All issues

Volume 57 (2014)
- Issue 6 Pages 237-
- Issue 5 Pages 197-
- Issue 4 Pages 155-
- Issue 3 Pages 95-
- Issue 2 Pages 65-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
Volume 57, Issue 6
Displaying 1-5 of 5 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Paper
-
Ichiro YamanakaArticle type: Review Paper
2014 Volume 57 Issue 6 Pages 237-250
Published: November 01, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDirect synthesis of H2O2 aqueous solutions from O2 and H2 using a fuel cell reactor was reviewed. H2O2 can be catalytically produced by electrochemical reaction without external electrical supply. New electrocatalysts and four types of fuel cell reactors were designed and developed to achieve higher performance of H2O2 formation, ex. an Au-mesh cathode and a type-1 reactor for H2O2/HCl aq. solutions, a heat-treated Mn–porphyrin/activated-carbon cathode and a type-2 reactor for H2O2/H2SO4 aq. solutions, a vapor-grown-carbon-fiber (VGCF) cathode and a type-3 reactor for H2O2/NaOH aq. solutions, and a heat-treated Co–porphyrin/VGCF cathode and a type-4 reactor for pure H2O2 aq. solutions. These studies indicated that synergy of selective electrocatalysis of the cathode and three-phase boundary of O2 (gas phase), electrocatalyst (solid phase) and electrolyte (liquid phase) were essential for the efficient reduction of O2 to H2O2. Therefore, direct synthesis of a pure H2O2 aq. solution of over 4.0 mol dm−3 was achieved with a good current efficiency of 42 %. View full abstractDownload PDF (1884K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1884K) -
Kazuya Yamaguchi, Noritaka MizunoArticle type: Review Paper
2014 Volume 57 Issue 6 Pages 251-260
Published: November 01, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis review article mainly describes our research on the development of highly active heterogeneous catalysts based on the properties of metal hydroxides and efficient green functional group transformations using these catalysts. Metal hydroxide species have both Lewis acid (metal center) and Brønsted base (hydroxy group) sites on the same metal sites. Combined action of the Lewis acid and Brønsted base paired sites can activate various types of organic substrates; for example, alcohols → alkoxides, amines → amides, nitriles → η2-amidates, and terminal alkynes → acetylides. In the presence of supported ruthenium hydroxide catalyst (Ru(OH)x/Al2O3), oxidative dehydrogenation of alcohols and amines efficiently proceeds, forming the corresponding carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) and nitriles, respectively. Ru(OH)x/Al2O3 can also catalyze hydration of nitriles to primary amides, ammoxidation of primary alcohols to nitriles, and formal α-oxygenation of primary amines to primary amides. In addition, oxidative alkyne homocoupling and 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition efficiently proceed in the presence of supported copper hydroxide catalysts (Cu(OH)x/OMS-2 for homocoupling, Cu(OH)x/TiO2 and Cu(OH)x/Al2O3 for cycloaddition; where OMS-2 is manganese oxide-based octahedral molecular sieve, KMn8O16). The catalytic processes for these transformations are heterogeneous, and the catalysts can be reused several times with maintained high catalytic activity.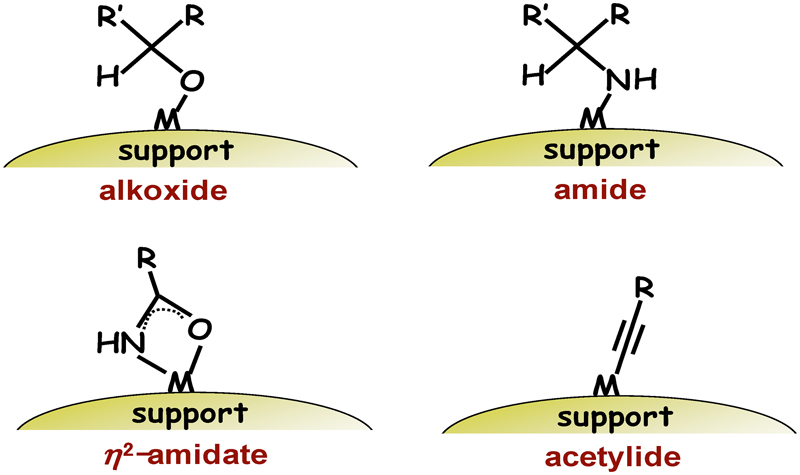 View full abstractDownload PDF (2589K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2589K) -
Takashi YamamotoArticle type: Review Paper
2014 Volume 57 Issue 6 Pages 261-270
Published: November 01, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecent X-ray absorption spectroscopic studies of solid acid-base catalysts were reviewed, which have been carried out to investigate the effects of lanthanum-ion addition to alumina for improving the thermal stability, acidity generation mechanism of siliceous mesoporous silica, or state of tungsten oxide species in WOx–ZrO2 strong solid acid. Remarks on EXAFS analytical procedures were also discussed about possibility of coexistence of multiple phases, mismatch between radial distribution functions and Fourier transforms of EXAFS, and effects of multiple excitations in an X-ray absorption spectrum.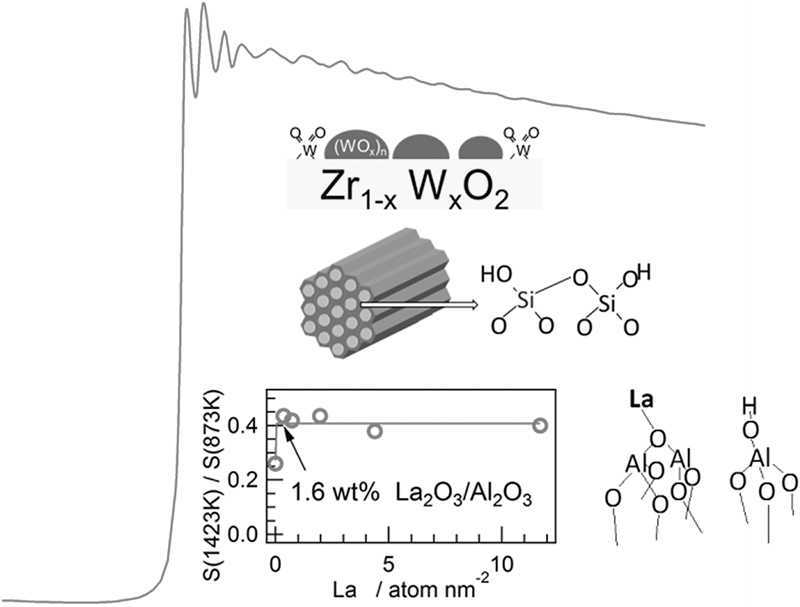 View full abstractDownload PDF (7133K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (7133K)
Regular Paper
-
Fang Zhao, Rui Shen, Shu Sheng Gao, Gang XuArticle type: Regular Paper
2014 Volume 57 Issue 6 Pages 271-275
Published: November 01, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWaterflood front dynamic has important significance in evaluating waterflooding effect. It also guides the design of well pattern infilling, the adjustment of infilling and the waterflood method. Modelling heterogeneity (if any) is an important factor in any geological and reservoir simulation model. The proper estimation of waterflood front is highly depending on geologic modelling able to capture heterogeneous feature of reservoir. Combined with core composition experiments and actual field data, a new method for heterogeneous reservoir waterflood front calculation was proposed depending on the equation of Buckley-Leverett. Using this method to calculate well group of Wangyao oilfield, distribution of waterflood front and water breakthrough time of production wells were predicted, position of infill wells drilling was proposed and the results show that they were perfectly matched with the micro-seismic test data. When calculating the same well group with the homogeneous model, the error is large. The new calculation method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, strong practicability and it functions just like a calculator to people that can easily identify the movement trend of the waterflood front which can not be achieved in numerical simulation or other calculation method. View full abstractDownload PDF (745K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (745K) -
Keisuke Kojima, Masaharu Tasaki, Kazuo Okamura, Mark Sueyoshi, Rashid ...Article type: Regular Paper
2014 Volume 57 Issue 6 Pages 276-286
Published: November 01, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPolymer flooding is being used as an enhanced oil recovery (EOR) method in Oman. In polymer flooding, injection water of increased viscosity reduces mobility difference between water and oil, thereby improving sweep and oil recovery. The quality of polymer flood produced water (PFPW) is different from produced water (PW) without polymer, and various techniques are being studied for the effective treatment of PFPW. In this paper, the effects of two different coagulants, aluminum sulfate (AS) and polyaluminum chloride (PAC), were examined for the treatment of PFPW. Laboratory tests indicated that the effects of coagulation by PAC were decreased when used for PFPW, compared to PW. This decrease was attributable to interaction of polymer and inorganic carbon, rather than to high pH or high alkalinity alone. On the other hand, laboratory tests indicated that AS would be an effective alternative coagulant for PFPW treatment. Based on these results, a treatment trial with actual PFPW, was conducted with a pilot plant. The pilot trials confirmed that with appropriate level of AS addition and a second coagulation step, PFPW could be effectively treated with AS.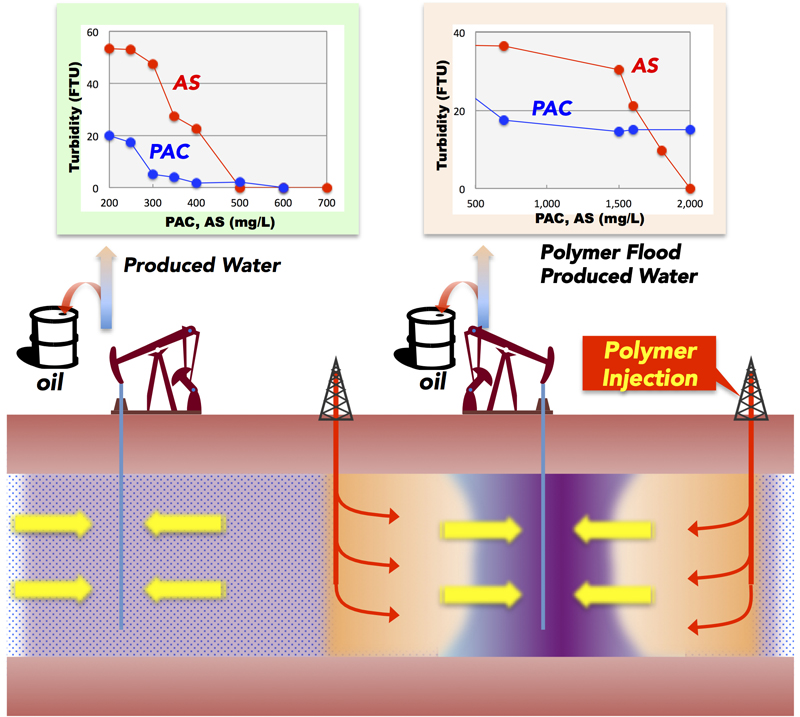 View full abstractDownload PDF (1220K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1220K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|