
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Shun Sato2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 289-295
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリー HTMLGlyceric acid (GA) is an oxidative product of glycerol, and its d-isomer is obtained as a phytochemical from tobacco leaves and fruits of some plants. However, the production and applications of GA have not yet been fully investigated. In this review, recent developments in the microbial production of GA and its application to bio-related materials are summarized. The sodium salt of diacylated GA showed superior surface tension-lowering activity and antitrypsin activity. GA and its glucosyl derivative had positive effects on the viability and collagen production of skin cells in vitro, respectively. Glucosyl derivatives of GA showed protective effects against heat-induced protein aggregation. In addition, the microbial production of GA using raw glycerol as the starting material was investigated. The effect of methanol, a major impurity in raw glycerol, on GA production was investigated, and mutant strains to tolerate methanol in the culture were constructed. Enantioselective production of GA using newly isolated microbial strains has also been developed.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (651K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Na Liu, Rui Han, Huanran Huo, Hui Wang, Wanming Bai, Weibao Kong, Xiao ...2011 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 297-308
発行日: 2011年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリーThe aim of this work was to evaluate the quality of the five mono-cultivar (Frantoio, Leccino, Picholine, Coratina and Ezhi-8) virgin olive oils (Mc-VOOs) produced in Longnan (China) from 2013 to 2017 through analysing the organoleptic quality, physicochemical properties, phenolic contents, antioxidant activity and fatty acid composition. The leading principal components for assessing the quality of Mc-VOOs were extracted by principal component analysis (PCA). The results indicated that the five Mc-VOOs showed obvious differences (p < 0.05) in flavour and substance composition with the variation of cultivar and production year; however, the same cultivar of VOO displayed certain homogeneity in five consecutive years of assessment. The five Mc-VOOs were rich in phenolic compounds and unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic acid. The quality of VOO was mainly determined by the genetic characteristics of olive cultivar, meanwhile, fruit maturity, soil and climate factors also affected its quality. The content of phenolic compound, DPPH· scavenging rate, proportion of unsaturated fatty acids and iodine value of Coratina were the highest, on the contrary, Ezhi-8 was the lowest in general. The results of PCA showed that the five leading principal components to evaluate the quality of Mc-VOOs were oleic acid, linoleic acid, acid value, total phenol and trace components (such as C20:1 and squalene) successively. In conclusion, the five Mc-VOOs from Longnan show excellent quality and have certain uniformity in different production years.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (944K) -
Janjira Tangsanthatkun, Thunchanok Sonprasert, Sopark Sonwai2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 309-319
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリーThis research investigated the effect of polyglycerol ester of fatty acids (PGE) on the crystallization of palm olein (POL). Three PGEs were studied: two solid-state PGEs (PGE1105 and PGE1117) and one liquid-state PGE (PGE1155). The addition of 0.5-5% wt. PGEs influenced the crystallization kinetics of POL and this depended on the type and concentration of the emulsifiers. During cooling down with a cooling rate of 5℃/min, the samples containing PGE1105 and PGE1117 started to crystallize at higher temperatures when compared with POL but the crystallization began at lower temperatures for the samples containing PGE1155. All samples with added PGEs exhibited lower solid fat content than that of POL after 12 h of crystallization time. The number of crystals decreased with an increase in the crystal size with PGE addition but there was no effect on polymorphism. Overall, the results suggested that PGE1105 and PGE1117 enhanced the early stages of POL crystallization possibly via the template effects but suppressed the later stages, whereas PGE1155 delayed the whole process of POL crystallization. The application of POL is often limited by its tendency to get cloudy at low temperatures during long-term storage. Based on the results, 1-5% wt. PGE1155 could be used to delay or prevent the crystallization of POL at low temperatures.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1686K) -
Sadok Mokbli, Hassen Mohamed Sbihi, Imededdine Arbi Nehdi, Mohammad Az ...2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 321-332
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリーOils play a key role as raw materials in a variety of industries. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential of Datura innoxia seed oil cultivated in Saudi Arabia for industrial purpose and to study the effects of hexane, chloroform, and isopropanol as extraction solvents on the compositions of the extracts. The results showed that the hexane and chloroform extracts were mainly neutral oils which were rich in linoleic (≈46%) and oleic (≈31%) acids. However, the isopropanol extract contained large amount of neutral oil and organic acids. Neutral oil contained mainly palmitic acid (40.2%) and some important and valuable epoxy (15.4%) and cyclopropane (13.2%) fatty acids. Analysis of the sterol and tocopherol levels of the crude and purified oil extracted revealed that they were significantly affected by the extraction solvent used.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (635K)
-
Kotaro Kaneko, Masaaki Akamatsu, Kenichi Sakai, Hideki Sakai2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 333-339
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリー
電子付録We synthesized hydrophilic amine-based protic ionic liquids (PILs) with hydroxy groups in their cations and anions, and characterized their adsorption at a solid (iron-based substrate) / aqueous solution interface. The IL samples employed in this study were triethanolamine lactate, diethanolamine lactate, and monoethanolamine lactate. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) measurements revealed that the adsorption mass of the hydrophilic PILs was larger than that of the comparative materials, including a non-IL sample (1,2,6-hexanetriol) and an OH-free sample in the cations (triethylamine lactate). Additionally, an increase in the number of hydroxy groups in the cations resulted in an increased adsorption mass. Force curve measurements by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements proved the high adsorption density of the hydrophilic PILs on the iron-based substrate. A decreased kinetic friction coefficient was also observed in the hydrophilic PIL systems. Moreover, hydrophilic PILs are expected to have potential applications as water-soluble lubricants and additives for metal surface treatments.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (875K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (875K) -
Issei Takeuchi, Yuuto Kato, Kimiko Makino2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 341-348
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリーThe effects of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) on the release behavior of polymer nanoparticles from nanocomposite particles using amino acids were investigated. Rifaximin (RFX) was used as a hydrophobic drug model. RFX-loaded poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLLGA) nanoparticles were prepared using an antisolvent diffusion method. They were then spray-dried with equal amounts of amino acids to prepare the nanocomposite particles. The mean diameters of nanocomposite particles were 2.86-5.42 μm. The particle size increased as the concentration of PVA aqueous solution increased. The mean diameters of RFX-loaded PLLGA nanoparticles were 150-160 nm; however, the particle size distributions of those prepared using 0.25% (w/v) PVA aqueous solution differed significantly immediately after preparation and after redispersion from nanocomposite particles. The release test results of nanocomposite particles revealed that those prepared using 0.25% and 0.50% (w/v) aqueous PVA solutions rapidly released RFX. In contrast, particles prepared using 2.00 and 4.00% (w/v) PVA aqueous solution showed sustained drug release. The results of drug release tests of nanoparticles redispersed from nanocomposite particles showed that the nanoparticles prepared using 0.50% and 2.00% (w/v) PVA aqueous solution suppressed the initial burst. Therefore, we considered that the results of the drug release behavior of the nanoparticles in these particles reflectsreflect the release behavior of the nanoparticles from the nanocomposite particles. These results indicate that the rate of redispersion from nanocomposite particles to nanoparticles can be controlled by changing the concentration of PVA aqueous solution.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1237K) -
Yusuke Kimura, Yuki Mashiyama, Haruka Maruyama, Atsuhiro Fujimori2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 349-362
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリーUsing glucose oxidase and salmon testis-derived DNA molecules, we sought to extend the recently proposed idea of interfacial adsorption denaturation. The surface pressure-time (π-t) isotherm of the glucose oxidase Gibbs monolayer exhibited a rapid increase in surface pressure and a relatively prompt transition to a liquid condensed film. The appearance of this rapid liquid expansion phase occurred much earlier than that previously identified for lysozyme, trypsin, cytochrome C, and luciferase. This experimental finding was linked to the number of hydrophobic residues in the constituent unit, and the number of hydrophobic residues in glucose oxidase was the highest among these biomolecules. On the other hand, DNA molecules do not have such hydrophobic groups, or present a positive surface on the π-t curve. However, interfacial adsorption occurred, and the existence of molecules at the air/water interface was confirmed, even in the two-dimensional gas phase state. Furthermore, it was confirmed that an increase in surface pressure was detected during the formation of a mixed film of DNA molecules and biomolecules, forming a stable Gibbs monolayer. This mimic the behavior of mixed monolayer formation with matrix molecules in Langmuir monolayers. Moreover, it was clarified that the interfacial adsorption denaturation behavior changed when pH dependence was evaluated considering the isoelectric point of the biomolecular group.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5097K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5097K) -
Puja Bhattarai, Tulasi Prasad Niraula, Ajaya Bhattarai2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 363-374
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリーThe physicochemical properties of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) in pure water and ethanol-water mixtures in the presence and absence of MnSO4.6H2O were studied by measuring the conductivity at room temperature. The concentration range of CTAB was ~1.00 × 10-5 M to ~1.00 × 10-2M and the concentration of MnSO4.6H2O was 0.001 M, 0.005 M, 0.01 M. With increasing ethanol content in the solvent composition, the critical micelle concentration (CMC) and the degree of micellar dissociation (α) of CTAB increased. With the help of CMC and α, the standard free energy of micellization (ΔG m ο ) was evaluated. With an increase in ethanol content, the negative values of ΔG m ο decreased. CTAB micellization was tested in the context of specific solvent parameters. The solvent conductivity ratio at CMC to limiting conductivity was employed as a solvophobic influence. The addition of salt (MnSO4.6H2O) decreases the CMC of CTAB due to the screening of the electrostatic repulsion of the head groups. Here, we report that micellization is strongly influenced by salt concentration.
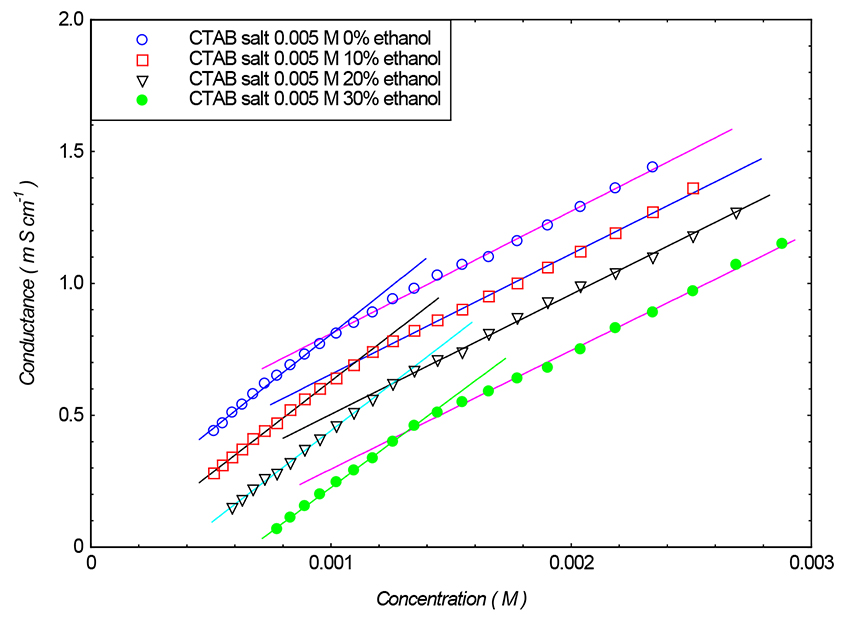 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (845K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (845K)
-
Ruihao Niu, Fusheng Chen, Chen Liu, Xiaojie Duan2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 375-383
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリーIn this study, the relationship between the composition and rheological properties of peanut oil bodies from aqueous enzymatic extraction was evaluated. Aqueous enzymatic extraction using a combination of cellulase and pectinase at a 1:1 ratio effectively destroyed the structure of the cell wall and resulted in the maximum oil body yield of 90.7%. The microstructure and interfacial membrane composition of the peanut oil bodies were observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The oil bodies contained three inherent proteins (oleosin, caleosin, and steroleosin) along with two adsorbed foreign proteins (arachin and lipoxygenase). Five phospholipids were detected using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Among them, phosphatidylcholine, which plays a major role in the stability of oil bodies, was the most abundant. The measured rheological properties indicated that the oil bodies were a typical elastic system. Elevated temperature and high-speed shear destroyed the binding between proteins and phospholipids, reducing the oil body stability. The findings will facilitate the commercial application of peanut oil bodies by improving the extraction rate of peanut oil bodies and clarifying their stabilization mechanism.
Practical Application: This paper studies the enzymatic extraction, composition and rheological properties of peanut oil bodies. It provides a theoretical basis for the large-scale application of peanut oil bodies in the food and cosmetic industries. It is beneficial to improve the application value of peanut resources.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1615K) -
Wenyi Chen, Maomao Kou, Shaoyan Lin, Nanjing Zhong2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 385-395
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリー
電子付録In this study, Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB), Rhizomucor miehei lipase (RML) and Lecitase® Ultra (LU) were immobilized onto the mesoporous silica SBA-15. The glycerolysis performance of the obtained supported lipases (lipase@SBA-15) in solvent systems was carefully investigated. LU@SBA-15 exhibited good glycerolysis performance in solvent-free system, with diacylglycerols (DAG) content and triacylglycerols (TAG) conversion at 52.4 and 98.6% respectively obtained after 12 h reaction at 60°C. CALB@SBA-15 showed good glycerolysis activity in tert-pentanol and tert-butanol systems, with TAG conversion over 90% obtained. In addition, the present CALB@SBA-15 exhibited selectivity for monoacylglycerols (MAG) production, with glycerol to TAG molar ratio increased to 3:1, MAG content over 80% and TAG conversion over 99% could be obtained from both tert-pentanol and tert-butanol systems. However, RML@SBA-15 showed low glycerolysis activity neither in solvent nor in solvent-free systems. The present results favor the practical enzymatic design for MAG and DAG production.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (708K) -
Nusrat Jahan Mukta, Shamim Mahbub, Md. Joynal Abedin, Md. Emdad Hossai ...2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 397-407
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリーThe fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug namely ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CFH) is widely prescribed for the treatment of different bacterial infections. The interaction of CFH with a synthetic polymer, polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), and biopolymer, bovine serum albumin (BSA) was studied by UVvisible and fluorescence spectroscopic methods at different temperatures. The binding constant (K b ) for the CFH-PVP complex was determined from the Benesi-Hildebrand plot. PVP of different molecular weights (MW) (such as 24,000, 40,000, 360,000, and 700,000 g. mole-1) were used for the interaction between CFH and PVP. The gradual increase in K b value and the complexation reaction was found to be much enhanced with the augmentation of the MW of PVP. The values of K b were also found to be increased with increasing temperatures as well as with the increase of electrolyte/acetic acid concentration. The Gibbs free energy of binding (∆G 0) values of the interaction process was negative which indicates the complex formation is thermodynamically spontaneous. The positive values of enthalpy (∆H 0) and entropy (∆S 0) of binding connote that the binding force for CFH-PVP complexation is hydrophobic in nature and the complexation is entropy controlled. The negative intrinsic enthalpy (∆H *,0) values indicate the high stability of CFH-PVP complexes. Molecular docking calculation discloses the existence of similar binding forces between CFH and PVP obtained by the analysis of experimental data from UV-visible spectroscopic method. The binding constant between CFH and BSA (K b ), quenching constant (K sv ), the number of binding sites (n), and the quenching rate constant (K q ) for the CFH-BSA system were also calculated. The values of K sv , K q , and n for the CFH-BSA system are lower in 0.05 mol L-1 urea solution and higher in PVP solutions compared to those of aqueous medium.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (990K) -
Salah A. Almaiman, Ibrahim Abdel Rahman, Mostafa Gassem, Dalal, Alkh ...2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 409-415
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリーEffect of traditional fermentation on pH, titratable acidity, proteins, amino acids, and sugars contents of three local sorghum cultivars namely Hamra, Biadah and Shahla used in making khamir local bread were investigated. During 24 fermentations, the pH of fermented dough dropped sharply and this was coincided with increase in total acidity. Fermentation was found to cause no significant change in protein content of the cultivars. Amino acid analysis, revealed slight insignificant improvement in lysine, and leucine content but there was a slight decrease in valine, phenyl alanine and arginine content in fermented dough. Glucose, fructose and maltose content of the three sorghum cultivars increased considerably in the early stages of fermentation, followed by decrease towards the end of fermentation. Low amount of sucrose detected in the three cultivars and it was completely utilized after 8 hrs. of fermentation.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (359K)
-
Yoshihiro Tsuchiya, Masayasu Ban, Mikiya Kishi, Takahiro Ono2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 417-430
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリーCeramide plays an important role in maintaining the skin barrier function. Aging and atopic dermatitis are known to reduce the levels of ceramide. Application of exogenous ceramide to the skin can restore the barrier function. In recent years, the effect of oral intake of ceramide has been demonstrated to improve the skin barrier function, and it has been marketed as a food supplement. Therefore, it is important to provide information on the safety of unintentional overdose of ceramide. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in 30 healthy adults, aged between 20 and 60 years of age (both female and male). The subjects consumed either dietary supplement, comprising 1197 mg of acetic acid bacteria containing 9.06 mg of ceramide, or placebo for four consecutive weeks. Safety was evaluated based on physical measurements, blood test, urinalysis, adverse events, and side effects. The results showed several significant differences in physical measures and blood tests between the two groups. However, these differences were considered to be unrelated to the intake of the ceramide-containing acetic acid bacteria or placebo. Thus, no adverse effects or clinically concerning changes in physical, blood, and urine parameters were observed due to the excessive intake of the ceramide-containing acetic acid bacteria in the present study.
TRIAL REGISTRATION: UMIN000035481
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (394K)
-
Seung-Heon Shin, Mi-Kyung Ye, Mi-Hyun Chae, Dong-Won Lee2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 431-438
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
ジャーナル フリーEssential oils extracted from plants contain protective volatile compounds and are known to processes antibacterial, antifungal, anti-oxidative, and anti-inflammatory effects. This study was conducted to explore the immunomodulatory effects of essential oil extracted from Chamaecyparis obtusa (EOCO) on house dust mite-induced mucosal inflammation. Cultured primary nasal epithelial cells were stimulated with Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (DP), and Dermatophagoides farina (DF) for 48 h. The production of interleukin (IL)-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the expression levels of nuclear factor (NF)-κB, activator protein (AP)-1, and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) were determined by western blot analysis. To examine the effect of EOCO on the production of chemical mediators and the expression of transcription factors, epithelial cells were pretreated with EOCO for 1 h before stimulation. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were cultured in nasal epithelial cell conditioned media (NECM) for 72 h, after which the levels of IL-5, interferon (IFN)-γ, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α were measured. DP and DF enhanced the production of IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP, and EOCO pretreatment inhibited their production from nasal epithelial cells. EOCO pretreatment also significantly suppressed the expression of NF-κB and AP-1. NECM induced the production of IL-5, IFN- γ, and TNF-α from PBMCs, and only TNF-α production was significantly inhibited by EOCO pretreatment. EOCO pretreatment inhibited the DP and DF induced nasal epithelial cell derived cytokine production and TNF-α production from PBMCs. These results indicate the potential value of EOCO in the treatment of airway inflammatory or immunological diseases.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (482K)
-
Jin-Hua Zhang, Min Zhang, Bao-Qing Bai, Huai-Wang Jia, San-Hong Fan2021 年 70 巻 3 号 p. 439-451
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/03/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/12ジャーナル フリーThis experiment treated perilla seeds with different concentrations of NaCl solution to enrich and purify their rosmarinic acid (RosA). The results showed that low concentrations of salt (0-20 mmol/L) promoted seed germination, while high concentrations (> 20 mmol/L) inhibited germination. When the salt concentration was 20 mmol/L, the germination rate was the highest. The content of RosA in germinated perilla seeds was 3.5 mg/g, which was 3.5 times as much as that in the seeds without germination. The RosA was purified using NK-109 macroporous resin and its adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics were determined. The adsorption kinetics showed that the adsorption behavior of RosA in NK-109 resin conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The model for RosA in the NK-109 resin exhibited Langmuir adsorption based on a spontaneous exothermic process according to its adsorption thermodynamics, which included both physical and chemical adsorption. The optimized process conditions were as follows: the loading concentration of 0.04 mg/mL, loading volume of 40 mL, 70% methanol as the eluent with the volume of 60 mL, and the purity of RosA was 42.1%.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1094K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|