
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Takanori KOSHIKAWA2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 149
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (157K)
-
Yoshiaki KIDOArticle type: Review
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 150-157
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIon scattering spectrometry has been widely used in materials analysis of thin films and atomic structures near surface regions. The notable point of this method is its reliability due to the simple and well-established principle and direct observation in real space, in contrast to diffraction (momentum space) techniques using electrons and X-rays. This article first represents the physical basis of ion scattering analysis and then introduces a recent topic of nano-particles analysis, i.e. determination of the shape and size of Au nano-particles and Au-Pd core cells.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1047K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1047K) -
 Kenji UMEZAWAArticle type: Current Topic
Kenji UMEZAWAArticle type: Current Topic
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 158-163
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLow energy ion scattering spectroscopy is a powerful tool for the analysis of the topmost surface composition and structure. Low energy atom scattering spectroscopy is a quite useful tool for the analysis of the topmost insulator surfaces, as well. Because the primary beams of low energy atom scattering are electrically neutral. This report provides some of the basic principles relating to the interaction between low energy particles (ions/atoms) and topmost surfaces. Due to the large amount of research carried out in this field, selected materials are shown in this report.
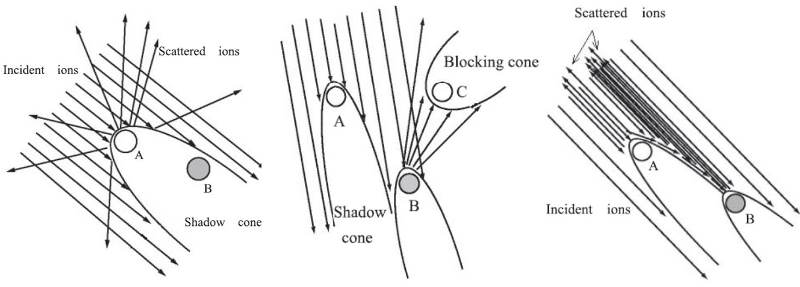 View full abstractEditor's pickDownload PDF (938K)
View full abstractEditor's pickDownload PDF (938K) -
Taku T. SUZUKI, Osamu SAKAIArticle type: Current Topic
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 164-169
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn electron-spin polarized 4He+ ion beam is useful for analyzing the spin polarization on outermost surfaces (spin-polarized ion scattering spectroscopy). This is because the neutralization of the He+ ion (the Auger neutralization) in the vicinity of the surface is dependent on the spin due to the Pauli principle. Thus, the element-selective spin polarization of the outermost surface is analyzed from the spin-dependent ion scattering (the spin asymmetry). We recently found that the spin asymmetry also appears on the surface of a non-magnetic material. The appearance of the spin asymmetry is quantitatively interpreted in terms of the anomalously large spin-orbit coupling (SOC) in the quantum mechanical intermediate state, where the SOC transiently acts on the spin of the virtually created hole in the target during the He+ ion-target atom binary collision.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (878K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (878K) -
Kaoru NAKAJIMA, Shunto NAKANISHI, Martin LíSAL, Kenji KIMURAArticle type: Current Topic
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 170-175
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSElemental depth profiles of typical ionic liquids (ILs), 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethane-sulfonyl) imide ([CnC1Im][Tf2N], n = 2, 6, 10), were measured using high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy (HRBS) and high-resolution elastic recoil detection analysis. The obtained depth profiles deviate from the uniform stoichiometric composition in the surface region, showing preferential orientations of ions at the surface. The results were well reproduced by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, demonstrating that the state-of-the-art MD simulations are a reliable method to study surface structures of ILs. The surface structures of 11 equimolar mixtures were also studied using HRBS. A general tendency that larger IL is enriched at the surface was found.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (714K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (714K) -
Tomoaki NISHIMURAArticle type: Current Topic
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 176-181
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMedium energy ion scattering is a simple and powerful technique for determining surface compositions and surface atomic structures. Two methods are mainly used for simulation. The first method is to virtually divide the sample into thin layers and add the scattering spectra from each layer. This can be treated as an extension of the simulation of Rutherford backscattering analysis except for factors of ionization probability, spectral shape and scattering cross section. The second method is to calculate the probabilities of incident ions hitting to the target atoms by performing trajectory simulation of incident ions in the crystal. This paper briefly describes the items needed for both the simulations of medium energy ion scattering.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (900K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (900K) -
Bun TSUCHIYAArticle type: Current Topic
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 182-187
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe migrations of lithium (Li) as well as hydrogen (H) in both Au and Pt electrodes sides of Au/LiCoO2/Li1+xAlxGeyTi2−x−yP3O12-AlPO4(LATP)/Pt (thickness: approximately 24 nm/65 nm/150 μm/16 nm) multilayers were dynamically investigated with applying various voltages in vacuum using an ion beam surface analysis, combined elastic recoil detection (ERD) with Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) measurements with 9.0-MeV O4+ ions. The ERD spectra clearly revealed that the Li concentrations at each Au/LiCoO2/LATP and Pt/LATP side decreased and increased, respectively, when the acquired voltages were more than 1.00 V and the Li atoms of approximately 80 at% migrated from the LiCoO2 cathode to the LATP (LixTiy(PO4)3) anode after applying the voltages up to 2.43 V. In addition, the presence of H was also observed at the Au/LiCoO2/LATP and Pt/LATP interfaces and in the LiCoO2 and LATP bulks and might significantly influence on the Li+ ion conduction for the battery materials. View full abstractDownload PDF (1199K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1199K) -
Mototsugu MIHARAArticle type: Current Topic
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 188-193
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe β-NMR technique and its application to the study of materials science are introduced. Using some different types of accelerator facility, β-NMR probe nuclei for various elements are useful as a beam with wide energy range, which enables us to select an implantation depth into a sample from surface to bulk. Our recent β-NMR studies on 8Li in Li ion conductor material Li7La3Zr2O12 and 12N in H2O are presented.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (892K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (892K)
-
Hiromichi ICHINOSE2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 194-196
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Kaori SEINO2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 197-198
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (249K)
-
Hitoshi NAKAHARA2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 199-200
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (573K)
-
2017 Volume 38 Issue 4 Pages 201
Published: April 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: April 22, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (150K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|

