All issues

Successor
Volume 36, Issue 3
Displaying 1-12 of 12 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Tetsuya ARUGA2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 103
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (159K)
Special Issue: Carrier Transport at Surfaces
-
Shuji HASEGAWAArticle type: Review
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 104-111
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThanks to advances in in situ measurements techniques in ultra-high vacuum and emergent materials (Rashba-type surfaces and topological insulators), surface states on crystals provide interesting topics such as two-dimensional super-conductivity, spin-polarized electronic transport, and spin current, due to broken symmetry and spin-orbit interaction. View full abstractDownload PDF (2772K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2772K) -
Takashi UCHIHASHI, Shunsuke YOSHIZAWAArticle type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 112-117
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSilicon surface reconstructions with metal adatoms are two-dimensional systems with atomic-scale thickness. We have successfully measured the superconducting transition of a representative silicon surface reconstruction Si(111)-(√7×√3)-In by electron transport measurement. In this article, we report our results together with the experimental techniques and future prospect for surface superconductors. View full abstractDownload PDF (1290K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1290K) -
Tohru OKAMOTO, Ryuichi MASUTOMIArticle type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 118-123
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis article reviews recent low-temperature magnetotransport measurements on cleaved semiconductor surfaces covered with other materials. The quantum Hall effect was observed in surface inversion layers of InAs and InSb. For an InAs(110) surface covered with a submonolayer of Fe, hysteresis in the magnetoresistance occurs. It is associated with spin-glass ordering in the Fe film. We also report two-dimensional superconducting state of monolayer Pb films grown on GaAs(110) in a strong parallel magnetic field. The experimental results are consistently explained in terms of an inhomogeneous superconducting state predicted for Rashba spin-split 2D systems.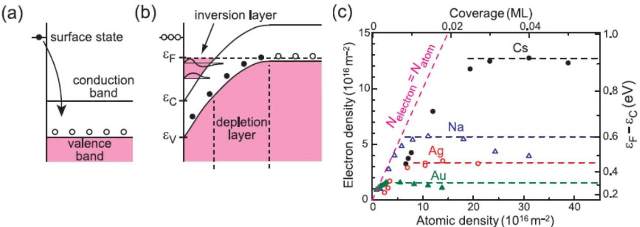 View full abstractDownload PDF (754K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (754K) -
Tomoki MACHIDA, Sei MORIKAWA, Satoru MASUBUCHI, Rai MORIYA, Kenji ...Article type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 124-128
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe report on coherent carrier transport in high quality dual-gate graphene encapsulated by hexagonal boron nitride. The graphene in-plane npn junction, which was realized by tuning the top and back gate voltages, showed a clear resistance oscillation due to the Fabry-Perot interference in the npn cavity. When a small magnetic field was applied, the oscillation phase was shifted by π, indicating the observation of the Klein tunneling at the pn interfaces. In high magnetic fields, the resistance across the npn junctions exhibited distinct oscillations, whose trajectories were well reproduced by the numerical calculation assuming the magnetic flux quantization in the insulating region between the co-propagating p and n quantum Hall edge channels. The results suggest the coherent interference of carriers at the graphene quantum Hall pn junction. View full abstractDownload PDF (1104K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1104K) -
Shintaro FUJII, Manabu KIGUCHIArticle type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 129-134
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCharge transport though single molecular junctions was investigated by break junction (BJ) technique. In the single molecular junction, a molecule is bounded to two metal electrodes to form metal-molecule hybrid. Due to the low dimensionality and interface effects at the metal-molecule contact in the hybrid system, the junctions display unique electronic properties not found in bulk counterpart. Here we demonstrate two examples of the unique electronic properties found in our recent studies. The first one is the electronic switching functionality that originates from external force-assisted reversible change in the contact geometries on the atomic scale at the metal-molecule interface for pyridine and thiophene junctions. The other one is the long range one-dimensional non-resonant tunneling transport for single π-stacked junctions. These findings on the unique electronic properties of the single molecular junctions provide fundamental guidance toward potential applications in molecular electronic devices. View full abstractDownload PDF (1086K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1086K) -
Shuichi MURAKAMIArticle type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 135-140
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe review various topics on surface physics related with topological insulators. We first explain properties of topological insulators and associated surface Dirac cones. The surface states of topological insulators are different from conventional surface states in that they are characterized by topological numbers calculated from bulk wavefunctions. We then show physics related with hybridization of multiple Dirac cones from topological insulator surfaces. Such hybridization is realized in thin films, interfaces, and superlattices of topological insulators. In thin films the hybridization opens a gap in the surface states, whereas in interfaces and superlattices, the presence or absence of the surface gap and resulting band structure depends on system parameters and chiralities of the surface Dirac cones. Lastly we review the physics of Weyl and Dirac semimetals, and their implications in novel surface states. View full abstractDownload PDF (540K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (540K)
Planning Series
Surface Science for Environmental Issues
-
Kazuhiko SAKAMOTO2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 141-143
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Science Café
Research Abroad
-
Akichika KUMATANI2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 144-145
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (403K)
Report
-
Tetsuya HASEGAWA2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 146
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (420K)
Qualifying Examination for Surface Science Engineers
-
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 147
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1243K)
News & Trends
-
2015 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 148
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 24, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (148K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|

