2018 巻, 63 号
選択された号の論文の11件中1~11を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
論文
-
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 1-4
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2527K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 5-11
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2521K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 13-18
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2444K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 19-26
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2101K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 27-39
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3879K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 41-44
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2109K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 45-52
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2782K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 53-62
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2588K) -
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 63-69
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2395K)
共同研究報告
-
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 71-89
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (9255K)
エラータ
-
2018 年 2018 巻 63 号 p. 103-104
発行日: 2018/03/31
公開日: 2018/10/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1468K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|

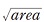 was evaluated. The relationship was defined by El Haddad’s short crack correlation substituting an intrinsic defect size
was evaluated. The relationship was defined by El Haddad’s short crack correlation substituting an intrinsic defect size 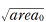 for an intrinsic crack depth. The relationship was characterized by the approximate formulation using the
for an intrinsic crack depth. The relationship was characterized by the approximate formulation using the  which is representative value of defect size. To evaluate the fracture strength of ceramics with arbitrary defect, a new evaluation equation was proposed based on the process zone size fracture criterion and the
which is representative value of defect size. To evaluate the fracture strength of ceramics with arbitrary defect, a new evaluation equation was proposed based on the process zone size fracture criterion and the