主催: 一般社団法人 日本機械学会
会議名: 第27回 動力・エネルギー技術シンポジウム
開催日: 2023/09/20 - 2023/09/21
主催: 一般社団法人 日本機械学会
会議名: 第27回 動力・エネルギー技術シンポジウム
開催日: 2023/09/20 - 2023/09/21
One of the essential parameters for the safety and optimal control of industrial facilities is the void fraction α, which represents the percentage of gas phase volume in a unit volume of a pipeline. Wire mesh sensor is a technique to directly measure the void fraction distribution at high speed at several kHz or faster. However, it is highly invasive and not easy to maintain. In this study, Void fraction estimation method that combines multi-electrode impedance measurement and machine learning (MCV-ML) is proposed. The MCV-ML is composed of four steps which are 1) in-situ void fraction measurement by wire-mesh sensor (WMs), 2) Simulated voltage by electrical simulation, 3) Measured voltage by MCV system, and 4) training ML model and estimated void fraction  . Experiments on the bubbly to slug flow were conducted in a vertical, inclined, and horizontal pipe. As a result, the MCV-ML predicts the
. Experiments on the bubbly to slug flow were conducted in a vertical, inclined, and horizontal pipe. As a result, the MCV-ML predicts the 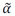 with an averaged normalized cross correlation of 0.70. The trained machine learning model clearly estimated slag but failed to capture non-slag bubbles.
with an averaged normalized cross correlation of 0.70. The trained machine learning model clearly estimated slag but failed to capture non-slag bubbles.