
- Issue 6 Pages 243-
- Issue 5 Pages 165-
- Issue 4 Pages 109-
- Issue 3 Pages 73-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Takashi MAKINO, Mitsuhiro KANAKUBOArticle type: Review Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 109-117
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe aim of this review is to provide some information on the CO2 absorption property of ionic liquids and the CO2 permselectivity for the separation membranes using ionic liquids. Ionic liquids are a unique solvent, of which the characteristics are non-volatile, non-flammable, miscible with various chemicals, and so on. The CO2 capture using ionic liquids is a promising technology, and a variety of studies have been reported on the natures of the ionic liquid absorbents and membranes. This review presents some fundamental data on the following three topics: (1) the CO2 solubility in the ionic liquid physical absorbents; (2) the high-pressure CO2 absorption behavior for the ionic liquid chemical absorbents; (3) the CO2 permselectivity for the inclusion membranes with ionic liquids and polymers. The first two topics describe the effects of the chemical structures of ionic liquids on the CO2 solubility, in particular, in terms of the oxygen containing groups and the interionic interactions. The second topic also contains how amino acid anions affect the physical and chemical absorptions under high CO2 pressure conditions. The last topic reported that the CO2 and N2 permeations in the inclusion membranes depend on the composition and kind of polymers.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3097K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3097K)
-
Norihisa FUKAYA, Takayuki MIYAJI, Shun-ya ONOZAWA, Seong Jib CHOI, Mas ...Article type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 118-125
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
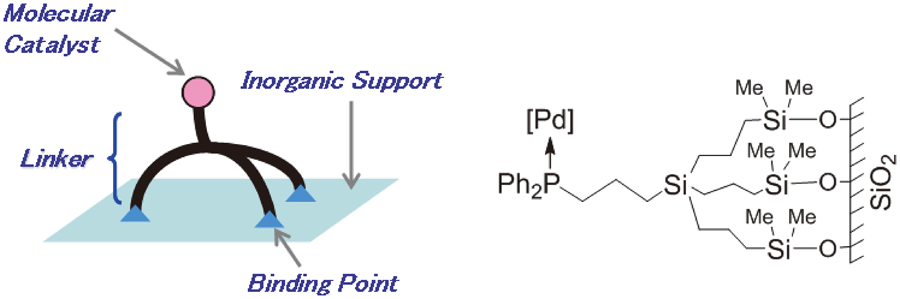
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA tripodal linker unit that tightly binds to a silica surface via three independent Si–O–Si bonds was applied to immobilize diphenylphosphino-palladium complex catalysts onto ordered mesoporous silica. The diphenylphosphino-functionalized silica materials were prepared by: (i) grafting the bromine-substituted tripodal linker unit onto mesoporous silica and a subsequent treatment with potassium diphenylphosphide (the “bottom-up” method), (ii) directly grafting pre-synthesized tripodal diphenylphosphino ligands onto silica (the “top-down” method). The catalytic properties were evaluated in the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction of aryl bromides. The tripodally immobilized catalyst prepared via the “bottom-up” method showed lower leaching levels of palladium and phosphorus compared to catalyst prepared via the “top-down” method.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1285K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1285K) -
Nasrollah MAJIDIAN, Saeed SOLTANALIArticle type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 126-139
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe purpose of this work is to study the performance of fixed and monolith bed reactors in Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis by modeling these reactors. A pseudo-homogeneous 2D model was proposed for FT fixed and monolith bed reactors. The model results shows good agreement with experimental data reported in literatures. The performance of the FT reactors was investigated in industrial scale under low temperature FT conditions (pressure = 2 MPa and temperature = 230 °C). The modeling results were organized in three sections, (1) effect of operating condition parameters, which have similar effects on both reactors, (2) effect of structure parameters, which have different effects such as pellet diameter on FT fixed bed reactors, and thermal support property, the number of channels per cross sectioon area (CPSI) and wash coated catalyst thickness on FT monolith bed reactors, and (3) comparison of FT fixed and monolith bed reactors.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1364K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1364K) -
Masakoto KANEZASHI, Shuji MIYAUCHI, Shinjiro HAYAKAWA, Hiroki NAGASAWA ...Article type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 140-148
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMetal-doped organosilica membranes for C3H6/C3H8 separation were fabricated via a sol-gel method. Al and Ag was selected as a doping material in the fabrication of metal-doped bis (triethoxysilyl) methane (BTESM) membranes, and the effects that doping materials exerted on the organosilica network size and on the C3H6/C3H8 permeation properties were evaluated. Gas permeance ratios such as H2/CH4, H2/C3H6, H2/C3H8, and C3H6/C3H8 were approximately independent of Ag concentration, indicating that network size did not change when doped Ag existed as Ag ions in BTESM networks, as suggested by the X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectrum. On the other hand, when Al was doped into BTESM, each permeance decreased as Al concentration increased, and the selectivity (H2/N2, H2/CH4) increased largely because of enhanced molecular sieving separation by densified networks. Ag-BTESM membranes showed negative values for activation energy (∼−10 kJ mol−1) for C3H6 permeation, which were a much smaller values than those for BTESM (∼−7 kJ mol−1) and Al-BTESM (∼3 kJ mol−1) membranes. BTESM, Al-, and Ag-BTESM membranes showed values for αmix (binary separation) that were higher than those for αsin (single permeation) at 50 °C. For example, Ag-BTESM (Si/Ag = 9/1) membrane showed higher C3H6/C3H8 selectivity (= 32.5) by binary separation than selectivity (∼19) by single permeation at 50 °C, but the selectivity by binary separation was approximately the same, irrespective of a different pressure ratio (feed pressure/permeate pressure).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (789K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (789K) -
Rozyanti MOHAMAD, Tsunehiro AKI, Yutaka NAKASHIMADA, Yoshiko OKAMURA, ...Article type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 149-154
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSorbitol is widely used in food industries, and its decomposition behavior under hydrothermal condition is needed for its recovery from biomass and processing. In order to elucidate the decomposition behavior of sorbitol under hydrothermal conditions, hydrothermal decomposition of sorbitol was investigated in a flow reactor between 170 °C and 250 °C at 25 MPa. The decomposition was well expressed using a first-order reaction rate, and the rate constant followed the Arrhenius law. The pre-exponential factor and the activation energy were also determined. Compared with the decomposition of the sorbitol isomer mannitol, sorbitol was decomposed more rapidly, likely due to the variation in water molecule accessibility owing to different isomeric configurations. In addition, although activation energies were comparable for both mannitol and sorbitol (29.1 kJ mol−1 and 28.3 kJ mol−1, respectively), the pre-exponential factor of mannitol (6.19 s−1) was an order of magnitude lower than that of sorbitol (42.9 s−1).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (475K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (475K) -
Aritomo YAMAGUCHI, Naoki MIMURA, Masayuki SHIRAI, Osamu SATOArticle type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 155-159
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIsosorbide and its derivatives are important monomers in the polymer industry and valuable intermediates in the pharmaceutical industry. Recently, one-pot conversion of cellulose into isosorbide has been reported using supported metal catalysts and acid catalysts. The present study investigated one-pot conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into isosorbide using supported metal catalyst and ion-exchange resin Amberlyst 70. Isosorbide could be obtained from one-pot conversion of Japanese cedar with 25.4 % yield using supported ruthenium catalyst and Amberlyst 70 at 463 K. Isosorbide yields from one-pot conversion of eucalyptus and bagasse were 8.3 % and 12.8 %, respectively. One-pot conversion has the potential to be a powerful method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to useful chemicals.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (372K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (372K)
-
Shinya FURUKAWA, Genki NISHIMURA, Takayuki KOMATSUArticle type: Letter
2016 Volume 59 Issue 4 Pages 160-163
Published: July 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPd-based intermetallic compounds having early transition metals (Pd3M; M = Nb, Ti, and Zr) prepared by arc melting were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. When the ingot of Pd3Zr was ground in N2 with an oxygen concentration below 1 ppb, a large part of the surface maintained its original intermetallic state; however, for Pd3Nb and Pd3Ti, their surfaces were completely oxidized even in the N2 atmosphere. This indicates the remarkably high oxygen sensitivity of the intermetallic compounds with early transition metal.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1622K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1622K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|