All issues

Successor
Volume 34, Issue 3
Displaying 1-11 of 11 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Daisuke FUJITA2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 107
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (233K)
Special Issue: Surface Science Contributing to Radioactive Decontamination
-
Kenji TAKESHITAArticle type: Review
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 108-118
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRadioactive fallout from the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP), which was caused by the Tohoku earthquake (March 11, 2011), contaminated large area around the nuclear facility. Just after the accident, many studies on the restoration of living environment contaminated by volatile radioactive nuclides such as 134Cs, 137Cs and 131I were started by many universities, national institutes, NGOs and commercial companies. In this report, the sequence of Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident and the spread of radioactive contamination in the living environment are presented firstly, and the decontamination techniques of polluted soil (the mechanical separation techniques such as classification, polishing and washing, and the chemical separation techniques such as sublimation, chemical washing and hydrothermal decomposition) and the water clean-up techniques such as coagulation settling and highly selective adsorption are introduced according to the evaluation results of the FY2011 Decontamination Demonstration Model Works by Ministry of the Environment.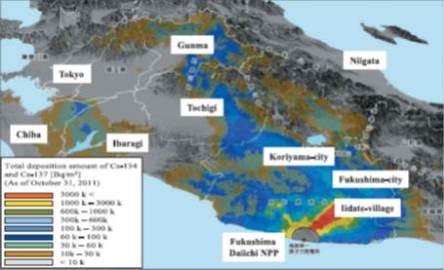 View full abstractDownload PDF (2847K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2847K) -
Yoshio TAKAHASHI, Yoko TOGO, Kazuya TANAKA, Aya SAKAGUCHIArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 119-124
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIt is important to grasp chemical species of radiocesium and radioiodine in various samples in Fukushima to understand and predict their behaviors in environment. In particular, interaction of clay minerals and humic substances are important for the migrations of radiocesium and radioiodine, respectively. XAFS spectroscopy and micro-XRF techniques are useful to identify these species. High stability of inner-sphere complex suggested by XAFS shows that the migration of radiocesium in aquatic system is primarily determined by that of particulate matters. Incorporation of radioiodine into humic substances indicated by XAFS can explain the retention of radioiodine at the surface of soil layer. View full abstractDownload PDF (1159K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1159K) -
Fumitaka ESAKA, Masaaki MAGARA, Daisuke SUZUKI, Yutaka MIYAMOTO, Takau ...Article type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 125-130
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAnalysis of individual particles containing nuclear materials in environmental samples gives important information on the origins. This paper describes analytical techniques of individual particles containing nuclear materials such as uranium and plutonium. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) combined with an X-ray detector, solid track detectors, and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) were used to identify particles containing uranium and/or plutonium in environmental samples. Isotope ratios for these particles were successfully determined with SIMS, thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The complementary use of these methods is effective to characterize individual particles rapidly, precisely and accurately. View full abstractDownload PDF (873K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (873K) -
Tamao HATTA, Seiko NEMOTO, Yuzo MANPUKU, Naruo MATSUMOTO, Hirohisa YAM ...Article type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 131-134
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe chemical shift of the 3d5/2 line of several cesium compounds were measured under the same condition by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. With the Auger line (M4N45N45) , the figure of chemical state plot (Wager plot) of the cesium compounds was drawn. When many materials are developed for decontamination of radioactive substances, and the new materials will be evaluated for the future, the measured data are used for the confirmation of the binding state. View full abstractDownload PDF (528K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (528K) -
Masahiko OKUMURA, Hiroki NAKAMURA, Masahiko MACHIDAArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 135-142
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSince large amounts of radioisotopes of Cs was released after the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi nuclear powerplants, a tremendous number of scientists and engineers have faced several issues in terms of decontamination ofradioactive Cs. In this paper, we present our recent two computational works based on density functional theory, one of which is to clarify mechanism of strong adsorption and retention of Cs in clay minerals to establish an effective Cs removal scheme from large amounts of radioactive wastes left by decontamination activities, and the other of which is to reveal why zeolites can selectively catch Cs even in the presence of other minerals and to make a guideline to create a more improved materials to remove Cs as well as other radioactive ions. View full abstractDownload PDF (1264K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1264K) -
Hirohisa YAMADA, Yujiro WATANABE, Takuya ECHIGO, Hidetaka MIYAHARA, Ke ...Article type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 143-148
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA large amount of radioactive substances has discharged from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant following the Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunami, and made the severe damages around the plants. Contamination resulting from the release of radioactive substances affects a wide range of environments including seawater, soil, plant and forest. It is necessary for us to remove radioactive substances, especially radiocesium, from this diverse range of sites. We reviewed the actions for the radioactive waste-water treatment system in the nuclear power plant and for decontaminating top soil and farmland by use of geomaterials including natural minerals. Furthermore their present situations and their issues in future were reviewed.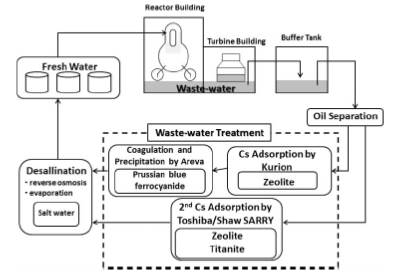 View full abstractDownload PDF (821K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (821K) -
Hideki ABE, Akira SATOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 149-153
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSJapan is facing a challenge of wide-spread radioactive contamination by isotopes of cesium (Cs). Here we demonstrate that titanium oxide (TiO2) can be an efficient material to immobilize high concentrations of Cs ions in a durable solid-state framework. TiO2 was dissolved in a Cs-containing melt of molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) at 950oC. The melt was then electrolyzed at −1200mV (vs. a Pt reference electrode) to obtain a single-crystalline titanate, Cs0.169TiO2 (titanium-oxide immobilizer) , which contained 1g cm−3 of Cs. Moreover, the titanium-oxide immobilizer exhibited a 170 times lower Cs leaching rate than did Cs-containing borosilicate glass. The titanium-oxide immobilizer will contribute to the Cs decontamination because of its high Cs content and low Cs leaching.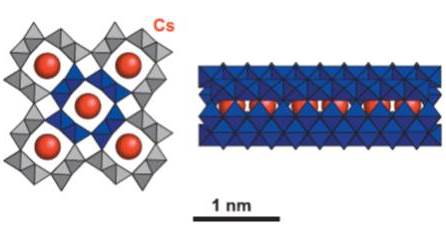 View full abstractDownload PDF (1048K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1048K)
Planning Series
Surface Science for Energy Issues
-
Teruhisa HORITA2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 154-155
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (407K)
Science Café
Research Abroad
-
Chisato NIIKURA2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 156-157
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (397K)
News & Trends
-
2013 Volume 34 Issue 3 Pages 158
Published: March 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (176K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
