All issues

Successor
Volume 34, Issue 8
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Jun YOSHINOBU2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 403
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (183K)
Transaction of the 32nd Conference on Surface Science [II]
-
Hiroshi ENDO, Fumihiko KONO, Tomonari KANASUGI, Takeshi KAWAIArticle type: Original
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 404-408
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSGraphene is a two-dimentional nanocarbon, which is stimulating great curiosity due to its superior mechanical, electrical, thermal and optical properties. Particularly attractive is the availability of bulk quantities of graphene which can be easily processed by chemical exfoliation, yielding graphene oxide (GO). In this study, poly(2-(N, N-dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) chains have been grafted from the GO surface via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), yielding a nanocomposite which can be formed polyioncomplex gel in polyanion (PAA) matrix. The GO and prepared film were characterized by FTIR, XRD, Raman, TGA, SEM and mechanical analysis. Moreover, the gel film can be converted from soft gel state into hard plasticization under ambient room temperature. View full abstractDownload PDF (598K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (598K) -
Ataru KOBAYASHI, Kenta TETSUMOTO, Hiroshi KUMAGAIArticle type: Original
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 409-414
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFor investigating the interaction of He and Ne in the field adsorption and ionization process above a single tungsten atom, field ion signals have been directly measured as a function of time using a micro-probe hole field ion microscope combined with a pulse counting analysis. Observed ion signals clearly show the transitions between a field adsorbed He state and a field adsorbed Ne state, and enable the determination of average adsorption time of He and Ne. Simple probabilistic model of adsorption and exchange of atoms at field adsorption site taking account of gas densities close to the surface well reproduced the observed behavior of average adsorption times. The results indicate the pronounced increase of Ne gas density near the sample surface. Particularly in the case of an initial mixed ratio of less than 0.5% of Ne for He, the increment reaches more than a hundred times. View full abstractDownload PDF (1877K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1877K) -
Norihiro HAYAKAWA, Toru KAWAI, Hiroshi SAKAI, Atsushi HONDA, Takashi O ...Article type: Original
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 415-420
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSoft X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements were carried out in order to clarify the chemical states of Li1−xNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for the cathode in lithium ion batteries. XANES spectra exhibited that Ni valence varies from divalent to tetravalent via an intermediate state of trivalent although Mn valence remains tetravalent. These phenomena originate from the formation of the occupied d-orbital of Ni in the vicinity of the Fermi level in the valence band of Li1−xNi0.5Mn1.5O4, which was supported by the first-principles calculations. Thus, it is concluded that Ni plays an important role in maintaining charge neutrality of Li1−xNi0.5Mn1.5O4 releasing Li+ ions by the charging of the battery.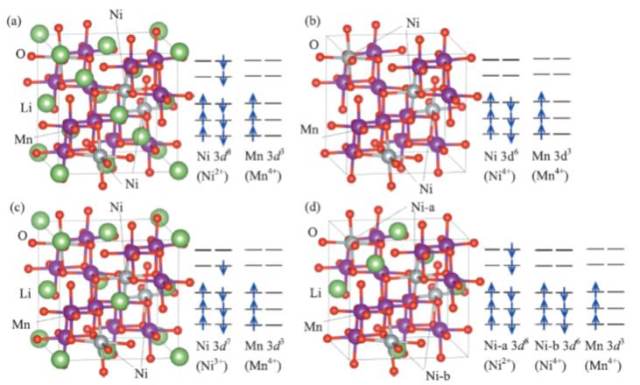 View full abstractDownload PDF (1506K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1506K) -
Takeo NAKAZAWA, Ryuichi ARAFUNE, Kazutaka MORITA, Noriaki TAKAGI, Maki ...Article type: Original
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 421-425
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHigh energy-resolved (ΔE∼9.5 meV) two-photon photoemission was used to study the electron dynamics of the image potential states on the clean Cu(001) surface. We constructed a system consisting of a picosecond Ti:sapphire laser system and a hemispherical analyzer equipped with a two-dimensional electron detector to achieve high energy resolution. The image states of Cu(001) were clearly resolved up to n=5, and the energy positions of these states were determined up to n=7. Linewidth analysis yielded pure dephasing rate for the lowest image states.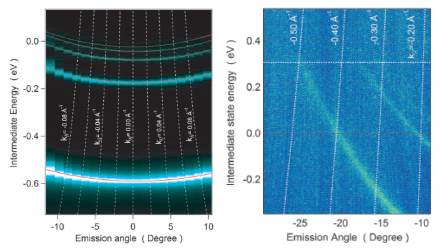 View full abstractDownload PDF (1139K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1139K) -
Yasuhide OHNO, Kenzo MAEHASHI, Kazuhiko MATSUMOTOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 426-431
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSChemical and biological sensors based on graphene field-effect transistors (FETs) were described. The transfer characteristics of the graphene FET were changed by the solution pH and the protein adsorption. Especially, the detection limit of the solution pH was 0.03, indicating the high sensitivity. In order to achieve the specific biomolecule sensing, aptamers were used as a receptor material. The aptamer was the single-stranded DNA binding to the specific molecules. The aptamer-modified graphene FET can detect only the target molecule while the graphene FET with the bare graphene channel detects all proteins with charges. These sensing results show that the graphene FET has high potential for the high sensitive biological sensors. View full abstractDownload PDF (1975K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1975K) -
Megumi ENDO, Masahiro YANO, Yuri HASEGAWA, Ryosuke OKADA, Yoichi YAMAD ...Article type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 432-436
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPotassium adsorption on the coronene monolayer has been investigated as a model of the alkali-metal doping of the organic superconductors. It was found that the coronene monolayer underwent a structural rearrangement upon K adsorption. Upon the rearrangement, significant chemical shift of the core levels of coronene was seen, indicating the strong interaction between K and coronene accompanied with charge transfer from K to coronene.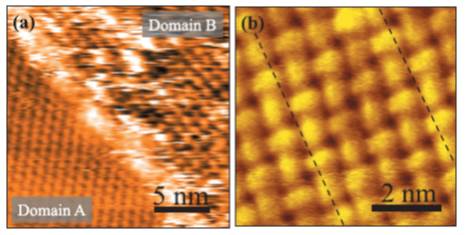 View full abstractDownload PDF (993K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (993K) -
Takanori KOITAYA, Jun YOSHINOBUArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 437-442
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNovel isotope effects were observed in desorption kinetics and adsorption geometry of cyclohexane on Rh(111) by the use of temperature programmed desorption (TPD), ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS), and spot-profile-analysis low energy electron diffraction (SPA-LEED). The desorption energy of deuterated cyclohexane (C6D12) is lower than that of C6H12. In addition, the work function change by adsorbed C6D12 is smaller than that by adsorbed C6H12, indicating that C6D12 molecules are slightly more distant from the surface than C6H12 molecules (vertical geometric isotope effect). These isotope effects originate from a shallower adsorption potential of C6D12 than that of C6H12. The lateral geometric isotope effect was also observed in the two-dimensional cyclohexane superstructures as a result of the different repulsive interaction between interfacial dipoles. The observed isotope effects should be ascribed to the quantum nature of hydrogen involved in the C−H⋅⋅⋅metal interaction. View full abstractDownload PDF (1491K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1491K) -
Spin Conductance through a Single Molecule by means of Spin-Polarized STMToyo Kazu YAMADAArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 443-448
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSGiant magnetoresistance (GMR) through a single phthalocyanine molecule (H2Pc) was studied by means of a spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) technique. Single molecular magnetic junction was fabricated by contacting a ferromagnetic STM tip to a single molecule on nano magnets. We obtained GMR of +60% and −50% through [Co/H2Pc/Co(111)] and [Fe/H2Pc/Mn(001)] junctions, respectively, in ultra-high vacuum at 4.6 K. Single organic molecules can be a new material for spintronics. View full abstractDownload PDF (3399K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3399K) -
Saori HANDA, Yingying YU, Toru YAJIMA, Masayuki FUTAMATAArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 449-454
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFlocculation method in Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) is elucidated to utilize coupled localized surface plasmon between closely adjacent metal nanoparticles towards single molecule characterization. In particular focus is placed on the distinct adsorption of cationic and neutral R123 and R6G molecules on Au nanoparticles (AuNPs), which are covered with much less amount of surface residuals than Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs). Indeed, the cationic dye molecules adsorb on AuNPs via electrostatic interaction with negatively charged metal surfaces, whereas neutral dye molecules adsorb via coordination bonds via lone pair electrons at nitrogen atoms in a tilted orientation. Flocculates of AgNPs were also formed using p-mercaptobenzoic acid (PMBA), providing enormous enhancement in surface enhanced Raman scattering. Electrostatic interaction between dissociated PMBA and counter ions, as well as van der Waals force between protonated PMBAs on AgNPs plays a crucial role in the flocculation. Mono- and divalent cations modified the νCOO− band at 1420 cm−1 by 20 cm−1 indicating distinct interaction of the hydrated cations with carboxylate anions of PMBA on AgNPs. View full abstractDownload PDF (1846K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1846K)
Planning Series
Surface Science for Energy Issues
-
Hiroki SUZUKI2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 455-457
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (551K)
Science Café
Research Abroad
-
Hisayoshi MATSUSHIMA2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 458-459
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (602K)
News & Trends
-
2013 Volume 34 Issue 8 Pages 460
Published: August 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: August 17, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (188K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
