
- 1 号 p. 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hisashi Kato-Noguchi2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 1-14
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/26ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLAllelopathy is the interaction between donor plants and receiver plants through allelochemicals. According to a great number of publications, allelopathy may be involved in several ecological aspects such as the formation of monospecific stands and sparse understory vegetation for certain plant species. Allelopathy also contributes to the naturalization of invasive plant species in introduced ranges. Autotoxicity is a particular type of allelopathy involving certain compounds. Many medicinal plants have been reported to show relatively high allelopathic activity. We selected plant species that show high allelopathic activity and isolated allelochemicals through the bioassay-guided purification process. More than 100 allelochemicals, including novel compounds have been identified in some medicinal and invasive plants, plants forming monospecific stands, plants with sparse understory vegetation, and plants showing autotoxicity. The allelopathic activity of benzoxazinones and related compounds was also determined.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (981K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (981K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Dinh Thi Chi, Ho Le Thi, Le Van Vang, Tran Thanh Thy, Masanobu Yamamot ...2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 15-21
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/02/21ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLA lure composed of (Z)-11-hexadecenal, (Z)-11-hexadecenyl acetate, and (Z)-11-hexadecen-1-ol at a ratio of 5 : 5 : 1 at a dose of 0.01 mg was optimal for the attraction of the Vietnamese strain of the diamondback moth (DBM). The combination of the sex pheromone with a plant volatile, allyl isothiocyanate, significantly increased the attraction of the pheromone trap. Females were also attracted, but they were only about 2% of all moths captured. In plots with 120–130 traps per ha, mass trapping with the combined lures reduced the DBM larval densities in cabbage fields as effectively as the spraying of insecticides 6 to 8 times. The weekly trap catches indicated that DBM adult densities in the mass-trapping fields were low until 28 days after transplantation, and then were kept to a modest increase until day 49. This field study also shows that the trap catches were well correlated with the DBM larval densities.
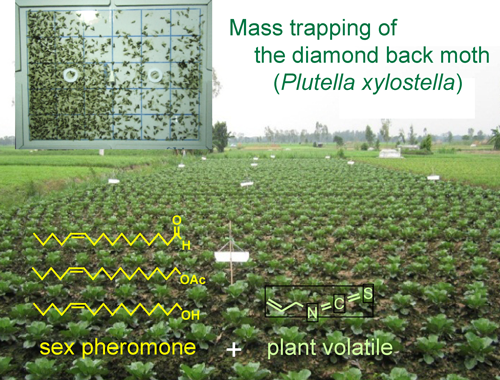 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (991K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (991K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ryosuke Nogami, Mari Nagata, Risa Imada, Kenji Kai, Takashi Kawaguchi, ...2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 22-30
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/26ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録From the 992 samples of culture extracts of microorganisms isolated from soil in Japan, we found that the extract of Streptomyces sp. no. 226 inhibited Orobanche minor seed germination without significantly affecting the seed germination of Trifolium pratense and the growth of Aspergillus oryzae and Escherichia coli. Using ESI-MS, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR, we identified the active compound as cycloheximide. Cycloheximide had half-maximum inhibitory concentrations of 2.6 ng/mL for the inhibition of seed germination of O. minor and 2.5 µg/mL for that of the conidial germination of A. oryzae. Since cycloheximide is known to inhibit translation by interacting with ribosomal protein L28 (RPL28) in yeast, we investigated whether RPL protein of O. minor plays a critical role in the inhibition of O. minor seed germination. Our data suggested that O. minor RPL27A was not sensitive to cycloheximide by comparing it to the strain expressing S. cerevisiae RPL28. These findings suggest the presence of an unidentified mechanism by which cycloheximide hinders O. minor seed germination.
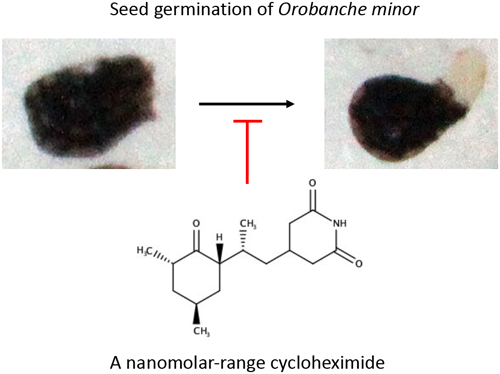 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3075K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3075K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masashi Kamezaki, Junko Otsuki, Katsuya Natsuhara2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 31-37
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/01/18ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe development and commercialization of new chemical classes of insecticides are important for efficient crop protection, particularly for combatting insecticide resistance and providing sustainable agricultural production. This study reports on oxazosulfyl, a novel “sulfyl” class of insecticide, against a wide range of insect pests of rice. In the laboratory assay, oxazosulfyl showed insecticidal activity against all developmental stages of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Phosphor imaging assays and soil drench bioassays demonstrated good systemic distribution in rice plants. Oxazosulfyl showed insecticidal activity against imidacloprid- and fipronil-resistant field populations of N. lugens, the white-backed planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horváth), and the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén), as well as the respective susceptible strains. No cross-resistance was observed among oxazosulfyl, imidacloprid, and fipronil. Oxazosulfyl with a wide insecticidal spectrum is a potentially useful pest management tool for sustainable rice production.
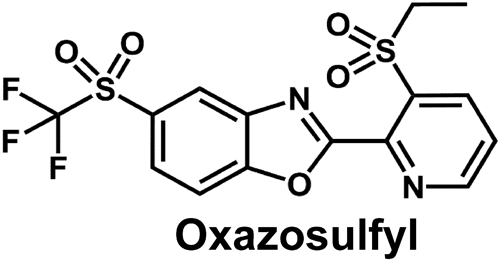 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (686K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (686K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Takeshi Adachi, Yusuke Suzuki, Takuo Fujisawa2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 38-45
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/02/21ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe degradation behavior of mandestrobin (1) was investigated in aerobic aquatic water–sediment systems exposed to continuous artificial sunlight (λ>290 nm). [14C]mandestrobin uniformly labeled at the phenoxy or benzyl ring was individually applied to the overlying water of the system at a rate equivalent to 262.5 g a.i./ha. The transformation of 1 was mainly proceeded via photoinduced bond cleavage at the benzyl phenyl ether and the subsequent rearrangement reaction. Interestingly, some of the photodegradates and microbial metabolites of 1 observed in the aquatic photodegradation and water–sediment (dark) studies, respectively, were never detected. Furthermore, the observed photoproducts were less formed and were steadily degraded or metabolized to carbon dioxide or strongly adsorbed to bottom sediment. The fate of 1 and its degradates in illuminated water–sediment systems was considered to reflect realistic conditions more precisely, as it accounts for various effects attributed to sunlight.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (353K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (353K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Takamitsu Otake, Yoshie Aoyagi, Takashi Yarita2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 46-51
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/26ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe objective of this study was to assess the long-term stability of pesticide residues in brown rice and soybean. The long-term stability of pesticide residues in brown rice and soybean was assessed for 5415 days (over 14 years) and 1801 days (about 5 years), respectively. The samples—certified reference materials (CRMs) 7504-a (brown rice) and 7509-a (soybean) —were prepared by freeze-pulverization. Two target pesticides (etofenprox and fenitrothion) were selected for brown rice and four (chlorpyrifos, diazinon, fenitrothion, and permethrin) for soybean. Our analytical results for long-term stability based on highly reliable isotope dilution mass spectrometry were in the range of expanded uncertainty (k=2) for the certified values of each CRM. The concentration showed a decreasing trend in none of the target pesticides when the samples were stored at temperatures between −20 °C and −30 °C, which indicated that the target pesticides were stable for the tested long terms.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (456K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (456K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Taito Sasaki, Ryohei Naito, Toshiaki Ohara, Kosei Sakane, Shuhei Tanak ...2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 52-57
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/01/23ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録Flusulfamide inhibits germination of Plasmodiophora brassicae resting spores to suppress clubroot disease, but its mechanism of action on the germination of P. brassicae resting spores remains unclear. In this study, P. brassicae resting spores were treated with flusulfamide and visualized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The gene expression of P. brassicae resting spores was analyzed using RT-PCR, followed by immunoblotting analysis. TEM results revealed that flusulfamide suppressed the primary zoosporogenesis of P. brassicae resting spores during the early phase, and RT-PCR results revealed that flusulfamide affected the gene expression during the germination of the resting spores. Immunoblot and RT-qPCR analyses revealed that PbCyp3, an immunophilin (peptidyl-prolyl-isomerase) gene, was highly expressed, resulting in the unusual accumulation of PbCYP3 protein in P. brassicae resting spores immediately after treatment with flusulfamide. This suggests that flusulfamide may cause aberrant folding of proteins involved in primary zoosporogenesis, thereby inhibiting germination.
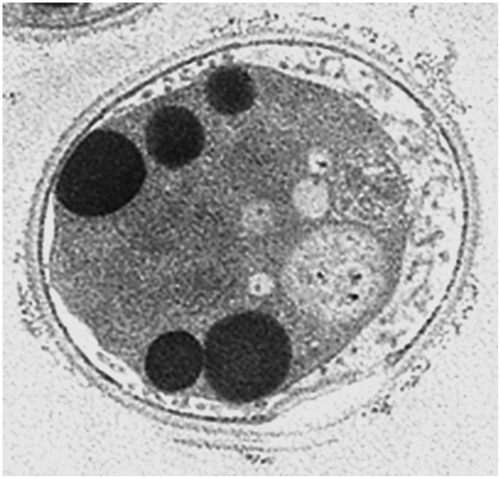 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1409K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1409K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Sebastien Ligonniere, Alexandre Bantz, Valerie Raymond, Delphine Goven2024 年 49 巻 1 号 p. 58-64
発行日: 2024/02/20
公開日: 2024/02/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/01/30ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録Insecticide accommodation and resistance are limiting factors to the much-needed increase in agricultural production. Various physiological and cellular modifications, such as the changes of insecticide molecular targets, have been linked to these events. Thus, a previous study demonstrated that the imidacloprid accommodation set up by the cockroach Periplaneta americana after an exposure to a sublethal dose of this insecticide involves functional alterations of two nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subtypes. As RNA interference (RNAi) is one of the most promising strategies for controlling pest insects, we evaluated, in this study, the use of RNAi that targets the β1 nAChR subunit to counteract the imidacloprid accommodation phenomenon in cockroaches. Interestingly, we showed that ingestion of dsRNA-β1 increased the sensitivity to imidacloprid of accommodated cockroaches. Thus, we have demonstrated for the first time that RNAi that targets an nAChR subunit can counteract the accommodation mechanism to insecticide targeting nAChRs set up by an insect.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (946K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (946K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|