mucosa of the pyloric region. Heterotopic gastric glands and ectopic pancreas were detected at the submucosa and muscle layer of the pyloric region. The patient is currently alive and without recurrence at 20 months after surgery.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3065K) Full view HTML -
Gen Tsujio, Toshiki Hirakawa, Junya Morimoto, Takuma Okada, Hironari M ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 329-335
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA 65-year-old man who had undergone distal gastrectomy with Billroth-II anastomosis for a duodenal ulcer 45 years previously was referred to our hospital because of weight loss and anemia. He was given a diagnosis of remnant gastric cancer with cT4aN (+) M0 cStage III. After neoadjuvant chemotherapy, we performed hand-assisted laparoscopic total remnant stomach resection and partial transverse colectomy. Macroscopic examination of the resected specimen showed a large type 3 tumor that had spread widely in the remnant stomach and a 3-cm prominent lesion on the anterior wall. Histopathological examination revealed the type 3 tumor to be an adenocarcinoma, while the prominent lesion was diagnosed as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Postoperative PET-CT revealed abnormal uptake in the periaortic lymph nodes. We also suspected extranodal DLBCL lesions. The final diagnosis was collision tumor composed of the remnant gastric cancer ypT4b (transverse colon) N2M0 ypStage IIIB and DLBCL. The patient was subsequently treated with chemotherapy for DLBCL.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1542K) Full view HTML -
Takayoshi Kishida, Hiroyuki Sugimoto, Tomohisa Otsu, Daigo Kobayashi, ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 336-343
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAmong the anatomical and physiological factors of traumatic duodenal injury, dehiscence is known to occur at a high incidence rate when only simple suture closure is performed. Various types of schemes are required for the surgical modality. We report the findings in a case of partial resection of the second portion of the duodenum for traumatic duodenal injury caused by a wire. The patient was a 14-year-old boy rushed to our hospital after he struck his upper abdomen on a net wire during tennis practice. At admission he had intense pressure pain accompanied by peritoneal irritation symptoms in the left upper abdomen. From the contrast-enhanced CT findings, traumatic duodenal and pancreatic injuries were suspected. Hence, an emergency surgery was performed. The intraoperative findings showed a slight subcircumferential perforation, 10 cm in diameter, in the second portion of the duodenum. Intraoperative pancreatic duct imaging revealed no injury of the main pancreatic duct. Partial resection of the second portion of the duodenum was performed. For traumatic duodenal injuries, diagnosis and the choice of surgical modality are not easy, and difficulties may be encountered due to postsurgical complications. To rescue such patients, rapid diagnosis and appropriate surgery in the early stage of injury must be performed to prevent over-invasion.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1445K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1445K) Full view HTML -
Yayoi Sato, Osamu Kainuma, Takashi Maruyama, Hajime Tanaka, Toshiyuki ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 344-351
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe report a case of an 81-year-old man who had undergone hemihepatectomy with caudate lobectomy for hilar cholangiocarcinoma at 77 years of age. The pathological diagnosis was papillary adenocarcinoma; the ductal margin was tumor-free. CT performed 3 years after surgery showed a papillary tumor in the remnant bile duct of the pancreas. A tumor biopsy revealed a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. Following pancreatoduodenectomy, the tumor was diagnosed as a high-grade papillary adenocarcinoma, pTis, med, ly0, v0, ne0, Stage 0, without invasion; further, based on the WHO 2010 classification, it was diagnosed as a pancreatobiliary-type intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct (IPNB). Re-examination of tissue specimens from the original hilar cholangiocarcinoma revealed that both original and recurrent tumors shared similar histopathological characteristics of IPNB. Generally, the curative resection of IPNB has a good prognosis; however, the present case shows that recurrence may occur at the remnant bile duct. Patients with IPNB should be followed-up closely after resection. Subsequent surgical procedures can be performed if the patient’s general condition is good.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1940K) Full view HTML -
Minimal Serotonin-Positive Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Stenosis of the Main Pancreatic DuctHidenori Tomida, Tsuyoshi Notake, Kiyotaka Hosoda, Akira Shimizu, Hiro ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 352-359
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA 59-year-old woman was found to have a 10-mm mass in the body of the pancreas, with stenosis of the main pancreatic duct, on abdominal CT. CT revealed that the periphery of the tumor had early-phase enhancement, whereas the center of the tumor had delayed-phase enhancement. A diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor with fibrosis was made and the body and tail of the pancreas were resected. A white, 10×9 mm tumor close to the main pancreatic duct was identified in the resected specimen. Histopathological analysis showed trabecular or alveolar atypical cells and proliferation of the fibrous stroma, which invaded the normal pancreatic tissue in the vicinity of the tumor. Immunostaining showed positive results for synaptophysin and chromogranin A. With a Ki-67 index of 3.1% and a mitotic index of 0/50 HPF, the tumor was identified as a grade 2 pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Around the site of stenosis, serotonin stain-positive tumor cells invaded by fibrous stroma were seen. In addition, metastasis was found in the lymph nodes of the superior mesenteric artery, suggesting that the tumor was small but highly biologically malignant.
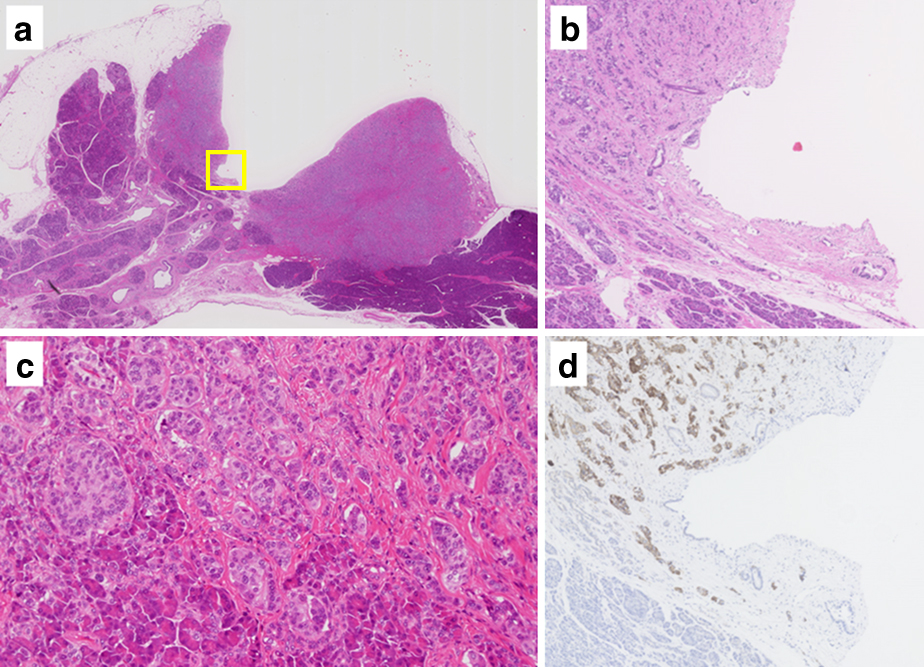 View full abstractDownload PDF (1871K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1871K) Full view HTML -
Yusuke Sakimura, Daisuke Yamamoto, Hiroaki Sugita, Kengo Hayashi, Yoji ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 360-370
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHypoganglionosis (HG) is characterized by the decrease in the number of intestinal glia cells and categorized as allied Hirschsprung’s disease. Usually it is recognized as a pediatric disease. Adult cases are extremely rare and to the best of our knowledge, there have been no reported surgical cases for colon cancer with HG. Here, we describe a case of right hemicolectomy for ascending colon cancer with HG. The patient was a 54-year-old man who had positive fecal blood test results from a medical checkup. The colonoscopy revealed a type 2 tumor in the ascending colon. CT and esophagogastroduodenoscopy indicated an abnormally dilated duodenum, and barium enema showed the dilated colon without folds. A laparoscopic right hemicolectomy was performed for ascending colon cancer. The laparoscopic view indicated the dilated and relaxed intestine. In the postoperative course, he had recurrence of obstruction at the anastomotic site. Laparoscopic assisted ileo-transverse bypass improved the obstruction. The histopathological diagnosis was ascending colon cancer pT3N0M0 pStage II and HG. There was no recurrent obstruction after the second surgery therefore, we believe securing an adequate diameter of the anastomosis is significant.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1942K) Full view HTML -
Shoko Moue, Yoshimasa Akashi, Koichi Ogawa, Katsuji Hisakura, Tsuyoshi ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 371-379
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe report a case of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) arising in the heterotopic pancreas of the stomach which was successfully removed by percutaneous endoscopic intragastric surgery (PEIGS). A 42-year-old man was given a diagnosis of gastric submucosal tumor (SMT) during a medical check-up. Abdominal CT scan and MRI imaging revealed a multicystic lesion in the tumor mass which was diagnosed as heterotopic pancreas with cystic component (IPMN or pseudocyst). The tumor was located in the antrum of the stomach and adjacent to the pyloric ring; therefore, we selected PEIGS as a surgical procedure to preserve gastric function for clinically benign tumor treatment. Pathological examination revealed multiple dilated pancreatic ducts with pyloric gland-like structures in the heterotopic pancreatic tissues. Based on pathological findings, the tumor was finally diagnosed as heterotopic pancreas with gastric type IPMN. We considered PEIGS as a suitable procedure for the intraluminal SMT adjacent to the pyloric ring for its functional preservation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2757K) Full view HTML
-
Kazuyuki Nagai, Shinji UemotoArticle type: SPECIAL REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 380-389
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML -
Keiichi Okano, Yasuyuki SuzukiArticle type: SPECIAL REPORT
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages 390-397
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
-
Susumu EguchiArticle type: EDITOR'S NOTE
2020Volume 53Issue 4 Pages en4-
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (686K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|