
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yasunori Takayama, Makoto TominagaArticle type: Basic Section–Research Reports
2024 Volume 39 Issue 1 Pages 1-8
Published: January 12, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: January 12, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSTransient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a capsaicin receptor, and anoctamin 1 (ANO1, also called TMEM16A), a calcium–activated chloride channel, are major ion channels involved in pain sensation in the peripheral nervous system. Pain–related behaviors dependent on each ion channel are reportedly reduced in its deficient mice. We previously found that TRPV1 and ANO1 interact with each other upon making a physical complex, and the functional linkage exacerbates capsaicin–induced acute pain sensation. However, the significance of TRPV1 and ANO1 interaction in the inflammatory condition remains unknown. Activation thresholds of TRPV1 become low upon its phosphorylation. Here, we performed whole–cell patch–clamp recordings using phorbol 12–myristate 13–acetate, an activator of protein kinase C to phosphorylate TRPV1, mimicking the inflammatory conditions in HEK293T cells expressing mouse TRPV1 and mouse ANO1. We also showed that phosphorylated TRPV1 interacts with ANO1 with a low concentration of capsaicin or innocuous heat stimulation of approximately 37°C. Furthermore, we performed immunoprecipitation to investigate whether TRPV1–ANO1 interaction is enhanced by phosphorylation. However, the protein–protein interaction was not changed. Thus, ANO1 activation could be enhanced by the acceleration of TRPV1 activity. These facts indicate that interactions between phosphorylated TRPV1 and ANO1 could explain inflammatory pain sensations, for instance, in heat allodynia. Therefore, our findings contribute to clarifying the new molecular mechanisms involved in pathological pain and development of analgesia.
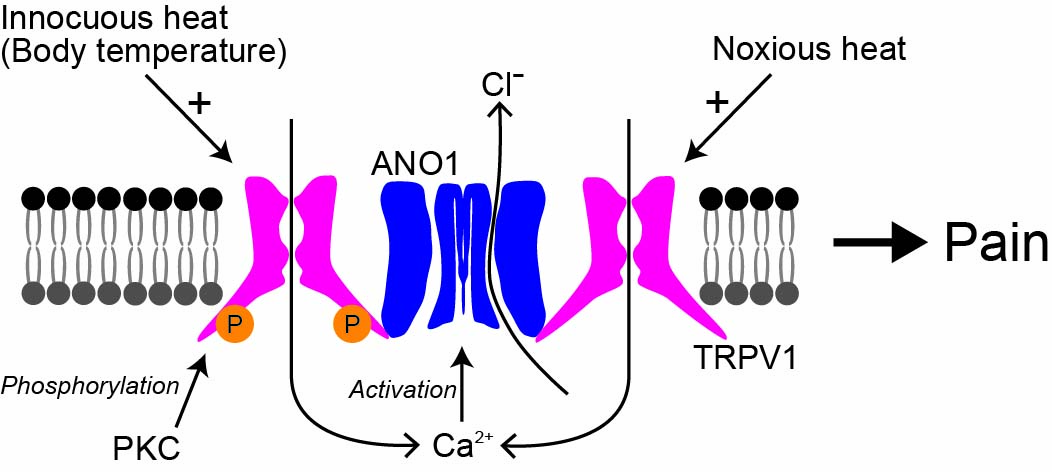 Phosphorylated TRPV1 and ANO1 ⁄ TMEM16A interaction induced by low concentration of capsaicin or innocuous heat stimulation Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1720K)
Phosphorylated TRPV1 and ANO1 ⁄ TMEM16A interaction induced by low concentration of capsaicin or innocuous heat stimulation Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1720K)
-
Aiko Kawai, Keiko Yamada, Satoko Chiba, Saeko Hamaoka, Keisuke Yamaguc ...Subject area: Clinical Section–Research Reports
2024 Volume 39 Issue 1 Pages 9-18
Published: January 26, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe aim of this study was to investigate the most important aspects of patient–reported outcome measures (PROMs) for pain assessment and their predictive value in treatment response. We analyzed 367 patients with acute–to–chronic pain (age: ≥ 20 years) who visited the pain clinic of a university hospital for the first time and responded to nine PROMs related to pain symptoms. Principal component analysis (PCA) was applied to the PROMs data, deriving principal components with their component scores (i.e., a composite scale). Data from 175 patients who completed the same PROMs three months after their initial visit were then analyzed. Multiple regression was used to examine whether these principal components, along with age, sex, and pain chronicity, could predict changes in pain intensity, as measured by a numerical rating scale (NRS) over three months. In addition, we stratified the patients based on pain chronicity and categorized pain as primary, neuropathic, or musculoskeletal. We also examined the relative risk associated with the principal components derived from PCA and other variables for clinically significant improvement in pain intensity, defined as a reduction of at least two points on the NRS. We identified four principal components (pain intensity, pain quality, disability, and cognition ⁄ affect for pain) for the clinical assessment of patients with pain. At the initial visit, pain intensity, pain–related cognition ⁄ affect, and pain chronicity were predictors of pain management difficulties. Pain quality was a specific predictor for primary and musculoskeletal conditions. Our findings provide evidence for the use of PROMs in pain management.
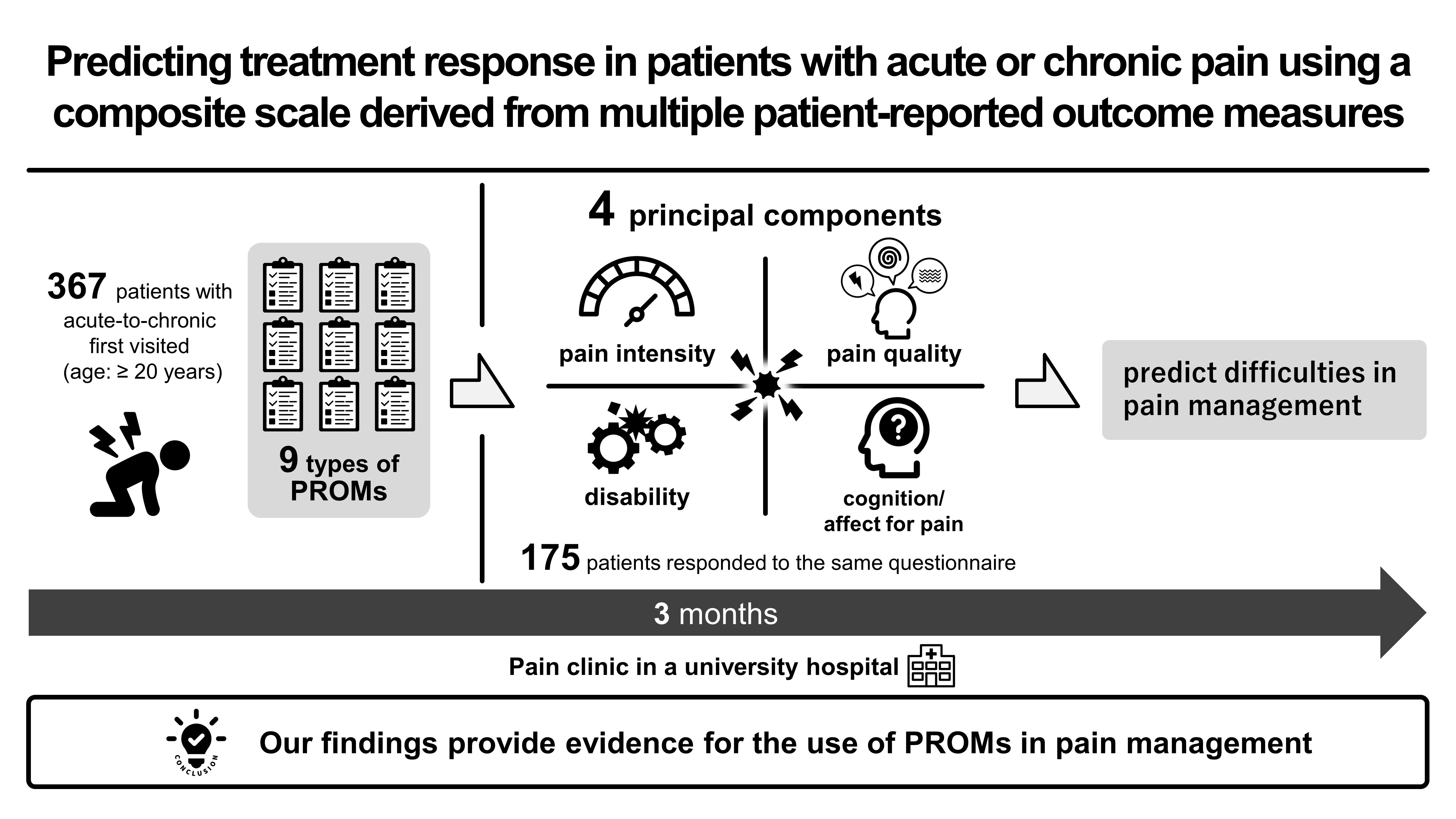 Predicting treatment response in patients with acute or chronic pain using a composite scale derived from multiple patient-reported outcome measures Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (297K)
Predicting treatment response in patients with acute or chronic pain using a composite scale derived from multiple patient-reported outcome measures Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (297K) -
Naoto Takahashi, Kozue Takatsuki, Satoshi Kasahara, Shoji YabukiArticle type: Clinical Section–Research Reports
2024 Volume 39 Issue 1 Pages 19-25
Published: January 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 02, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBackground: A therapeutic target for patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain is improvement in quality of life (QOL). However, factors associated with QOL are poorly understood.
Purpose: To explore factors affecting QOL among patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain.
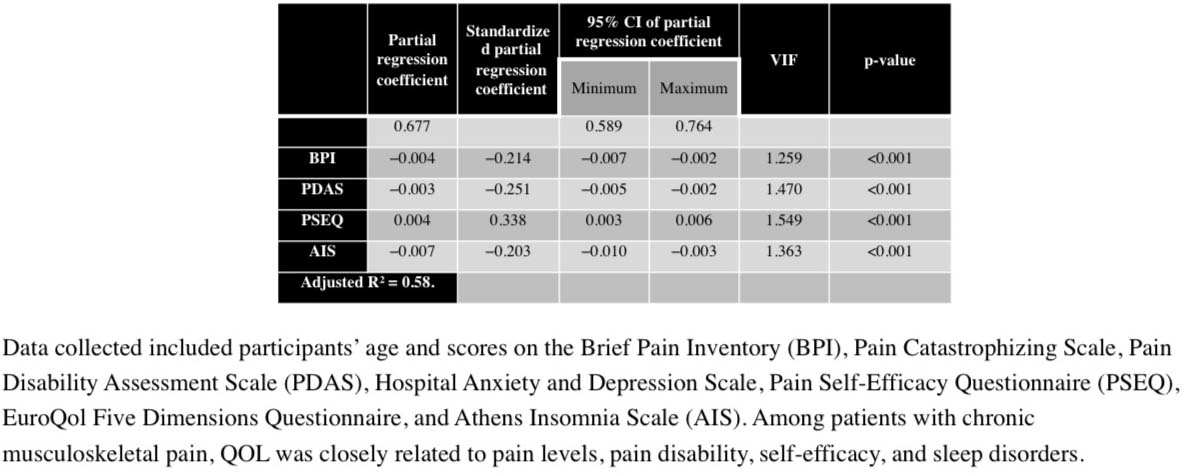
Methods: This was a cross–sectional study. Participants were 166 patients that attended our hospital from April 2015 to March 2020. Data collected included participants’ age and scores on the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI), Pain Catastrophizing Scale, Pain Disability Assessment Scale (PDAS), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Pain Self–Efficacy Questionnaire (PSEQ), EuroQol Five Dimensions Questionnaire (EQ–5D), and Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS). Standardized (beta) regression coefficients showed significant associations between the independent variables (BPI, PDAS, PSEQ, and AIS scores) and the dependent variable (QOL measured using the EQ–5D). For the statistical analyses, we performed Shapiro–Wilk tests, descriptive statistics, paired t–tests, and multiple regression analysis with forward stepwise selection.
Results: The paired t–tests showed a significant difference between males and females only in PSEQ scores. Multiple regression analysis with forward stepwise selection yielded an R2 of 0.58.
Conclusions: We clarified that among patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain, QOL was closely related to pain levels, self–efficacy, pain disability, and sleep disorders.
 Exploratory study of factors affecting quality of life among patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: A cross–sectional study Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (285K)
Exploratory study of factors affecting quality of life among patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: A cross–sectional study Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (285K)
-
Keiji Hashizume, Hiroaki Yamagami, Toshio Iwata, Aki Fujiwara, Keisuke ...Article type: Clinical Section–Technical Reports
2024 Volume 39 Issue 1 Pages 26-34
Published: January 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 02, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBackground: While severe complications after cervical selective nerve root block (CSNRB) with an anterolateral approach have been reported, CSNRB via a posterolateral approach (PL–CSNRB) could reduce inadvertent intravascular injections. Because fluoroscopy–guided PL–CSNRB is technically difficult, PL–CSNRBs are often CT– or ultrasound–guided. CT guidance is safe but time–consuming and has a higher risk of radiation exposure. Ultrasound guidance can visualize the vessels but whether it reduces intravascular injections remains debatable.
Purpose: This study described CSNRB using a fluoroscopy–guided posterolateral oblique technique (PLO–CSNRB) and assessed its clinical usefulness.
Methods: A total of 707 PLO–CSNRBs were performed on 260 patients (186 cervical diseases and 74 cervical zoster–associated pain; CZAP) between May 2016 and December 2020. Under fluoroscopy guidance, a needle was inserted posterolaterally and kept in contact with the articular pillar and advanced toward the exit of the intervertebral foramen (C3–C8). A block was considered successful if the intervertebral foramen was filled with contrast (foraminal filling; FF).
Results: The success rate was 94.5% (668/707). The main contrast pattern observed with FF was periradiculography (619) followed by transforaminal epidurography (233). Venography was observed in 135 (19.1%) injections with 52 (38.5%) simultaneously observed with FF. Contrast in the radicular and vertebral arteries was respectively observed in 4 and 2 injections, which disappeared after needle reposition. The effective rates were 83.9% and 55.1% for cervical diseases and CZAP, respectively. No serious complications were noted.
Conclusions: PLO–CSNRB is a useful technique that ensures safe needle advancement to the nerve root at the exit of the intervertebral foramen.
 Outcomes of 707 cervical selective nerve root blocks using a fluoroscopy–guided posterolateral oblique approach Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2697K)
Outcomes of 707 cervical selective nerve root blocks using a fluoroscopy–guided posterolateral oblique approach Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2697K)
-
Hiroki Ota, Rihito Oi, Kimiaki Katanosaka, Kazue Mizumura, Toru Taguch ...Subject area: Basic Section–Short Communications
2024 Volume 39 Issue 1 Pages 35-39
Published: February 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 09, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialRecently, multifunctional roles of Tmem120A ⁄ TACAN in mechanotransduction and mechanical pain hypersensitivity have been suggested. Here, we examined the mRNA expression of the molecule in the skeletal muscle and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) using two muscle pain models induced by exercise and myositis. The hind limb muscles of rats were subjected to either lengthening contractions (LC) or carrageenan injection. The muscles and DRGs were sampled and analyzed using real–time RT–PCR to examine the mRNA expression profiles of Tmem120A. Tmem120A mRNA in muscles increased 6–48 h after LC and 12 h after carrageenan injection. Tmem120B, a paralog of Tmem120A, was upregulated in the muscles of the myositis model, but not in the exercise–induced muscle pain model. Neither Tmem120A nor Tmem120B mRNA level was altered in the DRG of the two muscle pain models. These results indicate that upregulations of Tmem120A ⁄ TACAN and Tmem120B play a role in muscles after inflammation and/or exercise.
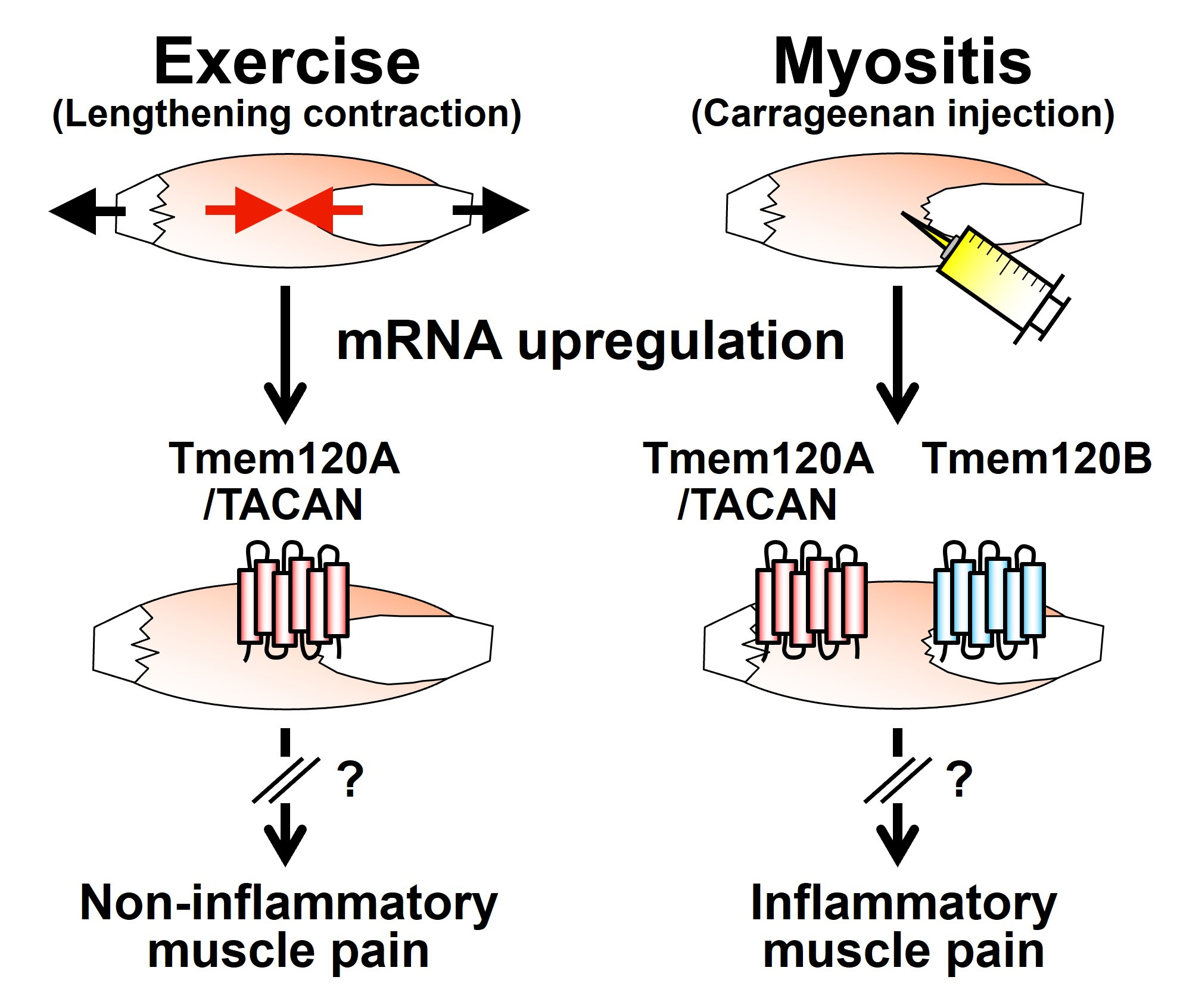 Expression profiles of Tmem120A ⁄ TACAN in rat skeletal muscle subjected to exercise and inflammation Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (371K)
Expression profiles of Tmem120A ⁄ TACAN in rat skeletal muscle subjected to exercise and inflammation Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (371K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|