
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Soek Sin Teh, Augustine Soon Hock Ong, Siau Hui Mah2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1183-1191
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe environmental impacts of palm oil mill effluent (POME) have been a concern due to the water pollution and greenhouse gases emissions. Thus, this study was conducted to recover the value-added products from POME source before being discharged. The samples, before (X) and after (Y) the pre-recovery system in the clarification tank were sampled and analysed and proximate analysis indicated that both samples are energy rich source of food due to high contents of fats and carbohydrates. GCMS analysis showed that the oil extracts contain predominantly palmitic, oleic, linoleic and stearic acids. Regiospecific analysis of oil extracts by quantitative 13C-NMR spectroscopy demonstrated that both oil extracts contain similar degree of saturation of fatty acids at sn-2 and sn-1,3 positions. The samples are rich in various phytonutrients, pro-vitamin A, vitamin E, squalene and phytosterols, thus contributing to exceptionally high total flavonoid contents and moderate antioxidant activities. Overall, samples X and Y are good alternative food sources, besides reducing the environmental impact of POME.
View full abstractDownload PDF (256K) -
Angelo Maria Giuffrè, Marco Capocasale, Clotilde Zappia, Marco Poiana2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1193-1205
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTwo important problems for the food industry are oil oxidation and oil waste after frying. Sunflower seed oil is one of the vegetable oils most commonly used in the food industry. Two variables were applied to the low oleic sunflower seed oil in this work i.e. heating temperature (180-210-240°C) and time of heating (15-30-60-120 minutes), to study from the edible point of view the variations of its physico-chemical properties. After 120 minutes heating at 240°C the following was found: refractive index (1.476), free acidity (0.35%), K232 (2.87), K270 (3.71), antiradical activity (45.90% inhibition), total phenols (523 mg kg–1), peroxide value (17.00 meq kg–1), p-anisidine value (256.8) and Totox (271.7), all of which showed a constant deterioration. In relation to the use as a feedstock for bio-diesel production, after 120 minutes heating at 240℃ the following was found: acid value 0.70 mg KOH g–1 oil, iodine value 117.83 g I2 100 g–1 oil, oil stability index 0.67 h, kinematic viscosity (at 40°C) 77.85 mm2 s–1, higher heating value 39.86 MJ kg–1, density 933.34 kg/m3 and cetane number 67.04. The parameters studied in this work were influenced, in different ways, by the applied variables. Heating temperature between 180 and 210°C and 120 min heating duration were found to be the most appropriate conditions for sunflower seed oil both from the deep frying point of view and from a subsequent use as feedstock for bio-diesel production. In light of the vegetable oils’ International standards for an edible use and for a bio-diesel production, findings of this work can be used to set heating temperature and heating duration to preserve as long possible the physico-chemical properties of a low oleic sunflower seed oil for both its edible use as a fat during cooking and for its re-use after frying.
View full abstractDownload PDF (301K) -
Angélica A. Ochoa-Flores, Josafat A. Hernández-Becerra, Adriana Cavazo ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1207-1215
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSStructured phosphatidylcholine was successfully produced by acidolysis between phosphatidylcholine and free medium chain fatty acid, using phospholipase A1 immobilized on Duolite A568. Response surface methodology was applied to optimize the reaction system using three process parameters: molar ratio of substrates (phosphatidylcholine to free medium chain fatty acid), enzyme loading, and reaction temperature. All parameters evaluated showed linear and quadratic significant effects on the production of modified phosphatidylcholine; molar ratio of substrates contributed positively, but temperature influenced negatively. Increased enzyme loading also led to increased production of modified phosphatidylcholine but only during the first 9 hours of the acidolysis reaction. Optimal conditions obtained from the model were a ratio of phosphatidylcholine to free medium chain fatty acid of 1:15, an enzyme loading of 12%, and a temperature of 45°C. Under these conditions a production of modified phosphatidylcholine of 52.98 % were obtained after 24 h of reaction. The prediction was confirmed from the verification experiments; the production of modified phosphatidylcholine was 53.02%, the total yield of phosphatidylcholine 64.28% and the molar incorporation of medium chain fatty acid was 42.31%. The acidolysis reaction was scaled-up in a batch reactor with a similar production of modified phosphatidylcholine, total yield of phosphatidylcholine and molar incorporation of medium chain fatty acid. Purification by column chromatography of the structured phosphatidylcholine yielded 62.53% of phosphatidylcholine enriched with 42.52% of medium chain fatty acid.
View full abstractDownload PDF (497K) -
Fumiaki Beppu, Keiko Yasuda, Ayako Okada, Yoshitsugu Hirosaki, Masako ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1217-1227
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHighly unsaturated fatty acid (HUFA) binding at the sn-2 position of phospholipids (PL) becomes a resource for prostaglandin, leukotriene, resolvin, and protectin synthesis. Both triacylglycerol (TAG) and PL synthesis pathways in vivo are via phosphatidic acid; therefore, the distribution of fatty acid species at the sn-2 position must theoretically be the same for TAG and PL if rearrangement does not occur. However, it is known that little HUFA is located at the sn-2 position of TAG in marine mammals. Therefore, distribution of fatty acid species at the sn-2 position of TAG and PL was compared between marine fishes and mammals in this study. The composition of fatty acids binding at the sn-2 or sn-1,3 position of PL and TAG was analyzed via hydrolysis with enzymes and GC-FID. The results showed that 20:4n-6, 20:5n-3, 22:5n-3, and 22:6n-3 were primarily located at the sn-1,3 positions of TAG in marine mammals. Comparison of the binding positions of HUFA and 16:0 in PL and TAG suggested the existence of Lands’ cycle in marine fishes and mammals. In conclusion, both marine fishes and mammals condensed HUFA as a source of eicosanoid at the sn-2 position of PL. Furthermore, abundance ratios for 22:5n-3 or 22:6n-3 at the sn-2 position (sn-2 ratio) in TAG and PL (calculated by the equation: [abundance ratio at sn-2 position of TAG]/[abundance ratio at sn-2 position of PL]) was less than 0.35 in marine mammals; however, it was greater than 0.80 in marine fishes. These differences suggested that the HUFA consisted of 22 carbon atoms and had different roles in marine fishes and mammals.
View full abstractDownload PDF (881K)
-
Wei-Han Chang, Yun-Ting Chuang, Cheng-Yeh Yu, Chien-Hsiang Chang, Yu-M ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1229-1238
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe incorporation of additive in lipid bilayers is one of the ordinary approaches for modulating their properties. Additive effect on phase transition of ion-pair amphiphile (IPA) bilayers, however, is not known. In this work, four double-chained IPAs with different hydrocarbon chain lengths and symmetry were designed and synthesized from single-chained cationic and anionic surfactants by the precipitation method. By using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), the thermotropic transition behavior from gel phase (Lβ) through rippled phase (Pβ’) if any to liquid-crystalline phase (Lα) was studied for bilayers of these lipid-like IPAs in excess water. The effects of three sterol-like additives (cholesterol, α-tocopherol, and α-tocopheryl acetate) in IPA bilayers on thermal phase behavior were then systematically investigated. The experimental results revealed that with increasing concentration of additive, the phase transition temperatures were unaffected on the one hand and the enthalpies of phase transition were decreased on the other hand. When the addition of additive exceeded a specific amount, the phase transition disappeared. More hasty disappearance of phase transition was found for IPAs with lower total number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chains. For IPAs with the same total number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chains, the disappearance of phase transition is more hasty for the asymmetric one than for the symmetric one. Similar effects on thermal phase behavior of four IPA bilayers were exhibited by the three additives with similar chemical structures. Possible mechanism of additive effects on phase transition of IPA bilayers was then proposed in line with that of lipid bilayers.
View full abstractDownload PDF (834K) -
Megumi Kaji, Yuichiro Takeyama, Atsushi Nioh, Moe Tsuyuki, Hidetaka Ak ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1239-1245
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe surface morphology of a cosmetic film consisting of an amphiphilic random copolymer (methoxy polyethylene glycol-23 methacrylate/glyceryl diisostearate methacrylate copolymer, MPM-GDM) and solvents has been studied. The cosmetic film was prepared through the evaporation of water from a homogeneous aqueous mixture of MPM-GDM, xanthan gum, and solvents. MPM-GDM was soluble in water, monohydric alcohols, and 1,3-butylene glycol (1,3-BG), whereas it hardly dissolved in glycerin. The surface morphology was examined by changing the solvent composition of 1,3-BG (good solvent) and glycerin (poor solvent). Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images of the cosmetic film showed that MPM-GDM spread through the whole film in the absence of glycerin, whereas the addition of glycerin led to the formation of a sea-island structure. It was assumed that the size of the MPM-GDM domain was determined by the balance between two factors: the miscibility (or the interfacial tension) of MPM-GDM against the solvents and the viscosity of the continuous phase. We also demonstrated that the concentration of both MPM-GDM and xanthan gum affected the surface morphology. Control of the surface morphology by changing the solubility of MPM-GDM is expected to be useful for improving the functionality and feel of cosmetic films.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1347K)
-
Akifumi Hosoda, Yuta Isomura, Syungo Takeo, Takuho Onai, Kazutaka Take ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1247-1256
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIt is important to construct microbiological treatment systems for organic solvent-contaminated water. We developed a continuous culture supplemented with a biostimulation agent named BD-C, which is formulated from canola oil, and Xanthobacter autotrophicus strain GJ10 for an aerobic dichloromethane (DCM)-dechlorinating microorganism. The continuous culture was a chemostat constructed using a 1 L screw-capped bottle containing artificial wastewater medium with 2.0 mM DCM and 1.0% (v/v) BD-C. The expression of genes for DCM metabolism in the dechlorinating aerobe was monitored and analyzed by reverse transcription–quantitative PCR. Strain GJ10 was able to dechlorinate approximately 74% of the DCM in medium supplemented with BD-C during 12 days of incubation. The DCM dechlorination rate was calculated to be 0.11 mM/day. The ΔΔCT method showed that expression of haloalkane dehalogenase increased 5.4 times in the presence of BD-C. Based on batch culture growth tests conducted with mineral salt medium containing three DCM concentrations (0.07, 0.20, 0.43 and 0.65 mM) with BD-C, the apparent maximum specific consumption rate (νmax) and the saturation constant (Ks) determined for DCM degradation in this test were 19.0 nmol/h/CFU and 0.44 mM, respectively. In conclusion, BD-C enhanced the aerobic degradation of DCM by strain GJ10.
View full abstractDownload PDF (743K)
-
Marina Komuro, Naoki Shimizu, Ryo Onuma, Yurika Otoki, Junya Ito, Shun ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1257-1262
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLutein, a type of xanthophyll, possesses antioxidative properties that contribute to the prevention of various diseases. Preliminary screening has shown that Japanese mugwort (Artemisia princeps Pamp.) contains high amounts of lutein. In this study, we evaluated the lutein concentration in a processed mugwort product (mugwort paste). By using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with visible light detection or mass spectrometry, the lutein concentration in mugwort paste was determined as 38 mg/100 g dry weight, which indicates that mugwort is a potentially valuable natural food source of lutein. We also investigated the effects of the manufacturing process and found that the lutein content was significantly increased by the boiling and dehydrating processes during the production of mugwort paste. Mugwort paste that is rich in lutein may therefore serve as an effective nutraceutical.
View full abstractDownload PDF (477K)
-
Hanaa M. Soliman, Shaker M. Arafat, Amany M. Basuny, Y. El- shattory2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1263-1271
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new amphiphilic antioxidant (tannyl stearate) derived from reaction of tannic acid with stearic acid was synthesized in order to improve tannic acid solubility in lipid materials. This reaction gives many products having different degree of esterification (tannyl mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta……stearate) which were separated using silica gel column chromatography and tentative identification was carried out using thin layer chromatography (TLC). The intrinsic viscosities (η) were used to differentiate between the different molecular weight of the produced esters1). Tannyl penta stearate is assumed to be the most suitable amphiphilic antioxidant derivative, where those derivatives with less degree of esterification would be less soluble in fat, and those of higher degree of esterification would exhaust more hydroxyl group that cause decreases of antioxidant activity. The structure of tannyl penta stearate was approved depending on its chemical analysis and spectral data (IR, H1 NMR,). The emulsification power of tannyl penta stearate was then determined according to method described by El-Sukkary et al.2), in order to prove its amphiphilic property. Then tannyl penta stearate was tested for its antioxidant and radical scavenging activities in three different manners, those are, lipid oxidation in sunflower oil using Rancimat, (DPPH) free radical scavenging and total antioxidant activity. {Pure tannic acid (T), butylhydroxyanisol (BHA) and butylhydroxytoluene (BHT) were used as reference antioxidant radical saving compounds}. Then tannyl penta stearate was added to sunflower oil, frying process was carried out and all physicochemical parameters of the oil were considered, and compared to other reference antioxidant in order to study the effect of this new antioxidant toward oil stability. Acute oral toxicity of the tannyl penta stearate was carried out using albino mice of 21–25 g body weight to determine its safety according to the method described by Goodman et al.3). Also liver and kidney functions of those mice were checked. Thus it could be concluded that the addition of tannyl penta stearate to frying oils offers a good protection against oxidation. The effectiveness of tannyl penta stearate as lipid antioxidant has been attributed mainly to its stability at high temperature. And according to acute lethal toxicity test tannyl penta stearate was found to be a safe compound that can be used as food additive.
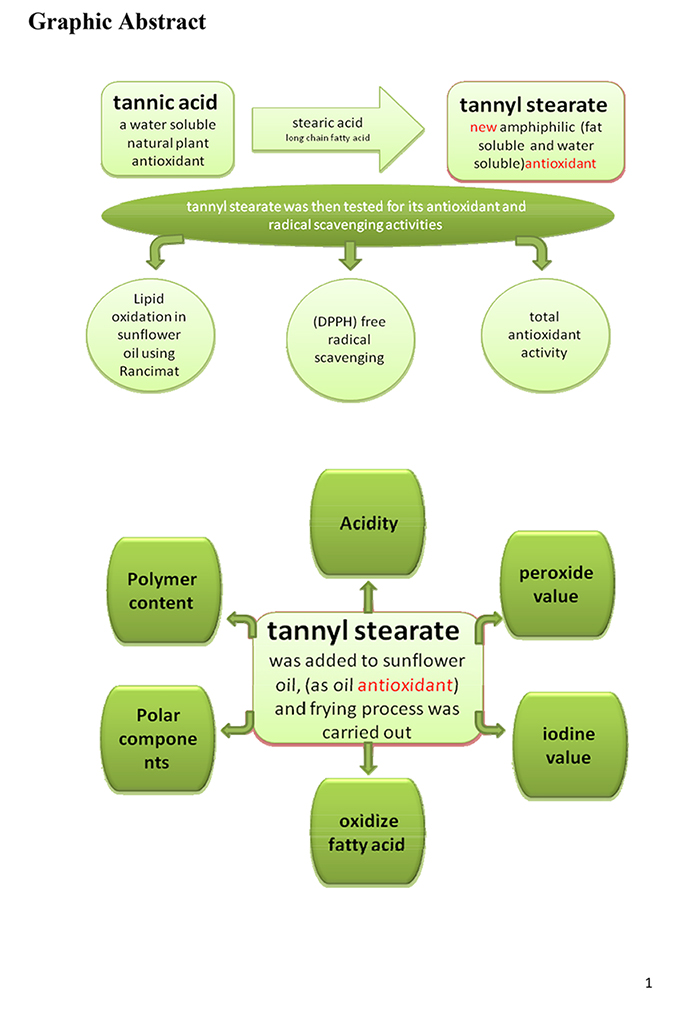 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (655K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (655K)
-
Yoshiharu Okuno, Shinsuke Marumoto, Mitsuo Miyazawa2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1273-1276
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe compositions of the essential oils from three kinds of Cryptotaenia japonica Hassk (“Mitsuba” in Japanese, Kirimitsuba (KM), Nemitsuba (NM), and Itomitsuba (IM)) were investigated by capillary GC/GC-MS. The oils contained 53 volatile components, of which 95% were terpenoids. The major constituents were sesquiterpenoids, which were α-selinene (KM: 39.1%; NM: 38.4%; IM: 13.2%), β-selinene (15.5%, 15.2%, 4.8%), germacrene D (12.1%, 7.2%, 24.1%), trans-farnesene (11.1%, 6.0%, 10.9%), β-elemene (2.9%, 2.9%, 6.8%), and trans-caryophyllene (1.7%, 1.7%, 2.6%). The main sesquiterpene found in KM and NM was α-selinene and in IM was germacrene D. The major monoterpenes found were β-myrcene (3.8%, 6.7%, and 3.5%) and β-pinene (2.8%, 0.2%, and 1.4%).
View full abstractDownload PDF (320K)
-
Tatsuo Aikawa, Kanta Sato, Hiroki Okado, Yukako Takahashi, Takeshi Kon ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1277-1284
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA liposome is a molecular assembly in the form of a vesicle comprised of a phospholipid bilayer. Liposomes can be used as molecular containers in various fields such as pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. It is difficult to maintain the original structure of liposomes in an aqueous medium. Phospholipids, which are components of liposomes, are susceptible to hydrolysis, which causes disruption of the liposomal structure and dysfunction of the molecular container. In this context, freeze-drying liposomes is a preferable method to improve the shelf life of liposomes. However, when freeze-drying liposomes, a lyoprotective agent is required to preserve their original structure. In this study, we investigate whether alkyl sulfobetaines (SBn, n: number of carbons in the alkyl chain, n = 1–18) can be used as lyoprotectants for 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) liposomes. The results indicated that the length of the alkyl chain of the SBn was an important factor to prevent liposome disruption during the freeze-drying and subsequent rehydration processes. The use of SBn with an alkyl chain of intermediate length (n = 6–10) could prevent liposome disruption and remarkably reduce the gel-to-liquid crystal phase transition temperature (Tm) of the freeze-dried liposomes. This indicates that these SBn could intercalate in the dried bilayer and reduce intermolecular interaction between DPPC in the bilayer. The Tm reduction of the freeze-dried liposomes should contribute to prevention of the gel-to-liquid phase transition of the liposomes during the rehydration process, which has been known to be a main cause of liposome disruption. We expect that the results from this study will provide an insight into the influence of zwitterionic additives on freeze-dried lipid bilayers and the lyoprotective effect, which should be useful in many biochemical and biomedical fields.
View full abstractDownload PDF (801K) -
Junji Matsuoka, Takumi Kusano, Yuuki Kasama, Etsuko Tominaga, Junya Ko ...2017 Volume 66 Issue 11 Pages 1285-1291
Published: 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 11, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe structures of micelles and microemulsions consisting of polyglycerol polyricinoleate (PGPR) were investigated by small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and rheological measurements. The SAXS results show that amphiphilic PGPR molecules form stable micelles in glycerol. When vitamin E is added to the PGPR micelles, it is encapsulated in the micelles and forms an emulsion. These micelles are stable towards mechanical shearing up to a shear rate of 1000 s–1, with shear thinning occurring in the emulsion above 100 s–1, indicating that the emulsion may undergo break up by shearing, but recovers the structure by releasing shear strain.
View full abstractDownload PDF (553K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|