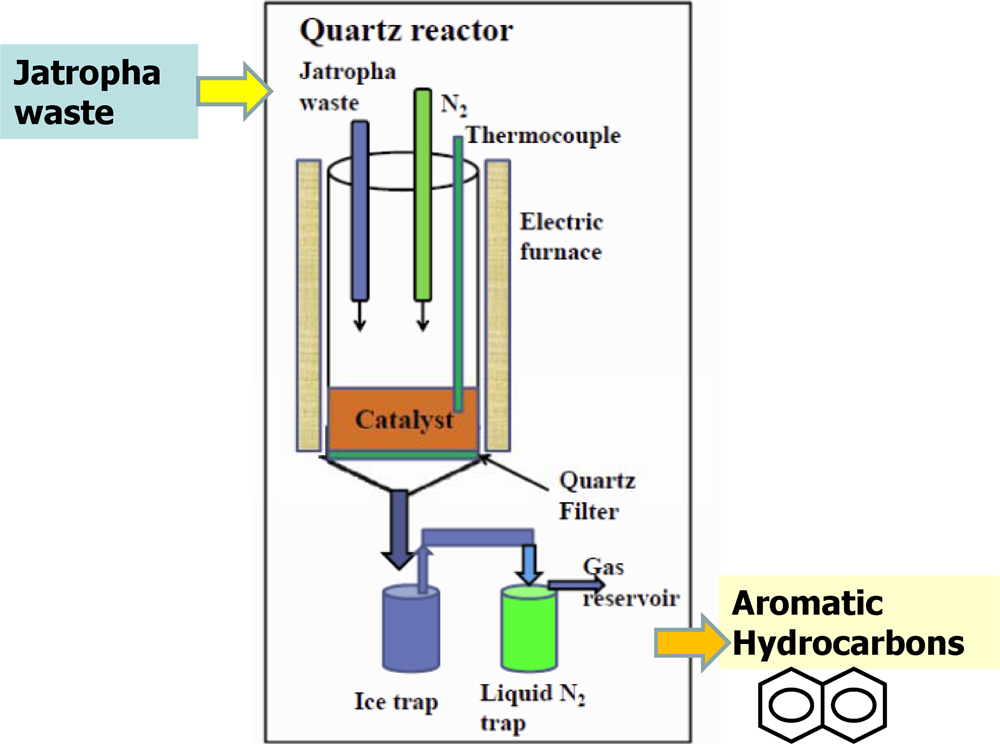
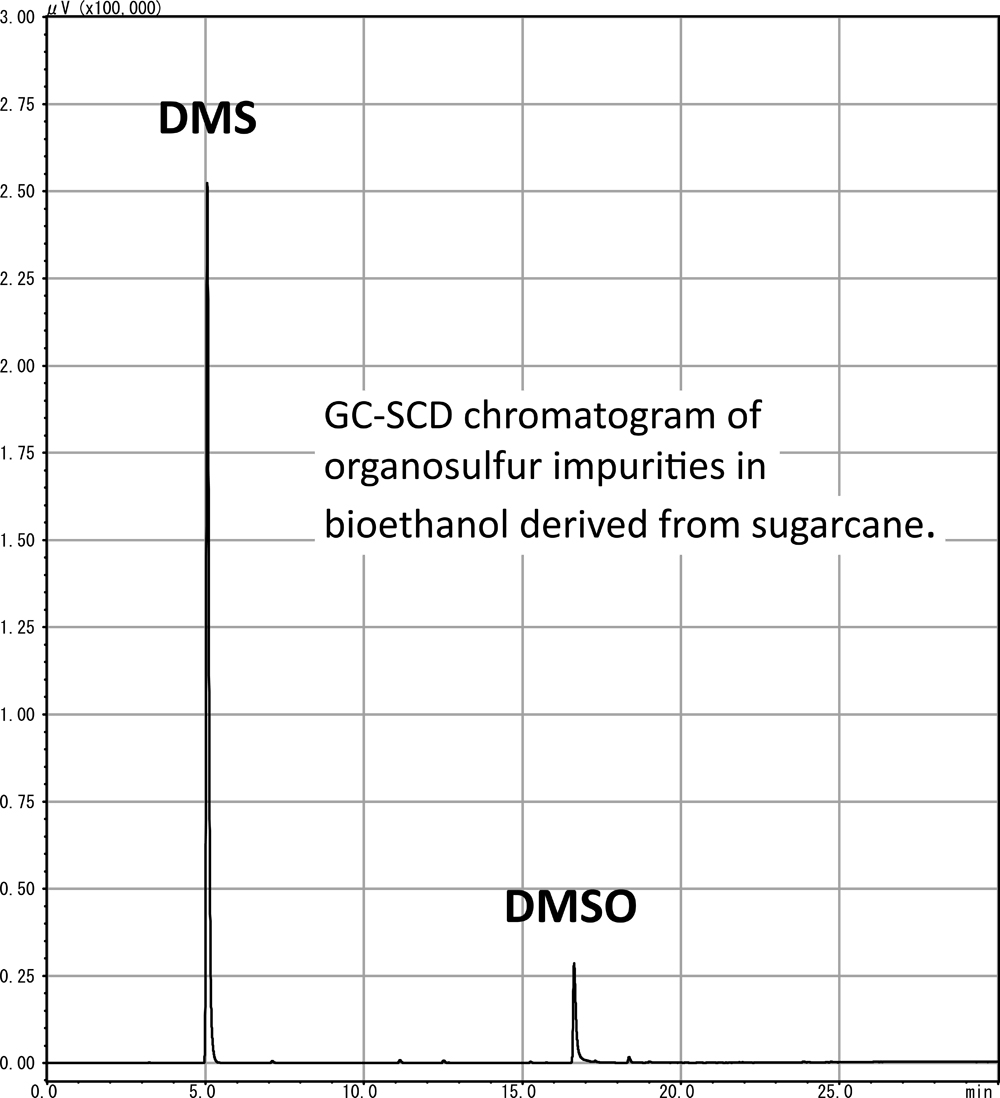
Volume 56, Issue 6
Displaying 1-9 of 9 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Paper
-
Article type: Review Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 357-365
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (3393K) -
Article type: Review Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 366-370
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (876K)
Regular Paper
-
Article type: Regular Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 371-380
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (790K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 381-387
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (381K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 388-394
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (610K)
Research Note
-
Article type: Research Note
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 395-400
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (640K)
Technical Report
-
Article type: Technical Report
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 401-405
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (564K) -
Article type: Technical Report
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 406-413
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (1174K) -
Article type: Technical Report
2013 Volume 56 Issue 6 Pages 414-422
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2014
Download PDF (405K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|