- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 97-102
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: December 29, 2018Download PDF (1066K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 103-112
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: December 27, 2018Download PDF (1338K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 113-120
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: December 29, 2018Download PDF (1190K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 121-128
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 07, 2019Download PDF (3902K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 129-137
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 19, 2019Download PDF (4756K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 139-146
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 26, 2019Download PDF (1679K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 147-153
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 19, 2019Download PDF (1091K) -
 Article type: Original Article
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 155-162
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 21, 2019Editor's pickCover Story:
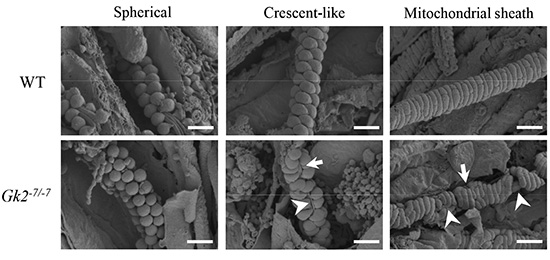
The mitochondrial sheath is composed of mitochondria that coil tightly around the midpiece of the sperm flagellum. Mitochondria are recruited from the cytoplasm to the flagellum late in spermatogenesis. Recruited mitochondria are initially spherical, but then elongate laterally to become crescent-like in shape. Subsequently, these crescent-like mitochondria elongate continuously to coil tightly around the flagellum. Mitochondrial sheath development in glycerol kinase 2 (Gk2)-disrupted mice, which show abnormal mitochondrial sheath formation, was observed using freeze-fracturing coupled with scanning electron microscopy (Shimada et al., Glycerol kinase 2 is essential for proper arrangement of crescent-like mitochondria to form the mitochondrial sheath during mouse spermatogenesis, pp. 155–162). Gk2-disrupted spermatids show abnormal localization of crescent-like mitochondria, despite initially exhibiting proper alignment of spherical mitochondria around the flagellum. These results indicate that GK2 is essential for proper arrangement of crescent-like mitochondria during mitochondrial sheath formation in mouse spermatogenesis.Download PDF (2479K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 163-170
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 31, 2019Download PDF (1781K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 171-175
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: February 11, 2019Download PDF (747K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 177-182
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: February 09, 2019Download PDF (666K) -
Article type: Original Article
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 183-190
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: February 11, 2019Download PDF (1261K)
-
Article type: Technology Report
2019 Volume 65 Issue 2 Pages 191-194
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2019
Advance online publication: January 10, 2019Download PDF (661K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|