
- 6 号 p. 337-
- 5 号 p. 291-
- 4 号 p. 241-
- 3 号 p. 161-
- 2 号 p. 79-
- 1 号 p. 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Asuka FURUTA, Toshinobu NAKAMURA原稿種別: Opinions and Hypotheses
Asuka FURUTA, Toshinobu NAKAMURA原稿種別: Opinions and Hypotheses
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 79-81
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/10ジャーナル オープンアクセスEmbryonic stem (ES) cells, derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, are believed to pluripotent cells and give rise to embryonic, but not extraembryonic, tissues. In mice, totipotent 2-cell stage embryo-like (2-cell-like) cells, which are identified by reactivation of murine endogenous retrovirus with leucin transfer RNA primer (MuERV-L), arise at a very few frequencies in ES cell cultures. Here, we found that a lipid droplet forms during the transition from ES cells to 2-cell-like cells, and we propose that 2-cell-like cells utilize a unique energy storage and production pathway.
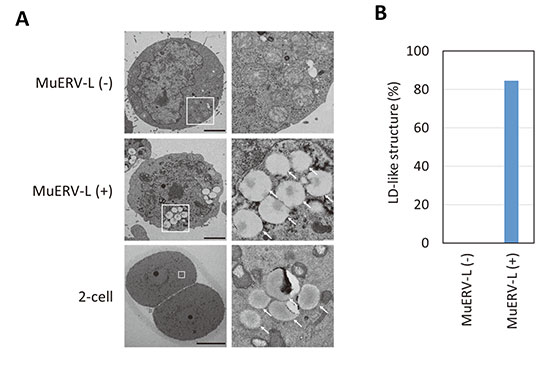 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickCover Story:
Recent studies suggested that a small sub-population of embryonic stem (ES) cells exhibit 2-cell stage embryo-like (2-cell-like) features, including the reactivation of murine endogenous retrovirus with leucin transfer RNA primer, high histone mobility, and dispersed chromocenters. Furuta et al. investigated the organelle morphology of 2-cell-like cells using electron microscopy (Furuta et al. Lipid droplets are formed in 2-cell-like cells. pp. 79–81). They demonstrated the formation of a lipid droplet during the transition from ES cells to 2-cell-like cells, and proposed that these cells utilize a unique energy storage and production pathway.PDF形式でダウンロード (1094K)
-
Sayaka MATSUMOTO, Tomomi TANAKA, Natsumi ENDO原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 83-88
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/01/29ジャーナル オープンアクセスEstrus synchronization requires multiple treatments of hormonal drugs, requiring considerable time and cost. The aim of the present study was to develop an estrus synchronization protocol using intravaginal administration of estradiol benzoate (EB) capsules in goats. Two types of capsules were prepared: an EB capsule that melted immediately after administration and a sustained-release (SR) EB capsule that dissolved slowly and reached a peak after 24 h. Goats with functional corpus lutea were intramuscularly treated with prostaglandin F2α (PG). At 24 h after PG administration, goats were administered 1 mg of EB solution intramuscularly (PG + 24IM; n = 6) or 1 mg of EB capsule intravaginally (PG + 24EB; n = 6). The SR EB capsule was administered intravaginally at the time of PG administration (PG + SR; n = 6). The control group (n = 6) received only PG. All groups showed estrus within 72 h after PG administration. The onset of estrus did not differ significantly between the PG + 24IM and PG + SR groups but was earlier than in the control group. Estradiol concentration in the PG + SR group peaked at 11.5 ± 6.1 h after EB and PG administration. Peak estradiol concentrations were not significantly different between the PG + 24IM and PG + SR groups (78.0 ± 25.8 and 64.0 ± 38.1 pg/ml, respectively), and were higher than the PG + 24EB and control groups (27.3 ± 8.8 and 14.6 ± 6.1 pg/ml, respectively). These results suggest that intravaginal administration of an EB capsule with a sustained-drug release base is applicable for estrus synchronization, as an alternative to intramuscular administration.
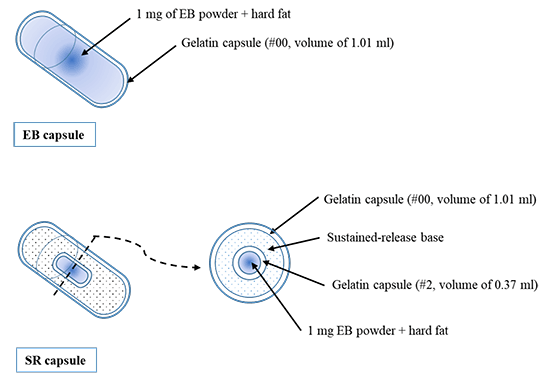 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (876K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (876K) -
Yeling MA, Xin YU, Yu-xia LI, Yan-Ling WANG原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 89-97
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/01/15ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録Depletion of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) in mice leads to fetal lethality and placental maldevelopment. However, the dynamic change pattern of HGF/c-Met signaling during placental development and its involvement in the early differentiation of trophoblasts remain to be elucidated. In this study, using in situ hybridization assay, we elaborately demonstrated the spatial-temporal expression of Hgf and c-Met in mouse placenta from E5.5, the very early stage after embryonic implantation, to E12.5, when the placental structure is well developed. The concentration of the soluble form of c-Met (sMet) in maternal circulation peaked at E10.5. By utilizing the induced differentiation model of mouse trophoblast stem cells (mTSCs), we found that HGF significantly promoted mTSC differentiation into syncytiotrophoblasts (STBs) and invasive parietal trophoblast giant cells (PTGCs). Interestingly, sMet efficiently reversed the effect of HGF on mTSC differentiation. These findings indicate that HGF/c-Met signaling participates in regulating placental trophoblast cell fate at the early differentiation stage and that sMet acts as an endogenous antagonist in this aspect.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5531K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5531K) -
Kumiko TAKEDA, Eiji KOBAYASHI, Kazuko OGATA, Akira IMAI, Shinya SATO, ...原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 99-107
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/01/14ジャーナル オープンアクセスFor semen suppliers, predicting the low fertility of service bull candidates before artificial insemination would help prevent economic loss; however, predicting bull fertility through in vitro assessment of semen is yet to be established. In the present study, we focused on the methylated CpG sites of sperm nuclear DNA and examined methylation levels to screen new biomarkers for predicting bull fertility. In frozen-thawed semen samples collected from Japanese Black bulls, for which the sire conception rate (SCR) was recorded, the methylation level of each CpG site was analyzed using human methylation microarray. According to regression analysis, 143 CpG sites related to SCR were significantly differentially methylated. Whole genome bisulfite sequence data were obtained from three semen samples and the differentially methylated regions (DMRs) that included the target CpG sites selected by human methylation microarray were confirmed. Using combined bisulfite restriction analysis, fertility-related methylation changes were detected in 10 DMRs. With the exception of one DMR, the methylation levels of these DMRs were significantly different between groups with high fertility (> 50%) and low fertility (< 40%). From multiple regression analysis of methylation levels and SCR, three DMRs were selected that could effectively predict bull fertility. We suggest that these fertility-related differences in spermatozoal methylation levels could be new epigenetic biomarkers for predicting bull fertility.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1241K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1241K) -
Juan QIU, Kazutsugu MATSUKAWA, Chihiro KOSHIMOTO, Keisuke EDASHIGE原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 109-114
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/10ジャーナル オープンアクセスWe previously developed a new vitrification method (equilibrium vitrification) by which two-cell mouse embryos can be vitrified in liquid nitrogen in a highly dehydrated/concentrated state using low concentrations of cryoprotectants. In the present study, we examined whether this method is effective for mouse embryos at multiple developmental stages. Four-cell embryos, eight-cell embryos, morulae, and blastocysts were vitrified with EDFS10/10a, 10% (v/v) ethylene glycol and 10% (v/v) DMSO in FSa solution. The FSa solution was PB1 medium containing 30% (w/v) Ficoll PM-70 plus 0.5 M sucrose. The state of dehydration/concentration was assessed by examining the survival of vitrified embryos after storage at –80°C. When four-cell embryos and eight-cell embryos were vitrified with EDFS10/10a in liquid nitrogen and then stored at –80°C, the survival rate was high, even after 28 days, with relatively high developmental ability. On the other hand, the survival of morulae and blastocysts vitrified in liquid nitrogen and stored at –80°C for four days was low. Therefore, morulae and blastocysts cannot be vitrified in a highly dehydrated/concentrated state using the same method as with two-cell embryos. However, when blastocysts were shrunken artificially before vitrification, survival was high after storage at –80°C for four days with high developmental ability. In conclusion, the equilibrium vitrification method using low concentrations of cryoprotectants, which is effective for two-cell mouse embryos, is also useful for embryos at multiple stages. This method enables the convenient transportation of vitrified embryos using dry ice.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (687K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (687K) -
Hao CHENG, Xue SUN, Fei CHEN, Liu-Zhu PAN, Guo-Liang WANG, Hong-Jie YU ...原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 115-122
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/17ジャーナル オープンアクセスWe have studied the mechanisms by which meiotic arrest maintenance (MAM) with roscovitine, female sexual maturity, and the surrounded nucleoli (SN) chromatin configuration improve the competence of mouse oocytes by observing the expression of oocyte competence-related genes in non-surrounded nucleoli (NSN) and SN oocytes from prepubertal and adult mice following maturation with or without MAM. The results demonstrated that MAM with roscovitine significantly improved the developmental potential of adult SN and prepubertal NSN oocytes, but had no effect on that of prepubertal SN oocytes. Without MAM, while 40% of the 2-cell embryos derived from prepubertal SN oocytes developed into 4-cell embryos, none of the 2-cell embryos derived from prepubertal NSN oocytes did, and while 42% of the 4-cell embryos derived from adult SN oocytes developed into blastocysts, only 1% of the 4-cell embryos derived from prepubertal SN oocytes developed into blastocysts. Furthermore, MAM with roscovitine, SN configuration, and female sexual maturity significantly increased the mRNA levels of competence-beneficial genes and decreased those of competence-detrimental genes. In conclusion, our results suggest that MAM with roscovitine, SN chromatin configuration, and female sexual maturity improve oocyte competence by regulating the expression of competence-related genes, suggesting that Oct4, Stella, Mater, Zar1, Mapk8, and Bcl2 are oocyte competence-beneficial genes, whereas Foxj2, Ship1, and Bax are competence-detrimental genes.
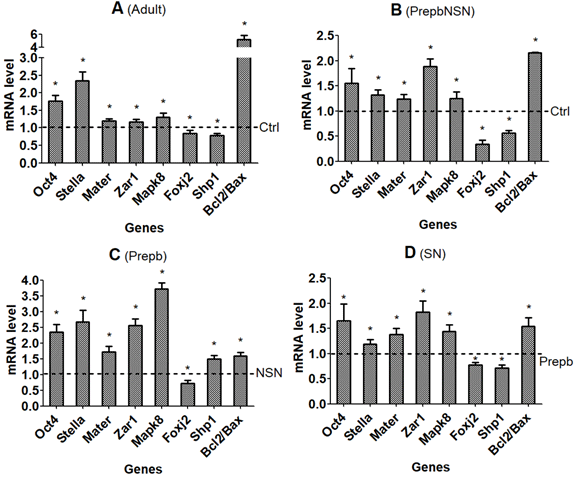 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1629K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1629K) -
Tatsuya NAKANO, Mizuki KONO, Kazuki SEGAWA, Satoshi KUROSAKA, Yoshihar ...原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 123-133
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録Methylglyoxal (MG) is a precursor for the generation of endogenous advanced glycation end-products involved in various diseases, including infertility. The present study evaluated the motility and developmental competence after in vitro fertilization of mouse sperm which were exposed to MG in the capacitation medium for 1.5 h. Sperm motility was analyzed using an SQA-V automated sperm quality analyzer. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), membrane integrity, mitochondrial membrane potential, and DNA damage were assessed using flow cytometry. The matured oocytes were inseminated with MG-exposed sperm, and subsequently, the fertilization and embryonic development in vitro were evaluated in vitro. The exposure of sperm to MG did not considerably affect the swim-up of sperm but resulted in a deteriorated sperm motility in a concentration-dependent manner, which was associated with a decreased mitochondrial activity. However, these effects was not accompanied by obvious ROS accumulation or DNA damage. Furthermore, MG diminished the fertilization rate and developmental competence, even after normal fertilization. Collectively, a short-term exposure to MG during sperm capacitation had a critical impact on sperm motility and subsequent embryonic development after fertilization. Considering that sperm would remain in vivo for up to 3 days until fertilization, our findings suggest that sperm can be affected by MG in the female reproductive organs, which may be associated with infertility.
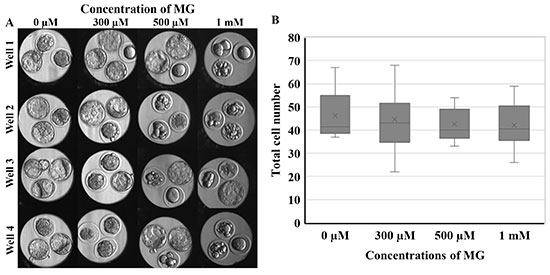 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1957K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1957K) -
Fernando LÓPEZ-GATIUS原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 135-139
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/15ジャーナル オープンアクセスSince the 1970s, luteolytic doses used for synchronizing estrus in dairy cattle have remained unchanged. This study aimed to evaluate the dose-response effect of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α), which is used for synchronizing estrus, and subsequent fertility in cows with two or more corpora lutea (CL). The study population consisted of 1,683 cows with a single CL (1CL), 501 cows with multiple CL receiving a single dose of PGF2α (2CL1), and 252 cows with multiple CL receiving a 1.5 × PGF2α dose (2CL1.5). Cows with a single CL (n = 1,245) showed estrus significantly (P < 0.01) earlier (3.01 ± 1.23 days; mean ± SD) than cows with multiple CL (n = 287; 3.33 ± 1.69 days). Using 1CL cows as reference, the odds ratio (OR) for the estrus response in 2CL1 cows was 0.13 (P < 0.0001), whereas the ORs for estrus response and pregnancy of 2CL1.5 cows were 1.8 (P = 0.0001) and 1.7 (P = 0.001), respectively. Based on the results for only the 2CL1 cows, the OR for the estrus response was 0.7 (P = 0.01) for cows producing ≥ 45 kg of milk at treatment, compared to the remaining cows producing < 45 kg of milk. Our results showed that the presence of multiple CL reduced the estrus response to that induced by a single PGF2α dose and milk production was inversely associated with this response, whereas an increased PGF2α dose improved the estrus response. Therefore, an increase in the standard PGF2α dose is recommended.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (567K) -
Mio KAGEYAMA, Jun ITO, Koumei SHIRASUNA, Takehito KUWAYAMA, Hisataka I ...原稿種別: Original Article
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 141-147
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/20ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe number of mitochondria in blastocysts is a potential marker of embryo quality. However, the molecular mechanisms governing the mitochondrial number in embryos are unclear. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of reduced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels on mitochondrial biogenesis in porcine embryos. Oocytes were collected from gilt ovaries and activated to generate over 4 cell-stage embryos at day 2 after activation. These embryos were cultured in media containing either 0.1 μM MitoTEMPOL (MitoT), 0.5 μM Mitoquinol (MitoQ), or vehicle (ethanol) for 5 days to determine the rate of development to the blastocyst stage. The mitochondrial number in blastocysts was evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Five days after activation, the embryos (early morula stage) were subjected to immunostaining to determine the expression levels of NRF2 in the nucleus. In addition, the expression levels of PGC1α and TFAM in the embryos were examined by reverse transcription PCR. One day of incubation with the antioxidants reduced the ROS content in the embryos but did not affect the rate of development to the blastocyst stage. Blastocysts developed in medium containing MitoT had lower mitochondrial DNA copy numbers and ATP content, whereas MitoQ showed similar but insignificantly trends. Treatment of embryos with either MitoT or MitoQ decreased the expression levels of NRF2 in the nucleus and levels of PGC1α and TFAM. These findings indicate that reductions in mitochondrial ROS levels are associated with low mitochondrial biogenesis in embryos.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1172K)
-
Yasumitsu MASUDA, Ryo HASEBE, Yasushi KUROMI, Masayoshi KOBAYASHI, Mis ...原稿種別: Technology Report
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 149-154
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/01/24ジャーナル オープンアクセスWhile embryo transfer (ET) is widely practiced, many of the transferred embryos fail to develop in cattle. To establish a more effective method for selecting bovine embryos for ET, here we quantified morphological parameters of living embryos using three-dimensional (3D) images non-invasively captured by optical coherence tomography (OCT). Seven Japanese Black embryos produced by in vitro fertilization that had reached the expanded blastocyst stage after 7 days of culture were transferred after imaged by OCT. Twenty-two parameters, including thickness and volumes of the inner cell mass, trophectoderm, and zona pellucida, and volumes of blastocoel and whole embryo, were quantified from 3D images. Four of the seven recipients became pregnant. We suggest that these 22 parameters can be potentially employed to evaluate the quality of bovine embryos before ET.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1627K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1627K) -
Takashi FUJII, Akira NAITO, Satoru MORIYASU, Soichi KAGEYAMA原稿種別: Technology Report
2021 年 67 巻 2 号 p. 155-159
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/04/21
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/02/28ジャーナル オープンアクセスPreimplantation genomic selection combined with an in vitro embryo production system is expected as a means of accelerating genetic improvement in cattle. While micromanipulation-based biopsy approaches are often used to collect embryonic cells for genetic testing, they require expensive equipment and sophisticated skills, hindering the adoption of this system. In the present study, to develop a simple method for preimplantation genomic selection using the blastomere separation (BS) technique in bovine in vitro fertilized embryos, we examined the accuracy of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping and optimal cryopreservation method in demi-blastocysts produced by the BS technique. We demonstrated reliable SNP genotyping using DNA derived from demi-blastocysts. We indicated a suitable equilibrium time in vitrification solution for demi-blastocysts and succeeded obtaining pregnancies by the transfer of vitrified demi-blastocysts. In conclusion, our findings suggest that the BS technique provides a simple method for preimplantation genomic selection in bovine in vitro fertilized embryos.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (758K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (758K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|