巻号一覧

41 巻, 2 号
April
選択された号の論文の17件中1~17を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Article
-
Sergey Shityakov, Ramin Ekhteiari Salmas, Ellaine Salvador, Norbert Ro ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 175-184
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリー
電子付録In this study, we investigated the cytotoxic effects of unmodified α-cyclodextrin (α-CD) and modified cyclodextrins, including trimethyl-β-cyclodextrin (TRIMEB) and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD), on immortalized murine microvascular endothelial (cEND) cells of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). A CellTiter-Glo® viability test, performed on the cEND cells showed significant differences among the different cyclodextrins. After 24 hr of incubation, TRIMEB was the most cytotoxic, and HPβCD was non-toxic. α-CD and TRIMEB exhibited greater cytotoxicity in the Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium than in heat-inactivated human serum indicating protective properties of the human serum. The predicted dynamic toxicity profiles (Td) for α-CD and TRIMEB indicated higher cytotoxicity for these cyclodextrins compared to the reference compound (dimethylsulfoxide). Molecular dynamics simulation of cholesterol binding to the CDs suggested that not just cholesterol but phospholipids extraction might be involved in the cytotoxicity. Overall, the results demonstrate that HPβCD has the potential to be used as a candidate for drug delivery vector development and signify a correlation between the in vitro cytotoxic effect and cholesterol binding of cyclodextrins.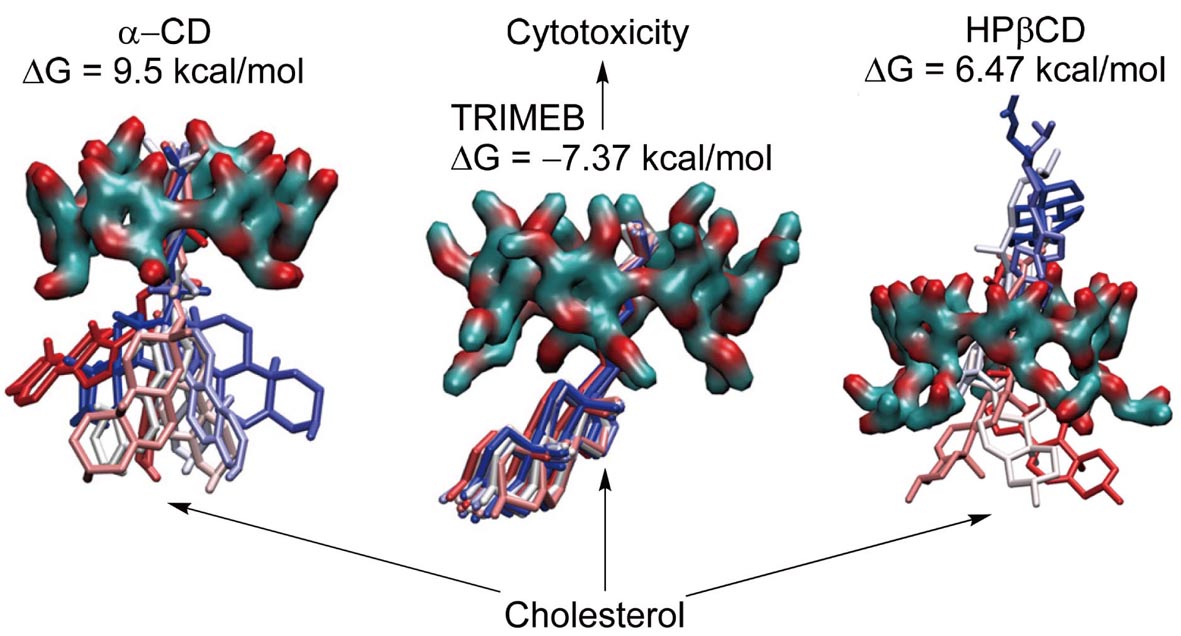 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1867K)
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1867K)
Original Article
-
Hongzhi Liu, Wei Hao, Xin Wang, Hao Su2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 185-193
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーLipopolysaccharide (LPS) has been confirmed to be the main inhibitor in osteogenic differentiation, posing a clinical challenge to bone healing, particularly for trauma followed by endotoxinemia/sepsis. However, the molecular mechanism remains ambiguous. miR-23b, which regulates multiple signaling pathways in inflammation, has been shown to be deregulated by LPS. In this study, we examined the LPS-mediated regulation on the expression of miR-23b and Smad 3 in preosteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells. Then we determined the regulation of miR-23b overexpression on the Smad 3 expression and on the LPS-mediated inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2)-induced osteogenic differentiation. Our results demonstrated that LPS significantly downregulated the expression of miR-23b, while upregulating Smad 3 in MC3T3-E1 cells. However, the transfection with miR-23b mimics markedly downregulated the Smad 3 in both mRNA and protein levels, via the specific binding to the 3’-untranslated region (UTR) of Smad 3. Moreover, though LPS markedly downregulated the BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by inhibiting the expression of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Osteocalcin (OCN), Osteopontin (OPN) and Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2). The upregulated miR-23b reversed such downregulation of ALP, OCN, OPN and RUNX2 in the MC3T3-E1 cells which were treated both with LPS and BMP-2. In conclusion, our data indicates that miR-23b ameliorates the LPS-mediated inhibition of BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells, implying the protective role of miR-23b in the LPS-mediated inhibition of osteogenic differentiation and bone formation.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (814K)
Original Article
-
Masaya Motohashi, Michael F. Wempe, Tomoko Mutou, Yuya Okayama, Norio ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 195-206
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリー
Original Article
-
Miki Asanagi, Shigeru Yamada, Naoya Hirata, Hiroshi Itagaki, Yaichiro ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 207-215
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリー
電子付録Organotin compounds, such as tributyltin (TBT), are well-known endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs). We have recently reported that TBT induces growth arrest in the human embryonic carcinoma cell line NT2/D1 at nanomolar levels by inhibiting NAD+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD-IDH), which catalyzes the irreversible conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate. However, the molecular mechanisms by which NAD-IDH mediates TBT toxicity remain unclear. In the present study, we examined whether TBT at nanomolar levels affects cell cycle progression in NT2/D1 cells. Propidium iodide staining revealed that TBT reduced the ratio of cells in the G1 phase and increased the ratio of cells in the G2/M phase. TBT also reduced cell division cycle 25C (cdc25C) and cyclin B1, which are key regulators of G2/M progression. Furthermore, apigenin, an inhibitor of NAD-IDH, mimicked the effects of TBT. The G2/M arrest induced by TBT was abolished by NAD-IDHα knockdown. Treatment with a cell-permeable α-ketoglutarate analogue recovered the effect of TBT, suggesting the involvement of NAD-IDH. Taken together, our data suggest that TBT at nanomolar levels induced G2/M cell cycle arrest via NAD-IDH in NT2/D1 cells. Thus, cell cycle analysis in embryonic cells could be used to assess cytotoxicity associated with nanomolar level exposure of EDCs.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (785K)
Original Article
-
Tomoya Fujie, Yukino Segawa, Akane Uehara, Takehiro Nakamura, Tomoki K ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 217-224
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーVascular endothelial cells are in direct contact with blood. Inorganic zinc is thought to be incapable of inducing metallothionein, which protects cells from heavy metal toxicity and oxidative stress, in vascular endothelial cells. Here, we aimed to further characterize the induction of metallothionein in vascular endothelial cells. Our results confirmed that inorganic zinc could not induce metallothionein in vascular endothelial cells. Moreover, ZnSO4 could not activate both the metal response element (MRE) transcription factor 1 (MTF-1)/MRE and Nrf2/antioxidant response element (ARE) pathways and was incapable of inducing metallothionein. In addition, bis(L-cysteinato)zincate(II), a zinc complex that activates the MTF-1/MRE pathway, increased MRE promoter activity but failed to induce metallothionein, suggesting that vascular endothelial metallothionein was not induced only by activation of the MTF-1/MRE pathway. Further analysis of a library of zinc complexes showed that zinc(II) bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) activated the MTF-1/MRE pathway but not the Nrf2/ARE pathway, increased MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2A mRNA levels, and induced metallothionein proteins. These data indicated that zinc complexes may be excellent tools to analyze metallothionein induction in vascular endothelial cells.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (760K)
Original Article
-
Tomoya Fujie, Yukino Segawa, Eiko Yoshida, Tomoki Kimura, Yasuyuki Fuj ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 225-232
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーMetallothionein (MT) plays a central role in cellular defense against heavy metals and oxidative stress. Since the induction of MT requires the activation of metal response element (MRE)-binding transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) by binding of zinc ions, inorganic zinc is regarded as a typical MT inducer. However, in a previous report, we showed that inorganic zinc could not induce MT in vascular endothelial cells. While it is suggested that endothelial MT presents mechanisms different from those of other cell types, these remain unclear. In this study, we investigated whether the induction of endothelial MT expression involves the Nrf2–ARE pathway using copper(II) bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), termed Cu10, using a culture system of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Cu10 induced MT-1/2 protein expression and increased the expression of mRNAs for MT-1A, MT-1E, and MT-2, MT isoforms expressed in the cells. Cu10 activated not only the MTF-1–MRE, but also the Nrf2–ARE pathway. MTF-1 knockdown resulted in the repression of Cu10-induced MT-1 and -2 expression. Cu10-induced MT-1 expression was down-regulated by Nrf2 knockdown. However, MT-2 expression was not affected by Nrf2 knockdown. These results suggest that the expression of endothelial MT is up-regulated by the Nrf2–ARE pathway as well as by the MTF-1–MRE pathway. Moreover, MT-1 regulation mechanisms differ from that of MT-2. Specifically, the present data support the hypothesis that MT-1 participates in the biological defense system, while MT-2 mainly regulates intracellular zinc metabolism.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1494K)
Original Article
-
Hiroki Kimoto, Yuko Ito, Satoshi Matsumoto, Eiji Hosoki2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 233-239
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーEvaluation of oral mucosal irritation is required by regulatory agencies when the intended clinical route of the drug candidate is intraoral administration. In this study, we investigated whether it was possible to evaluate oral mucosal irritation in rats by an intraoral instillation which was thought to mimic the clinical route of gargle products. Although no oral mucosal irritation was observed in the animals instilled with 0.5% and 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, an anionic detergent) solutions for 10 days, instillation of 15% SDS solution for 4 days induced oral mucosal irritation macro- and microscopically, and this was evaluated as moderate irritant. It was suggested that the oral mucosal irritation test by intraoral instillation in rats could be a simple and useful method mimicking the clinical route of gargle products.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (441K)
Letter
-
Yasumitsu Ogra, Shu Nagasaki, Ayako Yawata, Yasumi Anan, Koichi Hamada ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 241-244
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーWe aimed to establish an element array analysis that involves the simultaneous detection of all elements in cells and the display of changes in element concentration before and after a cellular event. In this study, we demonstrated changes in element concentration during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. This metallomics approach yielded unique information of cellular response to physiological and toxicological events.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1157K)
Original Article
-
Makoto Shirai, Shingo Arakawa, Munehiro Teranishi, Kiyonori Kai2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 245-253
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーWe previously reported that thioacetamide (TA)-induced hepatocellular necrosis was attenuated in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD mice) compared with mice fed a normal rodent diet (ND mice). In this study, we investigated whether p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) was involved in this attenuation. Western blot analysis revealed that hepatic phosphorylated p38 MAPK protein decreased at 8 and 24 hours (hr) after TA dosing in the HFD mice, while it decreased only at 24 hr in the ND mice in comparison to the time- and diet-matched, vehicle-treated mice. p38 MAPK regulates various biological functions including inflammation, therefore, hepatic metabolomics analysis focusing on pro-inflammatory lipid mediators was performed. At 24 hr after TA dosing, only one pro-inflammatory mediator, 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE), was higher in the HFD mice. On the other hand, in addition to 12-HETE, 15-HETE and 12-hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid (HEPE) were higher and omega-3/omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids ratios were lower in the ND mice at 24 hr. These results of metabolomics indicated that less pro-inflammatory state was seen in HFD mice than in ND mice at 24 hr. Finally, to confirm whether the observed decrease in phosphorylated p38 MAPK could attenuate TA-induced hepatocellular necrosis, we showed that SB203580 hydrochloride, an inhibitor of p38 MAPK, partially attenuated TA-induced hepatic necrosis in ND mice. Collectively, these results suggest that a prompt decrease in phosphorylation of p38 MAPK after TA administration is one of the factors that attenuate TA-induced hepatic necrosis in HFD mice.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2099K)
Original Article
-
Kanae Umeda, Yaichiro Kotake, Masatsugu Miyara, Keishi Ishida, Seigo S ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 255-264
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーGluR2, an α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor subunit, plays important roles in neuronal survival. We previously showed that exposure of cultured rat cortical neurons to several chemicals decreases GluR2 protein expression, leading to neuronal toxicity. Methoxychlor, the bis-p-methoxy derivative of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, and fenvalerate, a synthetic pyrethroid chemical, have been used commercially as agricultural pesticides in several countries. In this study, we investigated the effects of long-term methoxychlor and fenvalerate exposure on neuronal glutamate receptors. Treatment of cultured rat cortical neurons with 1 or 10 µM methoxychlor and fenvalerate for 9 days selectively decreased GluR2 protein expression; the expression of other AMPA receptor subunits GluR1, GluR3, and GluR4 did not change under the same conditions. Importantly, the decreases in GluR2 protein expression were also observed on the cell surface membrane where AMPA receptors typically function. In addition, both chemicals decreased neuronal viability, which was blocked by pretreatment with 1-naphtylacetylspermine, an antagonist of GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors, and MK-801, an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist. These results suggest that long-term exposure to methoxychlor and fenvalerate decreases GluR2 protein expression, leading to neuronal death via overactivation of GluR2-lacking AMPA and NMDA receptors.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2532K)
Letter
-
Fusako Mitsunaga, Masakazu Umezawa, Ken Takeda, Shin Nakamura2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 265-271
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーTo investigate the influence of nanomaterial exposure during fetal development, diesel exhaust particles (DEPs), carbon black (CB), or titanium dioxide (TiO2) was injected intradermally to pregnant rhesus macaques. The hippocampus and cerebellum of newborn infants were then examined. DNA microarray and quantitative real-time RT-PCR, western blot, and immunohistochemical analyses were used to measure the expression of the hemoglobin genes, HBA, HBB, and HBG. Of the nanomaterials tested, DEP elicited the greatest increase in mRNA and protein levels of hemoglobin genes in the brain tissues. Strong signal of HbA protein was detected in the pyramidal cell layer, the polymorphic cell layer and in the alveus of the hippocampi of the DEP-treated animals. The altered gene expression was likely due to responses to oxidative or nitrosative stress and/or hypoxia in the fetal/neonatal brain. Since excessive hemoglobin is reportedly neurotoxic, the vulnerability of developing brains by long-term upregulation of hemoglobin should be considered. Maternal exposure to nanomaterials may increase the risk of brain dysfunction in offspring.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1338K)
Letter
-
Kei-ichi Sugiyama, Masashi Muroi, Mawo Kinoshita, Osamu Hamada, Yuji M ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 273-279
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーMacrophages induce the innate immunity by recognizing pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which sense pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), which is an essential adaptor molecule for most TLRs, mediates the induction of inflammatory cytokines through nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). Trichothecene mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) shows immunotoxic effects by interrupting inflammatory mediators produced by activated macrophages. The present study investigates the effect of DON on NF-κB in activated macrophages through MyD88-dependent pathways. DON inhibited NF-κB-dependent reporter activity induced by MyD88-dependent TLR agonists. In addition, lipopolysaccharide-induced phosphorylation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 and inhibitor κBα were attenuated by DON. Furthermore, DON downregulated the expression level of MyD88. These results suggest that DON inhibits NF-κB activation in macrophages stimulated with TLR ligands via MyD88-dependent TLR signals. Therefore exposure to DON may lead to the inhibition of MyD88-dependent pathway of TLR signaling.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (436K)
Original Article
-
Masayuki Kanki, Min Gi, Masaki Fujioka, Hideki Wanibuchi2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 281-292
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリー
電子付録Several studies have successfully detected hepatocarcinogenicity in rats based on gene expression data. However, prediction of hepatocarcinogens with certain mechanisms of action (MOAs), such as enzyme inducers and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) agonists, can prove difficult using a single model and requires a highly toxic dose. Here, we constructed a model for detecting non-genotoxic (NGTX) hepatocarcinogens and predicted their MOAs in rats. Gene expression data deposited in the Open Toxicogenomics Project-Genomics Assisted Toxicity Evaluation System (TG-GATEs) was used to investigate gene marker sets. Principal component analysis (PCA) was applied to discriminate different MOAs, and a support vector machine algorithm was applied to construct the prediction model. This approach identified 106 probe sets as gene marker sets for PCA and enabled the prediction model to be constructed. In PCA, NGTX hepatocarcinogens were classified as follows based on their MOAs: cytotoxicants, PPARα agonists, or enzyme inducers. The prediction model detected hepatocarcinogenicity with an accuracy of more than 90% in 14- and 28-day repeated-dose studies. In addition, the doses capable of predicting NGTX hepatocarcinogenicity were close to those required in rat carcinogenicity assays. In conclusion, our PCA and prediction model using gene marker sets will help assess the risk of hepatocarcinogenicity in humans based on MOAs and reduce the number of two-year rodent bioassays.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1959K)
Original Article
-
Yan Cai, Chao Zhang, Le Hao, Jun Chen, Ping Xie, Zhidong Chen2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 293-302
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリー
電子付録Microcystin-LR (MCLR) is one of the most toxic cyanotoxins produced in algal blooms. The toxic effects of MCLR on the expression of some organelles genes (mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, and cytoskeleton etc) have been widely investigated, but little is known how it impacts on the expression of ribosomal genes. In this study we identified seven ribosomal protein genes RPS6, RPS12, RPS24, RPS27a, RPL12, RPL27 and RPL29 in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis), whose expression was regulated by MCLR. The amino acid sequences of those 7 genes shared more than 90% identity with corresponding sequences from zebrafish, and were well conserved throughout evolution. The 3D structure prediction showed that the structures of these ribosomal proteins were conserved, but had species specificity. Q-PCR analysis revealed that expression of seven genes changed dramatically at 3 hr, then went back to a moderate change- level at 24 hr in almost all tested tissues (liver, kidney, intestine, heart, spleen and gill) post MCLR injection, but in brain expression of the seven genes stayed same as the normal level. This study will help us to know not only about the evolution and functions of ribosomal proteins in anti-MCLR response in bighead carp, but also about the MCLR toxicity and its impact on aquaculture and human health.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (710K)
Letter
-
Ruili Dang, Yujin Guo, Hualin Cai, Ranyao Yang, Donglou Liang, Chuanfe ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 303-309
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーPatients with schizophrenia (SCZ) are at higher risk for developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) and neuregulin-1 (NRG1)/ErbB signaling has been identified as a common susceptibility pathway for the comorbidity. Antipsychotic treatment can change NRG1/ErbB signaling in the brain, which has been implicated in their therapeutic actions, whereas the drug-induced alterations of NRG1/ErbB pathway in cardiovascular system might be associated with the prominent cardiac side-effects of antipsychotic medication. To test this hypothesis, we examined NRG1/ErbB system in rat prefrontal cortex (PFC) and myocardium following 4-week intraperitoneal administration of haloperidol, risperidone or clozapine. Generally, the antipsychotics significantly enhanced NRG1/ErbB signaling with increased expression of NRG1 and phosphorylation of ErbB4 and ErbB2 in the brain and myocardium, except that clozapine partly blocked the cardiac NRG1/ErbB2 activation, which could be associated with its more severe cardiac adverse actions. Combined, our data firstly showed evidence of the effect of antipsychotic exposure on myocardial NRG1/ErbB signaling, along with the activated NRG1/ErbB system in brain, providing a potential link between the therapeutic actions and cardiotoxicity.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1562K)
Original Article
-
Yui Nakajima, Hirotoshi Iguchi, Shinji Kamisuki, Fumio Sugawara, Teiic ...2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 311-319
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーCitrinin, a natural mycotoxin that is found in fermented foods, is known as a cytotoxin and nephrotoxin. Exposure to high doses of citrinin result in apoptosis; however, the effects of low doses are not fully understood. Glutamate excitotoxicity is responsible for neuronal death in acute neurological disorders including stroke, trauma and other neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we show the neuroprotective effect of low doses of citrinin against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. We examined the effect of citrinin exposure on glutamate-induced cell death in cultured rat cortical neurons under two conditions: simultaneous treatment with citrinin 0.1 to 1,000 nM and glutamate (30 μM) for 1, 3 hr; the same simultaneous treatment for 3 hr after pretreatment with citrinin for 21 hr. Both the MTT and immunocytochemical assay showed significant neuroprotective effects at several doses and exposure times tested. All concentrations of citrinin tested showed no remarkable cell death following 14-day exposure, and no marked alterations to synapses. These data suggest that low doses of citrinin can be used as a neuroprotective agent against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity without additional harmful cellular alterations.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1773K)
Original Article
-
Yu Haranosono, Shingo Nemoto, Masaaki Kurata, Hideyuki Sakaki2016 年 41 巻 2 号 p. 321-328
発行日: 2016/04/01
公開日: 2016/03/10
ジャーナル フリーAlthough phospholipidosis (PLD) often affects drug development, there is no convenient in vitro or in vivo test system for PLD detection. In this study, we developed an in silico PLD prediction method based on the PLD-inducing mechanism. We focused on phospholipid (PL)-compound complex formation, which inhibits PL degradation by phospholipase. Thus, we used some molecular interactions, such as electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, and intermolecular forces, between PL and compounds as descriptors. First, we performed descriptor screening for intermolecular force and then developed a new in silico PLD prediction using descriptors related to molecular interactions. Based on the screening, we identified molecular refraction (MR) as a descriptor of intermolecular force. It is known that ClogP and most-basic pKa can be used for PLD prediction. Thereby, we developed an in silico prediction method using ClogP, most-basic pKa, and MR, which were related to hydrophobic interactions, electrostatic interactions, and intermolecular forces. In addition, a resampling method was used to determine the cut-off values for each descriptor. We obtained good results for 77 compounds as follows: sensitivity = 95.8%, specificity = 75.9%, and concordance = 88.3%. Although there is a concern regarding false-negative compounds for pKa calculations, this predictive ability will be adequate for PLD screening. In conclusion, the mechanism-based in silico PLD prediction method provided good prediction ability, and this method will be useful for evaluating the potential of drugs to cause PLD, particularly in the early stage of drug development, because this method only requires knowledge of the chemical structure.抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (813K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|