
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Jingqi Ran, Yong Zhu, Tingyuan Ren, Likang Qin2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 631-639
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFatty acid profile and thermal stability of 7 varieties zanthoxylum bungeanum (GZF, GDJ, CJJ, SHY, SMN, SJY, GTS) seed oils (ZBO) were studied. Fatty acid profile, thermal stability were determined using gas chromatography equipped with flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and thermogravimetry analysis (TGA), respectively. Chemical properties, total phenolics and antioxidant activities of ZBO were determined as well. Palmitoleic acid and oleic acid (OA) were the dominant fatty acids, the ratio of ω-6/ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) of ZBO ranged from 0.66 ± 0.01 to 1.17 ± 0.01, seven varieties ZBO showed a higher thermal stability, with the 50% mass loss temperature ranged from 397.35 ± 4.02°C to 412.50 ± 2.35°C, GZF seed oil showed a balance fatty acid profile, the ratio of ω-6/ω-3 PUFA was 0.90 ± 0.01, GDJ seed oil showed a higher thermal stability, which the 50% mass loss temperature was 412.50 ± 2.35℃. These results suggested that fatty acid profile and thermal stability of ZBO were affected by cultivars and geographic region, and it may serve as a functional dietary oil.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (672K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (672K) -
İsra Toptanci, Mustafa Kiralan, Onur Ketenoglu, Mohamed Fawzy Ramadan2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 641-649
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBlack cumin oil (BC) contains certain phytochemicals, including phenolics, tocopherols, and sterols, which show strong oxidation stability. In this study, BC was blended with refined corn oil (CO) at two concentrations (5% and 10%, w/w) and stored in plastic and glass bottles under light and dark conditions. Under light-storage conditions, blended oils in plastic bottles showed lower peroxide value (PV) and conjugated diene value (CD) compared to the control sample than dark-storage. It was also aimed to examine the phthalate levels in oil samples and evaluate the products’ safety. Five main phthalates, namely di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP), butyl-benzylphthalate (BBP), diisononyl phthalate (DiNP), and diisodecyl phthalate (DiDP), were evaluated. In dark and light storage conditions, the phthalate level was determined below the LOQ value in CO without added BCO in the plastic and glass bottles. In the plastic-packaged blended samples, DEHP was determined above the LOQ value in dark storage, while BBP was detected in addition to DEHP in the samples stored under the light. On the other hand, phthalate values were determined below the LOQ value in all samples stored in glass packages under the light. DEHP was the most abundant phthalate in plastic-packaged blended oils under light storage, ranging from below the LOQ (0.23 mg/kg) to 0.83 mg/kg. Based on the present findings, BC improved the stability of CO under light storage, and the phthalate levels of blended oils did not exceed the specific migration limits (SMLs) for each phthalate.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (611K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (611K) -
Buket Aydeniz-Guneser, Emin Yılmaz2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 651-662
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: March 16, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSSunflower oil oleogels consisting of 3% and 8% polyglycerol stearate (PGSO) were studied as an alternative frying media for onion rings. The physicochemical properties and thermo-rheological characteristics of oleogels were provided. The sensorial quality and texture profiles of onion rings fried in oleogels were compared with those fried in control sunflower oil. Free fatty acids at the end of 6 h were determined, and decreasing trend was reported in order as PGSO-8, control (sunflower) oil, and PGSO-3. The oxidation induction time for PGSO-8 was significantly lower (1.46 min) than those of the control and PGSO-3 samples following frying. Compared to the control group, the onion ring samples fried in oleogels absorbed approximately 33-37% less oil. It was thought that this reduction would help consumers to less total calorie and weight gain from the fried products. There were no negative effects of oleogel usage on the L* value, aroma, crispness/texture, and overall acceptability scores for the onion ring samples fried in the oleogels.
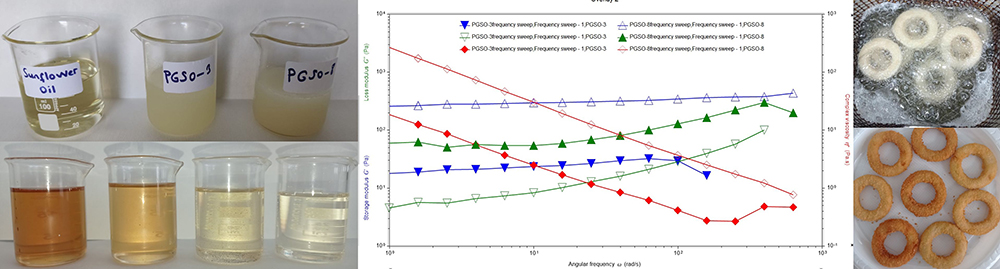 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2234K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2234K)
-
Hiroaki Kaga, Aoi Nakamura, Masanori Orita, Koji Endo, Masaaki Akamats ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 663-670
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialBiofilms are communities of microorganisms that have been widely studied because they can cause hospital-acquired infections and skin disorders. Polysaccharides secreted by microorganisms are constituents of biofilms, contributing to their adhesion and mechanical stability. Sophorolipids are biosurfactants with the ability to disrupt and remove biofilms. Biosurfactants have been targeted as potential substitutes for classical petrochemical-based surfactants in cosmetics. In this study, we fabricate a β-glucan film as a model biofilm, and quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) measurements are used to assess the biofilm removal. The viscoelasticity of the β-glucan films is monitored while sophorolipid solutions are introduced into the system, and we found that the film removal performance increases with the sophorolipid concentration. In addition, Δf (change in frequency)-ΔD (change in energy dissipation) plot analyses reveal that two processes are involved in the removal mechanism. The first process involves the adsorption of water (hydration) on the β-glucan film. The second process involves the removal of the β-glucan film from the sensor surface. Furthermore, it is suggested that sophorolipids interfere with the hydration of the β-glucan film and suppress increases in its viscosity. This is expected to be an essential factor for the removal of the β-glucan film. Sophorolipids, therefore, show potential for use in cosmetics as an eco-friendly agent for biofilm removal.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2100K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2100K) -
Saad M. Alshahrani2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 671-683
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe purpose of this study is to determine whether the complexing hydroalcoholic extract of Cuscuta reflexa (HECR) with phosphatidyl choline increases its bioavailability. As a result, a novel phytosomal delivery system for the HECR-soya lecithin complex was developed (HECR-phytosome). The HECR-phytosome complex was synthesized and characterized as phytovesicles. The formulation was prepared using a variable concentration of soya lecithin (1:1-1:3 percent w/v), a temperature range of (45-65°C), and sonication time (4-8 min). Optimization of HECR-loaded phytosomal formulations was performed using Design Expert software. A three-factor, three-level Box-Behnken design was used to optimize this HECR delivery system, as dependent variables, vesicular size and entrapment efficiency were evaluated using a Box Behnken factorial design. Further characterization of the optimized formulation included vesicle size, PDI, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency, FTIR, DSC, TEM, and in vitro release. Vesicle sizes ranged from 173.5±6.17 nm to 215.9±6.53 nm, and response rates for entrapment efficiency ranged from 52.9±1.65 to 77.2±1.1%. The uniform structure and spherical shape were demonstrated by transmission electron microscopy. Among the drug release kinetic models, the formulation followed the Higuchi model (R2 = 0.9978), releasing 96.3±3.7% of the polyphenol and flavonoids phytoconstituents from HECR-loaded phytosomes in 12 hours, compared to 49.3±2.5% in the plain extract. In addition, the optimized formulation passes the stability test. Therefore, the results demonstrated that phytosomal nanocarriers have the potential to increase the bioavailability of Cuscuta reflexa extract.
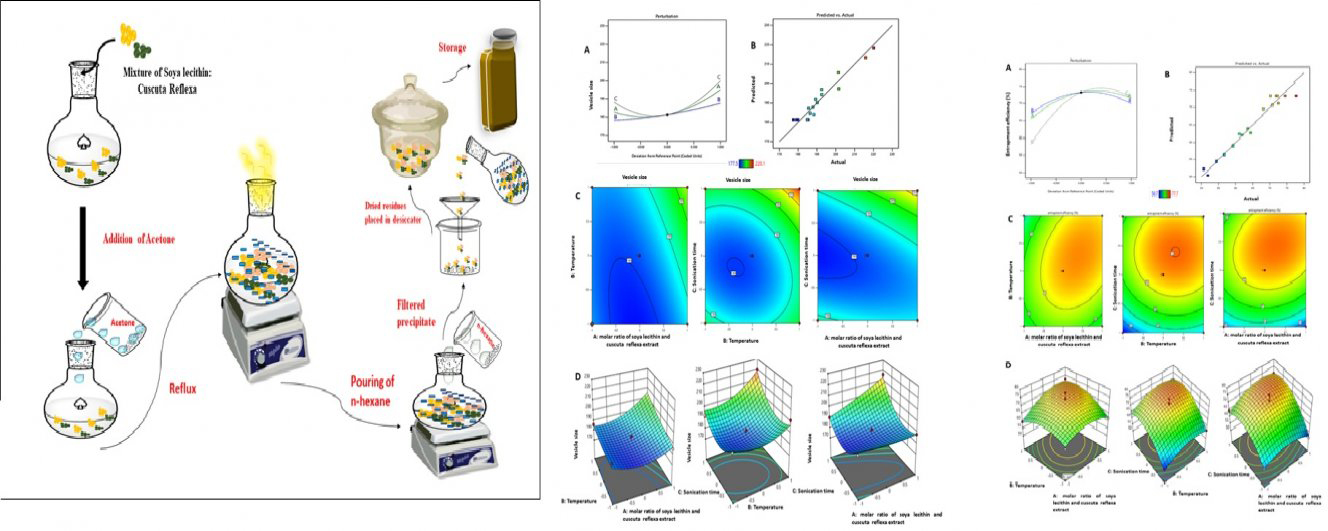 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3000K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3000K) -
Md. Abdullah Al Nahid, Michinori Karikomi, Eri Nasuno, Norihiro Kato, ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 685-692
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSAbstract: This paper presents a feasible and reliable phase transfer protocol for polyoxyethylene alkyl amine surfactant (AMIET)-coated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in aqueous media to chloroform using a pH-triggered method, through the liquid-liquid interface. In the initial stage, the colloidal aqueous dispersion is destabilized by pH adjustment towards the isoelectric pH of the nanoparticle, which promotes the separation of the particles from water. We further explored a mechanistic view of this phase transfer phenomenon, considering the orientation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic moieties depending on the nature of the surrounding solvent. It was proposed that the AMIET molecules bound to the AuNPs undergo conformational changes through phase transfer. Ultraviolet visible absorption spectra before and after the phase transfer reveal that the original morphology and dispersion states of the particles were preserved.
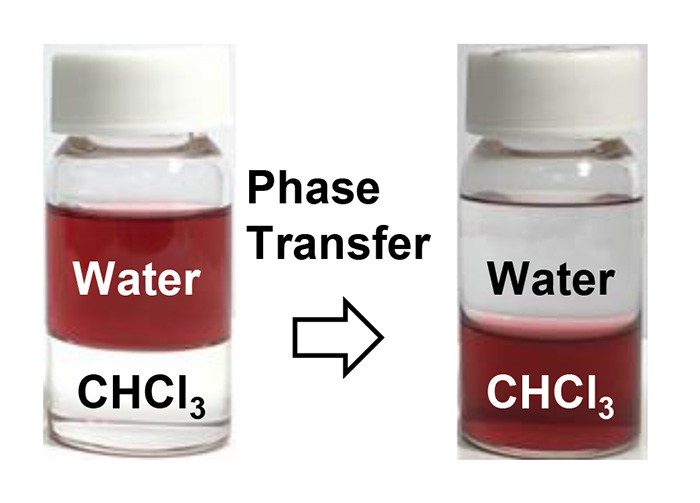 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1608K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1608K)
-
Iram Liaqat, Sikander Ali, Abida Butt, Arjumand Iqbal Durrani, Urooj Z ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 693-700
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFeather wastes-byproduct of commercial poultry processing plant is produced in large amounts. Keratinolytic enzymes produced by feather degrading bacteria can easily degrade these waste products releasing pure keratin as a residue. The aim of present study was to isolate, and characterize feather degrading bacteria as well as assess the keratinolytic potential of purified enzyme. Three feather degrading bacteria (dps3, wps1 and dcs1) were isolated from feathers of domestic chickens. Preliminary characterization of isolated bacteria revealed these isolates belonging to genus Bacillus. 16S rRNA gene sequencing identified the isolates as B. subtilis dps3 (MW255302), B. cereus wps1 (MW255303) and B. licheniformis dcs1 (MW255304). Cell free supernatant of B. licheniformis dcs1 degraded feathers completely in 14 days indicating its keratinolytic ability. Purification of keratinase enzyme from B. licheniformis dcs1 was performed using column chromatography. SDS-PAGE indicated its molecular weight as 32 KDa. Kerotinolytice activity was maximum at optimum pH of 7 and 45℃ temperature. Enzyme showed the potential to degrade keratin material such as hairs and nails of humans. Findings of current study suggested that purified enzyme possess potential to upgrade nutritional quality of poultry waste containing keratin and might play as important biotechnological tool for keratin hydrolysis.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (456K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (456K) -
Shahzad Tufail, Iram Liaqat, Sikander Ali, Mobina Ulfat, Ayesha Shafi, ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 701-708
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe use of bacteria in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) emerges as an ecofriendly and exciting approach. In the present study, we reported the biosynthesis of AgNPs by using culture supernatant of the bacteria Bacillus licheniformis (MN900686). The biogenically synthesized AgNPs were confirmed by the change in the color of the culture filtrate from yellow to brown after the addition of AgNO3. Further characterization performed by means of UV vis-spectroscopy showed absorption peak at 414 nm which confirmed the formation of AgNPs. Fourier Transfer infrared (FTIR) confirmed the involvement of biological molecules in the formation of nanoparticles (NPs). The SEM revealed that the NPs have approximately 38 nm size. The agar well diffusion assay was used to determine antibacterial activity while tube dilution method was used to determine minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC). The human pathogenic bacterial strains i.e., P. aeruginosa (MN900691) and B. subtilis (MN900684), were used as test strains. The anti-bacterial assay against test strains revealed that these NPs showed concentration dependent increased zone of inhibition (ZOI). The maximum ZOI at 25 µL of AgNPs was 20 mm against B. subtilis after 24 hours of incubation. One-way ANOVA test showed significant ZOI (p ≤ 0.05) against B. subtilis. The MIC was ranged from 4.3-6.6 μg/mL while MBC ranged from 8.3 to 6.6 μg/mL. Overall, this study suggested that the biogenically synthesized NPs are an effective alternative source of antimicrobials against pathogenic bacteria.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (846K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (846K) -
Lin Zhang, Yujun Li, Daqing Sun, Feng Bai2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 709-720
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCurrent time obesity is the major challenges globally and the incidence of the obesity has raised dramatically in current years. The obesity enhanced the various metabolic diseases such as diabetes, cardiac, cancer and steatohepatitis. Natural drug having the long history to ameliorate the obesity and its related metabolic disorder. In this experimental study, we scrutinized the anti-obesity effect of nimbolide against high fat diet (HFD) induced obesity in rats. Wistar rats were divided into 5 groups and each group contains 10 rats. The body weight, tissue weight was estimated at regular time. Carbohydrate, lipid, hepatic, inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant and inflammatory parameters were estimated. The mRNA expression was also estimated. Nimbolide treated groups significantly (p < 0.001) suppressed the body weight at dose dependent manner. Nimbolide significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the hepatic parameters and altered the antioxidant parameters such as thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide mutase (SOD), glutathione S transferase (GST); decreased the level of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α). Nimbolide suppressed the mRNA expression of glucose-6-phosphatase HO-1 and nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor-2 (Nrf2). Collectively, we can say that nimbolide having the capability to suppressed the HFD induced obesity via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
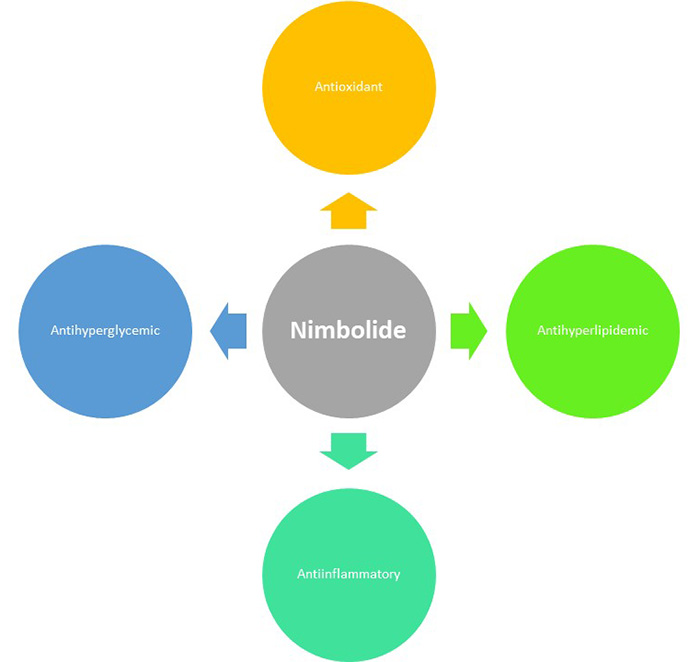 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1759K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1759K) -
Wenyi Chen, Maomao Kou, Lin Li, Bing Li, Jianrong Huang, Shudong Fan, ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 721-733
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, SBA-15 was functionalized by organic groups (-CH3, -C4H9, -C8H17, -CH2CH2NH2, -C6H5, et al.), and then Lecitase® Ultra (LU) was immobilized onto the modified SBA-15 for soybean oil degumming. The hydrolysis activity, degumming performance, reusability in degumming, and the composition of phospholipids in the gum, of the immobilized LU samples, were carefully studied. Hydrolysis activities over 1800 U/g were obtained from all the immobilized LU samples. The highest activity of up to 4554.17 U/g was observed from the 3-ureidopropyl group-modified SBA-15-supported LU. Most of the immobilized LU samples removed the phospholipids effectively from crude soybean oil (initial phosphorous content 314.23 mg/kg), with a residual phosphorus content of less than 10 mg/kg. The reusability of the immobilized LU samples in the degumming process was evaluated. No loss of activity was observed from the methyl and N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl group-modified SBA-15-supported LU samples after five cycles of reuse. In addition, 3-aminopropyl and 3-glycidyloxypropyl group-modified SBA-15-supported LU samples retained over 90% of their initial activity; N-phenylaminomethyl and 1-isocyanatopropane group-functionalized SBA-15-supported LU samples retained approximately 80% of their initial activity. The phospholipids in the gum were analyzed. The n-octadecyl and N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl group-functionalized SBA-15-supported LU samples were selective for lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) preparation, and LPE percentages up to 37.14 and 38.80% were obtained, respectively. The N-phenylaminomethyl group-modified SBA-15-supported LU showed selectivity toward lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) production, with an LPC percentage of up to 38.5%.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1871K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1871K)
-
Hiroko Yatsuhashi, Hiroko Takumi, Yoshinobu Terada, Takashi Kuriki2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 735-745
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCarotenoids, classified into carotenes and xanthophylls, are natural lipophilic pigments that are widely distributed in plants. Red paprika is unique in its high levels of various xanthophylls. Dietary paprika xanthophylls have been shown to reduce UV-induced photo damage by the strong antioxidant activity in the skin. However, the precise effects of paprika xanthophylls on skin condition are still unknown. Here we show that skin moisture is enhanced by the intake of red paprika supplements including seven xanthophylls. We conducted a 4-week randomized, single-blind, parallel-group controlled trial to clarify the effects of dietary paprika xanthophylls on facial skin. The results showed that the moisture was significantly higher in the paprika intake group than in the control (21.0±8.9 vs 13.4±6.0 (A.U.)). There was no significant difference between the paprika and control groups in other parameters such as viscoelasticity, the number of wrinkles, and the amount of water evaporation. On the other hand, the number of brown stains in the paprika group increased significantly, to 190±26 from 173±30 (p < 0.05). In vitro experiments, quantitative real-time PCR showed that paprika extract led to increases in the gene expression of Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) and hyaluronic acid synthase 3 (HAS3) in cultured keratinocytes. Western blotting showed that the paprika extract enhanced AQP3 expression. Taken together, taking supplements containing paprika xanthophylls may provide beneficial effects of moisture on facial skin. The study provides new insights into understanding the role of paprika xanthophylls in the skin.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2677K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2677K)
-
Kasumi Kasai, Noriyoshi Nagahora, Kentaro Okuma, Kouki Matsubara, Kose ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 747-757
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialLiving cells and organelles are separated by a lipid membrane bilayer. It is possible to induce morphological changes in this membrane by disturbing the order of the membrane using external stimuli and understanding the details of this mechanism is expected to be applicable to intracellular transport. DBA (DBAB-BODIPY-aminopropyl), which contains (1) a DBAB (4-[di(biphenyl-4-yl)amino]azobenzene) moiety that undergoes photo-isomerization under visible light irradiation, and (2) a BODIPY (borondipyrromethene) fluorophore was synthesized. The π-π* transition absorptions of both the azo moiety and that of BODIPY moiety in DBA were observed, independently. The photo-isomerization rate constant of the DMSO solution of DBA at 299K is 5.5 ×10-3/s. The structure of the fluorescent group in DBA did not readily influence the isomerization. Upon introducing DBA into the lipid bilayer membranes of a vesicle suspension and irradiating the vesicles with visible light to isomerize the azo group, a morphological change in of the vesicles was observed due to the disturbance of the membrane order. Thus, DBA is a useful molecule for artificial modulation of the lipid membrane morphology.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2123K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2123K) -
Dwiprayogo Wibowo, Riski Hul Akma Malik, Faizal Mustapa, Toshiyuki Nak ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 759-770
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: April 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSElectrochemical processes are an effective method for detecting dangerous food ingredients. The synergistic between the reduction-oxidation (redox) processes inspired several papers and spurred research towards studying the new materials that can further adapt to optimize the rapid detection of chemical compounds. In this study, we report the eco-synthesis using graphene/TiO2 rutile (G/TiO2) electrode microstructures easily prepared through the physical method by mixing graphene and TiO2 powder and its application for sensing L-tryptophan (Trp) compound. The material characterization results show that the graphene surface is smoother than the G/TiO2 material. Graphene has been detected using X-ray diffraction (XRD) at a value of 2 thetas 26.39° and TiO2 forms rutile crystals (110). The FTIR spectrum exhibits the functional groups from graphene of -OH, C-H, C=C, C-O, and TiO2 identified with Ti-O bonds. The electrochemical test against G/TiO2 electrode microstructures for Trp compound shows that 0.5 g TiO2 rutile was the best composition functionalized with graphene material under 0.1M K3[Fe(CN)6] + 0.1M NaNO3 electrolyte with a scan rate of 0.1 V/s. Determination of the detection limit was obtained at 0.005 mg/L with a HorRat value of 1.05%. The stability test was carried out for 25 days, and the addition of Pb(NO3)2 as an interference compound had a significant effect on the decrease in electrode performance.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3419K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3419K) -
Masato Amano, Mariam C. Recuenco, Kazuaki Hashimoto, Hirobumi Shibata2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 771-778
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
Advance online publication: March 16, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWe synthesized Au nanoparticle (AuNP)/ZnO composite particles in presence of an anionic surfactant and evaluated their photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation. AuNPs synthesized from HAuCl4 in the presence of amylase and the precursor solutions of ZnO were mixed, followed by a hydrothermal process, to synthesize crystal face-controlled AuNP/ZnO composite particles. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectra confirmed the formation of AuNP/ZnO composite particles. Furthermore, different Au to Zn concentration ratios in the precursor solutions resulted in different amounts of AuNPs in the composite particles. In addition, the average size of the AuNP/ZnO composite particles decreased with increasing Au to Zn concentration ratio. We believe AuNPs act as the nuclei for ZnO particle formation. The photocatalytic activity of the AuNP/ZnO composite particles was evaluated by the photodegradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible-light irradiation. The photodegradation rate of MB was higher with AuNP/ZnO composite particles compared to that with the ZnO particles synthesized in the absence of AuNPs. The AuNP/ZnO composite particles exhibit photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation owing to the enhanced charge separation efficiency and the localized surface plasmon resonance effect.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1982K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1982K) -
2022 Volume 71 Issue 5 Pages 779
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 29, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (96K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|